2013 KCSE Biology Past Paper
4.3.1 Biology Paper 1 (231/1)
1 (a) What is meant by the term wilting? (1 mark)
(b) Explain how an increase in temperature affects the rate of active transport.
2 The diagram below represents a cell as seen under an electron microscope.
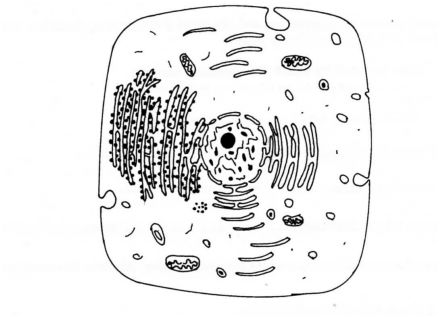
(a) Based on the diagram, state whether it represents an animal cell or a plant cell.
(b) Give two reasons for your answer in 2(a) above. (2 marks)
(c) Why is the palisade layer a tissue? (1 mark)
(3)(a) State two external features found in the class Mammalia only. (2 marks)
(b) Name the taxonomic unit that comes immediately after a phylum in classification. (1 mark)
(4)(a) State two roles of mucus in the stomach. ‘ (2 marks)
(b) Explain how age determines a person’s energy requirements. (2 marks)
(5)(a)Describe how turgor pressure builds up. (3 marks)
(6)Using a microscope, a student counted S5 cells a cross a field of view whose diameter was 6000;4m. Calculate the average length of the cells. Show your working. (2 marks)
(7) Explain how the following forces contribute to the movement of water up the xylem vessels: (2 marks)
(a) cohesion;
(b) adhesion.
(8) Construct a step in a dichotomous key using two leaves one with a serrated and the other with a smooth margin. (2 marks)
(9) State one way in which each of the following is structurally adapted to its function:
(a) neurone; (2 marks)
(b) mitochondrion. (2 marks)
(10) How are lenticels adapted for gaseous exchange? (2 marks)
(11)State the advantage of possessing blood group AB. (1 mark)
(12)(a) A student collected an organism and observed the following features: simple eyes.
(b)four pairs of legs and two body parts.
(13) State the class to which the organism belongs. (1 mark)
(14) Give an example of an organism in this class. (1 mark)
(15) Name the kingdom to which plasmodium belongs. (1 mark)
(16)State two characteristics of living organisms that are specific to plants. (2 marks)
(17)Name the three end products of anaerobic respiration in plants. (3 marks)
(18)State two reasons why accumulation of lactic acid leads to an increase in heart beat. (2 marks)
(19)Name three mechanisms that ensure cross pollination takes place in flowering plants. (3 marks)
(20)Name the flower part that produces gametes. (1 mark)
(21)(a)How is the human sperm cell structurally specialised? (2 marks)
(b)State three factors in seeds that cause dormancy. (3 marks)
(21)Explain the theory of evolution by natural selection. (2 marks)
(a) Explain the role of continental drift in evolution. (3 marks)
(b) What is meant by the term organic evolution? (1 mark)
(22)The diagram below illustrates a response by a certain plant.
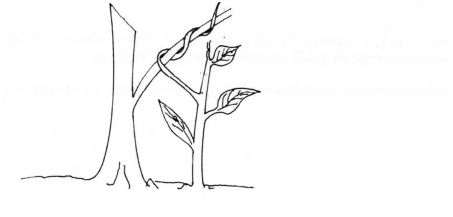
(a)Name the type of response.
(b)Explain how the response illustrated above occurs.
23 The diagram below illustrates a defect in the eye.
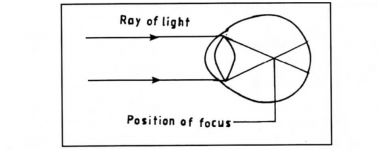
(i)Explain how the defect illustrated above can be corrected.
24 Explain three protective functions of mammalian blood.
25 State one adaptation of xylem vessels to their function.
26 (a)What is meant by the term sex linked genes?
(b) Name two sex linked traits in human beings.
27(a) State two differences between complete and incomplete metamorphosis.
(b)State the importance of moulting to an insect
28(a) State two features of a ball and socket joint.
(b) Name the bone that allows the head to:
(i) nod; ………….. ..
(ii) turn side ways
29 State two functions of pelvic girdle in mammals.
30 State two ways in which osmosis is significant to plants.
Biology Paper 2 (231/2)
SECTION A (40 marks)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided
1 (a) The diagram below represents a plant in the division Bryophyta.
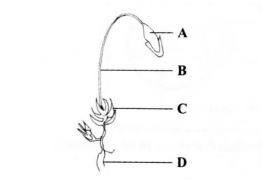
(i) Name the parts labelled B and D. (2 marks)
B …………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. .. D ………………………………………………………… ..
(ii) State one function for each of the parts labelled A and C. (2 marks)
A …………………………………………………………………………. ..
C …………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. ..
(b) The diagram below represents a member of the kingdom Animalia.
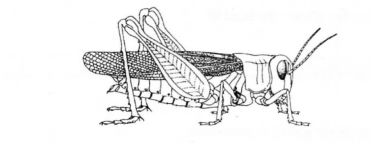
(i) Name the phylum to which the organism belongs. ( 1 mark)
(ii) Using observable features in the diagram, give three reasons for the answer in b(i). V (3 marks)
2.The diagram below represents the human ear.
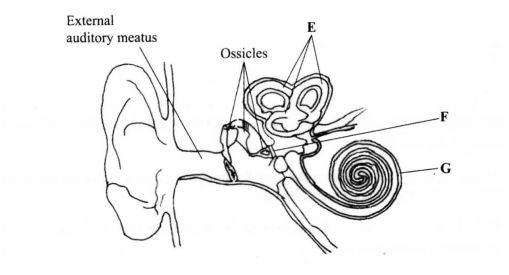
(a) Name the parts labelled E, F and G.
E …………………….. ..
F …………………….. ..
G …………………….. ..
(b) How is each of the following adapted to its function?
(i) External auditory meatus;
(ii) Ear ossicles.
(c) Name one defect of the human ear.
3.(a) Explain the importance of the following in photosynthesis:
(i) light;
(ii) carbon(lV) oxide;
(iii) chlorophyll.
(b) Name one appropriate food substance for each of the following enzymes:
(i) ptylin ….. ..
(ii) pepsin …… ..
(c) State the cause and two symptoms of Beri-beri.
Cause ……………… ..
Symptoms (2 marks)
(i) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
.. (ii) ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ..
4.ln an investigation, a variety of pea plants grown from seeds with smooth coats were crossed with plants grown from seeds with wrinkled coats. All the seeds obtained in the first filial (F I) generation had smooth seed coats.
(a) Using the letter R to represent the gene for smooth seed coat, ‘work out the genotype of the Fl generation. Show your working. (3 marks)
(b) l f the Fl generation was selfed, detennine the phenotypic ratio of the second filial (F2) generation. Show your working. (3 marks)
(c) If the total number of seeds in the F2 generation was 14 640, calculate the number of seeds with wrinkled coats. Show your working. (2 marks)
5.The diagram below represents a mammalian pelvic girdle.
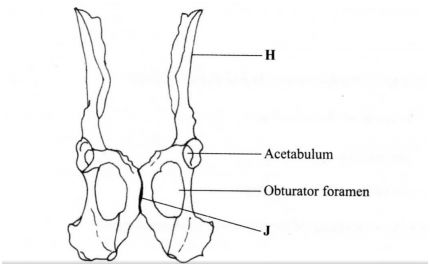
(a) How are the structures labelled H and J adapted to their function?
(i) H (2 marks)
(ii) J (2 marks)
(b) State the function of obturator foramen. ( l mark)
(c) (i) Name the bone that articulates with the pelvic girdle at acetabulum. (1 mark)
(ii) Name the type of joint formed by the acetabulum and the bone named in (c)(i) above. (I mark)
(d) Name the bone fonned by the fusion of caudal vertebrae in human beings. (l mark) 125
SECTION B (40 marks)
Answer question 6 (compulsory) and either question 7 or 8 in the spaces provided after question 8.
6.A scientist carried out an investigation to find out the population growth of mice under laboratory conditions. Twenty young mice were placed in a cage. The results obtained from the investigation were as shown in the table below.
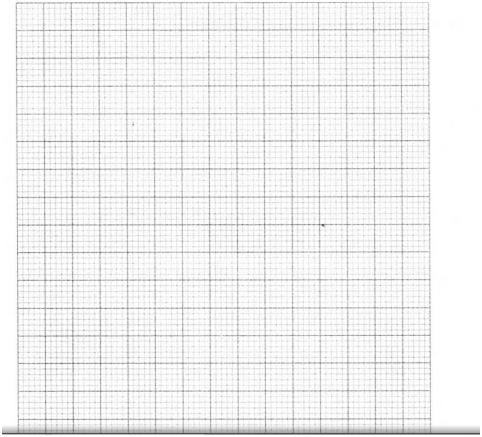
(a) On the grid provided, draw a graph of the number of mice against time. (6 marks)
(b) Account for the changes in mice population between
(i) 0 to 2 months (2 marks)
(ii) 2 to 6 months (2 marks)
(m) 6 to I0 months (2 marks)
(iv) I0 to 12 months. (2 marks)
(c) (i) Between which two months was the population change greatest? (1 mark)
(ii) Calculate the rate of population change over the period in (c)(i) above. (2 marks)
(d) What change in population would be expected if the investigation was continued to the 19th month? (l mark)
(e) To obtain the observed results state two variables that were kept constant during the investigation. _
7(a) Describe the process of blood clotting in human beings.
(b) How are respiratory surfaces in mammals adapted to their functions?
ii Describe the role of the following organs in excretion and homeostasis.
(a) the liver
(b) the skin during hot environmental conditions.
Biology Paper 3 (231/3)
1.(a) The photograph below shows the inner surface of the upper lefi side of the rib cage.
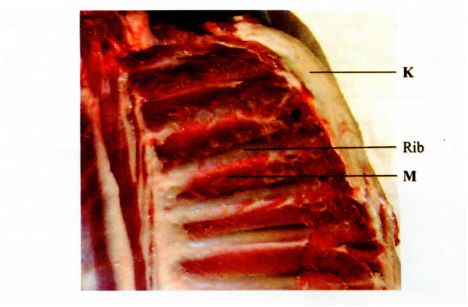
(i) Name the bone covered by the fatty tissue labelled K. (l mark)
(ii) Explain the role of the part labelled M in inhalation. (5 marks)
(b) The photograph below shows a mammalian vertebra.
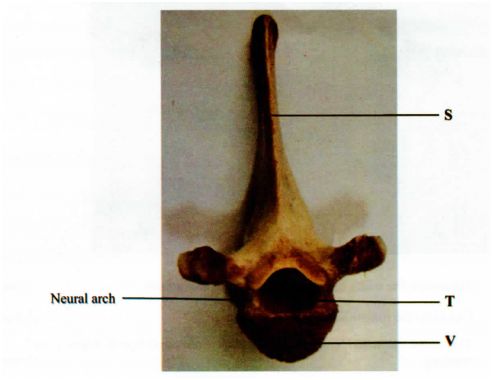
(i) State the view of the vertebra presented. (1 mark)
(ii) Name and state one function of the part labelled T.
Name
…………………………………………………………………………………………………… .. (1 mark)
Function
………………………………………………………………………………….. .. (1 mark)
(iii) How are the parts labelled S and V adapted to their functions? (4 marks)
S ………………………
V ………………………
c) The actual width of the vertebra below in cm is shown by a section of the ruler in the photograph.
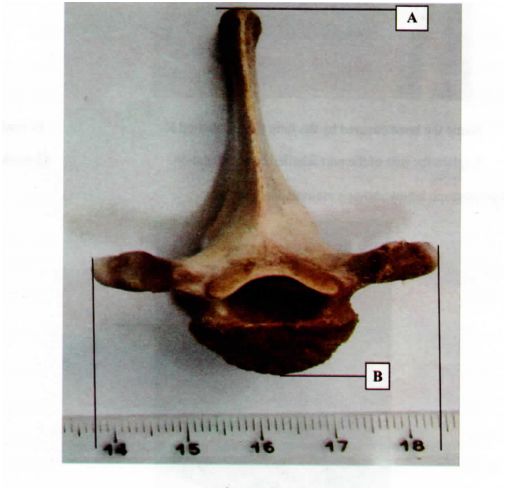
(i) Determine the width of the vertebra on the photograph. ( l mark)
(ii) Calculate the magnification of this image. (2 marks)
(iii) Determine the actual length of the vetebra from point A to B. Show your working. (2 marks)
2You are provided with a food sample labelled solution C. Using the reagents provided, carry out tests to identify the food substances present in the sample.
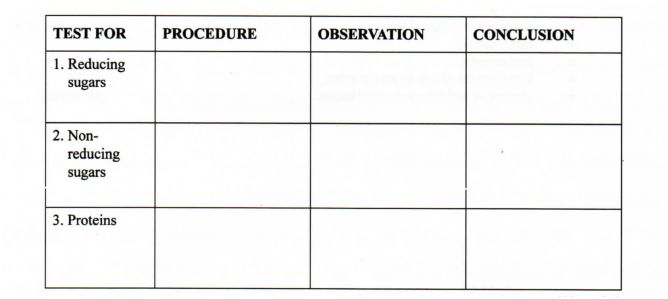
TEST FOR PROCEDURE OBSERVATION CONCLUSION l. Reducing sugars
2. Non- reducing sugars
3. Proteins
Below are photographs showing some observebal features of leaves. (12 marks)
Using the features in the order given below, construct a dichotomous key that can be used to identify the specimens. simple or compound leaves; leaf venation; leaf margin; arrangement of leaves on the stem; pinnate or trifoliate nature of leaves. (10 marks)

2013 KCSE Biology Past Paper-Marking Scheme/Answers
5.3 BIOLOGY (231)
53.1 Biology Paper 1 (231/1)
1 a)Is when the rate of water loss is more than the rate of absorption and the plant droops; l mark
b)The rate of active transport increases with increase intemperature up to the optimum temperature; 1 mark
Further increase in temperature slows down the rate of active transport until it stops because it denatures enzymes; _ 1 mark
2 a)Animal cell; 1 mark
b)Has cell membrane only/has no cell wall; Has numerous small vacuoles; Has central nucleus; Max. 2 marks
c) Consists of many similar cells performing the same function; l mark
3 a)Have mammary glands; have extemal ears/pinna;
Body covered with fur/hair; ‘ Max. 2 marks
b)Class; l mark
4 a)Lubrication; Protection; 2 marks
b)Young people are more active; requiring more energy;/
Older people are less active; requiring less energy; 2 marks
5 As the cell gains water by osmosis; the sap/cell vacuole enlarges; pushing the cytoplasm outwards; exerting pressure on the cell wall; Any 3 3 marks
7 Water molecules cling to each other maintaining a continuous column of water/preventing the break of water column;
8Water molecules cling to the sides of the xylem vessel walls; l mark
1(a) – Leaf with serrated margin — go to 2;
(b) – Leaf with smooth margin — go to –; 2 marks
9.a)Presence of myelin sheath for insulation/increases transmission; Axon for transmission of impulses;
Large cell body controls activites of cell; Nerve endings/dendrites receives impulses from receptors cells;
Node of Ranvier speeds up impulse transmission. b)Inner membrane highly folded/cristae to increase S A for attachment of (respiratory) enzymes.
4 marks
10. Cells loosely arranged; to facilitate air circulation;
Cells have moist surfaces; to dissolve respiratory gases; 2 marks
11. Can receive blood from any donor/ universal recepient; l mark
12.a)(i) Arachnida; l mark
(ii) Spider/scorpion/tick/mite; l mark
13.Protoctista/protista; l mark
Autotrophic nutrition; show alternation of generation; Limited movement;
Limited excretory products/unspecialized respiratory structures; Localised growth; 2 marks
14 .Alcohol/ethanol; Carbon (IV) oxide; Energy/Adenosine Triphosphate; 3 marks 15 To increase supply of oxygen to the tissues;
The oxygen is used to oxidize lactic acid (to carbon (IV) oxide, water and energy);
2 marks
16 . Protogyny; protandry; Dioecious; Dichogamy;
Self sterility/incompatibility; Heterostyly;
Presence of structures/substances to attract agents of pollination; Max. 3 marks 17 .Ovary /Anther; l mark
18Acrosome/Lysosome contain enzyme to digest membrane of the ovum;
– Numerous mitochondria to provide energy for movement;
– Long tail for faster movement; Max. 2 marks
19Embryo not fully developed;
– Chemical inhibitors/presence of abscisic acid;
– Hard/impermeable testa/seed coat;
– Low horrnones/low enzymes concentration; Max. 3 marks
20. Genetically acquired beneficial characteristics which occur spontaneously; are perpetuated through reproduction; 2 marks
21. Continents existed as one large Landmass/Pangea/Laurasian and Gondwana Land;
Present continents drifted from it leading to isolation of organisms; organisms in each continent evolved along different lines hence emergence of new species; 3 marks
22. a)Emergence of new life/species/organisms from pre-existing simple forms, gradually over a long period of time, to present complex forms; 1 mark
b) Thigmotropism/haptotropism; l mark
Part of the tendril in contact with support causes migration of auxins to the opposite side;
leading to faster cell division/growth on the side not in contact with the support; This causes the tendril to curl around the support;
3 marks
23.Use of biconcave/concave lens/divergent lens; to diverge the rays and make image be focussed on the retina; 2 marks
24.Contains antibodies that defend the body from foreign antigens;
– Has white blood cells that produce antibodies/while blood cells engulf antigens;
– Has platelets that initiate blood clotting to prevent excessive bleeding at an open wound prevent entry of pathogens;
3 marks
25. Thin and long to allow for capillarity;
– Walls lignified to strengthen the stem/to prevent collapse of vessels;
– Have bordered pits to allow for exchange of materials;
Max. 2 marks
26. Genes inherited along with the sex chromosomes; l mark
Haemophilia; hairy ears/pinna/nose; colour blindness/red green; blue-green colour blindness;
Muscular diastrophy; baldness
2 marks
27 . a)Complete metamorphosis – eggs hatch into larvae while in incomplete metamorphosis hatch
into nymphs which resemble the adult;
Complete metamorphosis has four stages; egg, larvae. pupa and adult while an incomplete metamorphosis has three stages; egg, nymph and adult. 2 marks
b)To allow for growth of the insect; l mark
28. a)Ligaments; synovial fluid; synovial membrane; articular cartilage;
synovial capsule; a bone with rounded head fitting into a cavity of another bone;
Max. 2 marks
b)(i) Atlas; (ii) Axis allows movement in all planes; 2 marks
29Form\joints with the legs to make walking possible; l mark
– Provide large surface area for attachment of muscles; l mark
– Offers support (to the body weight)
30Absorption of water; support;
Opening and closing of stomata;
Feeding in insectivorous/plants; 2 marks
Biology Paper 2 (231/2)
1.a)(i) B -Seta/stalk;
D- Rhizoid;
(ii) A- Production of spores/sporulation;
C -Photosynthesis;
b)(i) Arthropoda;
(ii) – Segmented body;
– Jointed appendages;
– Presence of exoskeleton
2 a)E Semi circular canals;
F Oval window/Fenestra ovalis/Fenestra vestibuli;
G Cochlea; 3 marks
b)(i) Lined with hair/secretion of wax/(has glands that secrete wax) to trap foreign bodies;
Hollow/tubular/tube; to direct sound waves to the ear drum/tympanum/tympanic membrane;
(max) (2 marks
(ii) Small/form a lever system/solid; to amplify (sound) vibrations; (2 marks) c) Deafness! absence of pinnal vertigo/tinnitus; (max) (1 mark
3.a) (i) Provides energy needed to split water molecules into oxygen and hydrogenl photolygis;
Provides energy for formation of ATP molecules (which is used in dark stage) (1 mark)
(ii) Combines with hydrogen ions to make glucose; (1 mark)
(iii) Used to trap light energy; (1 mark)
b) (i) Starch;
(ii) Protein; (2 marks)
c) (i) Lack of vitamin Bl/thiamine; (1 mark)
(ii) – Stunted growth;
– Paralysis of legs/arms/limbs/damage to peripheral nerves;
– Heart failure
– Swelling of feet/oedema
– Gastrointestinal disturbances/loss of appetite/sonstipation/diarrhoea/vomiting;
– Weight loss/muscle wasting
– Pale skin (2 marks)
4.(a) Parental phenotypes Smooth Wrinkled
Meiosis
(b) Parental genotypes
(i) Genotypic ratio
(ii) Phenotypic ratio 3 smooth coats 1 wrinkled coat;
(c) The total number of wrinkled seeds.
(1 mark)
1/4 x 14,640 = 3660 ; (2 marks)
5.a)(i) H – It is long/wide/broad/fiat; to provide a large surface area for attachment of muscles;
– Has facets; for articulation with sacrum; (2 marks)
(ii) J Has flexible cartilage; which allows for widening of the (female) pelvic girdle when giving birth/to absorb shock.
(2 marks)
b)Allows passage of blood vesselslnervesl and muscles: (1 mark)
(i) Femur; 1 mark
(ii) Ball and socket; l mark
Coccyx; l mark
See graph on the next page. c) (i) No change in population/population is constant; mice still maturing/have not given birth; (2 marks)
(ii) Slow/gradual population growth; few mice have reached sexual maturity; (2 marks)
(iii) Faster/rapid rate of population growth/exponential;
Many mice sexually matured/reproducing/enough food/space/no competition/ birth rate higher than death/no diseases: (2 marks)
(iv) Population decline;
Competition is high / food is limiting / space is limiting/accumulation of toxic waste/disease (outbreak) deathrate higher than birth rate.
(2 marks)
6.(i) 6 and 8 ; (l mark)
(ii) 310 – 115 = 195 mice per month;
(2 marks)
Population would increase; (1 marks)
Food; space ; cage size; water;
(max) (2 marks)
7 .a) When a blood vessel is cut/injured platelets/thrombocytes/damaged tissue/wound is exposed to the air; they release thrombokinase/thromboplastin ; an enzyme that activates the conversion of prothrombin; to thrombin; in the presence of calcium ions;
vitamin Kl phylloquinone ; is needed for the formation of prothrombin;
Thrombin convens (soluble blood protein) fibrinogen ; into (the fibrous form) fibrin;
which forms a mesh / network across the wound; The clot so formed prevents excessive bleeding; and entry of disease agents/pathogens/micro-organisms/microbes;
Max 10 marks
b)Many to provide a large surface area; across which large amounts of gases diffuse;
moist surfaces; to dissolve respiratory gases; so as to diffuse. Made of a thin membrane/epithelium/one cell thick wall ; to reduce diffusion distance;
Highly vascularized; to carry away oxygen; and bring in carbon (IV) oxide; creating a steep diffusion gradients. (10 marks)
8.Regulation of blood sugar ;
when blood sugar is below nomtal/90 mg/ 100 cm3 glucagon ;
triggers the conversion of glycogen to glucose in the liver ;
the glucose is released into the blood stream.
When blood sugar is in excess above normal/10 mg/100 cm’, insulin;
causes the liver to convert glucose excess to glycogen ;
which is stored.
Production of heat energy ;
by increasing the rate of metabolic activities;
Excretion of bile pigments ;
produced due to breakdown of wom out red blood cells;
Deamination/removal of amino group of excess amino acids to form urea; and detoxication/poisonous/toxic substances;
(Max l0 marks)
b) Sweat glands excrete urea; excess water;
and salts;
hence maintaining salt & water balance in the blood. Evaporation of sweat;
cools the body due to loss of latent heat of vaporization;
when the body temperature rises ;
blood vessels in the skin vasolidate;
allowing more blood to flow near the skin surface;
thus heat is lost to the environment byfadiation/convection.
The erctor pili mucle relaxes hair flattens ;
in a hot environment reducing insulation;
hence heat is lost from the body by radiationl convection; to the environment.
(max 10 marks)
Biology Paper 3 (231/3)
1 (i)Sternum; (1 mark)
(ii)The intemal intercostal muscles relax; pulling the ribs upwards; and outwards;
This increases the volume of the rib cage while pressure decreases;
Forcing air into the lungs;
(5 marks)
b)(i)Anterior/dorsal view; (1 mark)
(ii)Name – Neural canal; (1 mark)
(iii)Function – Passage of the spinal cord. (l mark)
V: It is thick and solid; for bearing the weight of the body (back) (2 marks)
S: It is long; to provide a large surface area for attachment of muscles;
(2 marks)
(i)image width = 9.8 cm;
(ii)Magnification = image length / width _
(iii)Actual lengthl width ‘
= 9.8:0.| 4.610.] Mg = >< 3 .12 ; Actual length AB – lO.4 1 0.] : 2.13 = 4 83$ cm ; (5 marks)
3 .
1 a)Simple leaves …………………………..go to 2;
b)Compound leaves …………………….. …..go to 4;
2 a) Leaves net-veined/reticulate …………….go to 3;
b)Leaves parallel veined …………………….Commelinaceae;
3 a)Leaves with serrated margins ……………. Malvaceae;
b)Leaves with smooth (entire) margins…………….Nystaginaceae;
4 a) Leaves opposite ………………………… .go to 5;
b)Leaves pinnate ………………………………Bignoniceae;
5 a)Leaves trifoliate ………………………….Papilionaceae;
b)Leaves alternate ………………………….. .Compositae;
( 10 marks)

