2013 KCSE Building and Construction Past Paper
4.4.1 Building Construction Paper 1 (446/1)
SECTION A (40 marks)
1. a) Define the term “shelter”.KCSE
b) State two environmental factors that influence the type of shelter.
2.a) Outline three qualities of each of the following safety attire:
(i) boots;
(ii) helmet;
b) State one reason for proper storage of each of the following:
(i) tools;
(ii) materials.
3. a) List four regulations that are considered in site selection.
b) State one purpose of each of the following activities on site:
(i) site clearing;
(ii) site stripping.
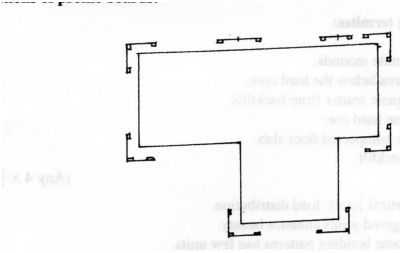
4. Figure 1, shows an outline of a floor plan of a building.
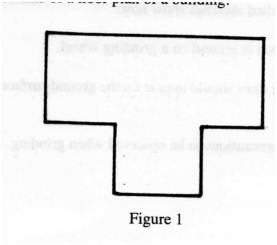
Make sketches to show the positions of the profile boards for setting out the building.
(4 marks)
5 State two functions of each of the following materials in concrete:
(a) water; (1 mark)
(b) coarse aggregate. (1 mark)
6 (a) Outline four functions of foundations in buildings. (4 marks)
(b) State four factors that are considered when choosing a type of a foundation. (2 marks)
7 State four ways of controlling termites on site. (2 marks)
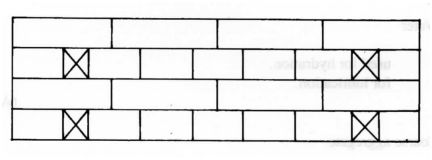
8 (a) Give four reasons for bonding a wall. (4 marks)
(b) Sketch an elevation of a wall built in English bond to show four courses high and four bricks in length with a stopped end. (2 marks)
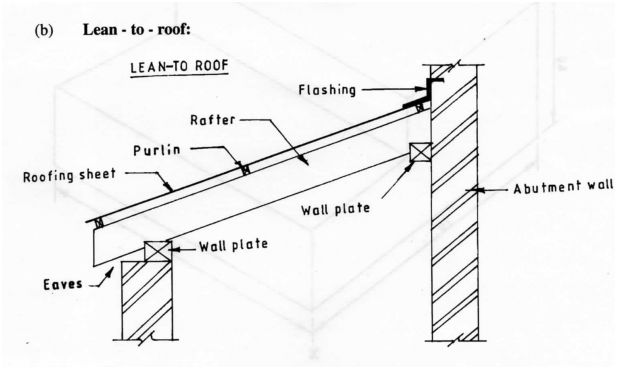
9 (a) State four factors which influence the selection of a roof of a building. (2 marks)
(b) Sketch and label a section through a lean-to roof. (2 marks)
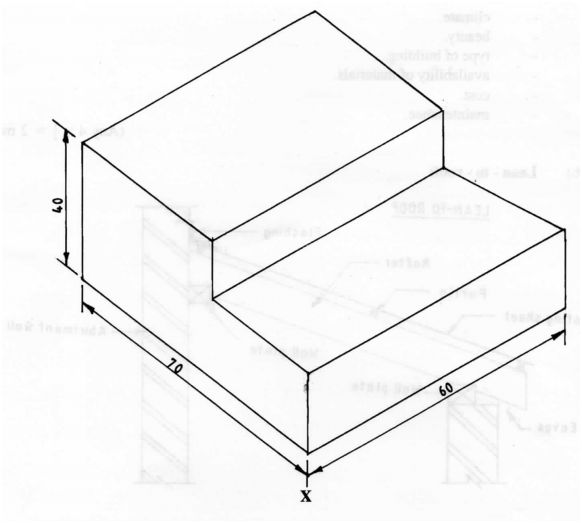
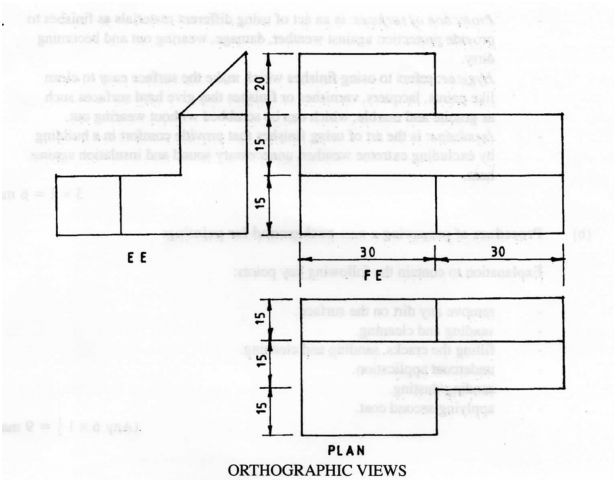
10 Figure 2 shows the views of a shaped block in 3″‘ angle projection.
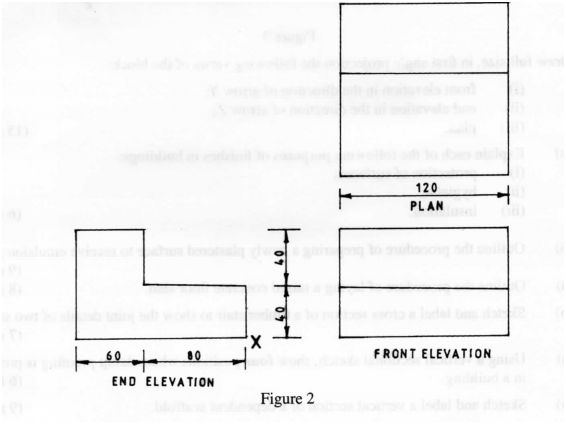
Using the scale of 1:2, draw the block in isometric projection with X as the lowest point. (4 marks)
SECTION B (60 marks)
11 Figure 3 shows a pictorial view of a shaped block.
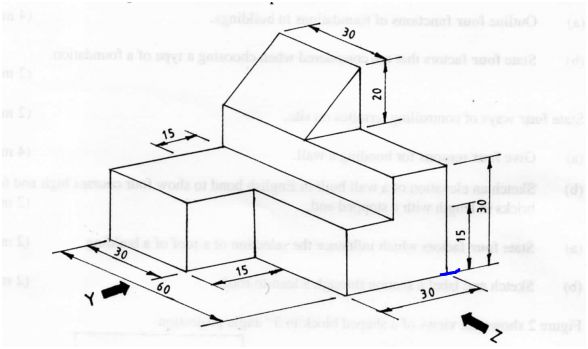
Figure 3
Draw full size, in first angle projection the following views of the block:
12. a) (i) front elevation in the direction of arrow Y;
(ii) end elevation in the direction of arrow Z;
(iii) plan. (15 marks)
b) Explain each of the following purposes of finishes in buildings:
(i) protection of surfaces;
(ii) hygiene;
(iii) insulation. (6 marks)
13 a) Outline the procedure of preparing a newly plastered surface to receive emulsion paint. (9 marks)
b) Outline the procedure of laying a raised concrete floor slab. (8 marks)
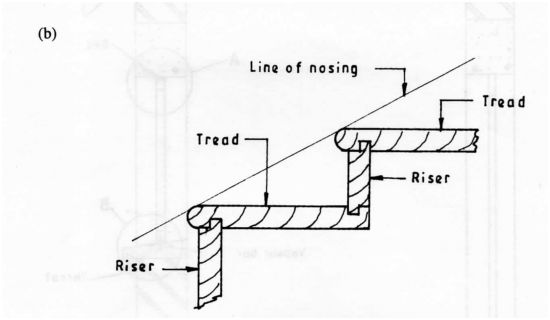
14. a) Sketch and label a cross section of a timber stair to show the joint details of two steps. – (7 marks)
b) Using a vertical sectional sketch, show four positions where damp proofing is provided in a building. (6 marks)
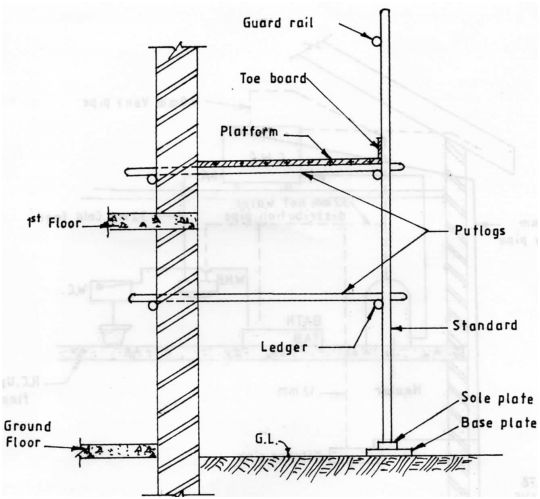
b) Sketch and label a vertical section of a dependent scaffold. (9 marks)
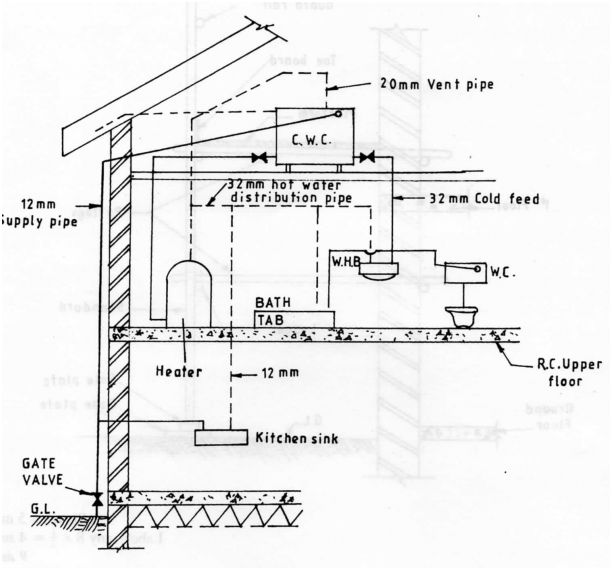
15 Sketch and label a cross-section of a direct domestic hot water supply system, up to the first floor by incorporating an immersion heater. (15 marks)
2013 KCSE Building and Construction Past Paper-Marking Scheme/Answers
5.4 BUILDING CONSTRUCTION (446)
5.4.1 Building Construction Paper 1 (446/1)
SECTION A
1 a) Shelter is an enclosure which excludes weather elements, provides security and privacy. (2 marks)
b) The environment influences the type of shelter in the following ways:
– availability of materials.
– weather conditions. (2 marks)
2 a) Qualities of safety attire:
(i) Boots
hard soles.
rubber soles.
metal toe caps.
stiff hard leather.
(ii) Helmet
hard material.
covers the whole head.
cushioned inside.
neck strap.
bright coloured.
b) Reasons for storage
– tools: avoid damage, easy access, avoid theft.
– materials: wastage, damage, theft.
3 a) Regulations
– wayleave.
– service lines.
– access roads (road reserve).
– environmental.
– local authority by-laws.
(b) Purposes for:
(i) Site clearing:
– removal of vegetation
– removal of existing structures.
(ii) Site stripping:
– removal of top soil
– site levelling
4. Positions of profile boards:
5. a) Functions of concrete materials:
(a) Water
– used for hydration.
– for lubrication.
(b) Coarse aggregate
– provides density.
– provides volume.
6. a) Functions of foundations:
load distribution over a wide area.
support the building.
provide a level base for walls.
transfer the loads to a firm base.
cover soft area in the firm base.
(b) Factors considered when choosing a types of foundation:
total loads of the building.
nature and bearing capacity of the sub soils.
land terrain.
type of building.
nature of ground.
7. Ways of controlling termites:
removing termite mounds.
treating the area below the hard core.
removing organic matter from backfills.
use of DPM on hard core.
using densely compacted floor slab.
treating the backfill.
8 a) Strength – vertical joints, load distribution.
Beauty – staggered joints enhance beauty.
Economy – some bonding pattems use few units.
Lateral stability – thicker walls provide more lateral stability.
b)
9. (a) Factors influencing the selection of roof type:
climate
beauty.
type of building.
availability of materials.
COSI.
maintenance.
b) Lean- to – roof:
10.
11.
12. a) Purpose of fisheries
Prozection of surfaces is an act of using different materials as finishes to provide protection against weather, damage, wearing out and becoming dirty.
Hygiene: refers to using finishes which make the surface easy to clean like paints, lacquers, varnishes or finishes that give hard surfaces such as granite and marble, which can be scrubbed without wearing out.
lnsulafion: is the art of using finishes that provide comfort in a building by excluding extreme weather, unnecessary sound and insulation against heat. –
3 X 2 = 6 marks
b) Procedure of preparing a new background for painting:
Explanation to contain the following key points:
remove any din on the surface.
sanding and cleaning.
filling the cracks, sanding and cleaning.
undercoat application.
sanding/dusting.
applying second coat.
13. a) The procedure of laying a raised concrete floor:
erect form work.
mix the concrete.
transport the concrete.
pour the concrete.
spread the concrete.
compact the concrete.
level the concrete.
cure the concrete.
Line of nosing
Tread
Riser
b)
14 (a)
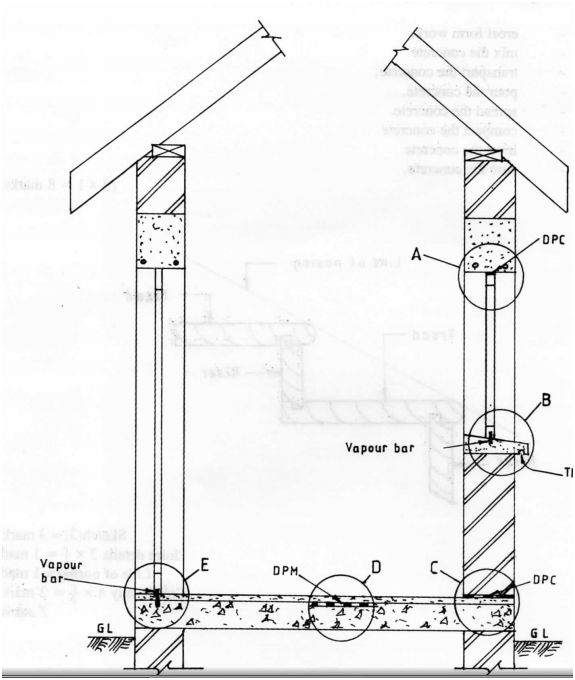
b) Between window and lintel.
At window sill.
150 mm above GL. –
On or within floor slab.
at threshold.
15.