2013 KCSE Agriculture Past Paper
48.1 Agriculture Paper 1 (443/1)
SECTION A ( 30 marks)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided.
(1) State four reasons for inter-cropping. (2 marks)
(2) Give four advantages of intensive farming. (2 marks)
(3) Give four reasons why land should be prepared early in readiness for planting. (2 marks)
(4) State four reasons for deep ploughing during land preparation. (2 marks)
(5) State two conditions that must exist for a market to be purely competitive. (1 mark)
(6) Distinguish between grading and standardization in agricultural marketing. (2 marks)
(7) State our benefits of agro-forestry to a maize crop. (2 marks)
(8) Distinguish between intensive hedgerow and border planting forms of agroforestry.
(9) What is meant by each of the following terms:
(a) Mixed cropping
(b) mono cropping
(c) inter cropping
(10) State four advantages of timely planting. (2 marks)
(11) State four advantages of row planting in crop production. (2 marks)
(12) State four reasons why a nursery is important in crop production. (2mark)
(13) Distinguish between monopoly and monopsomy. (2 marks)
(14) Name the plant part used for vegetative propagation of each of the following plants:
(a) cassava
(b) sisal
(c) pyrethrum
(d) sweet potatoes.
(15) State four characteristics of a good vegetable seedling. (2 marks)
SECTION (20 marks)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided.
(16) The photograph below illustrates a method of irrigation.

(a) Identify the method of irrigation illustrated above. (1 mark)
(b) State two maintenance practices that are carried out on the equipment used in the method illustrated above_ (2 marks)
(c) Give one advantage drip irrigation has over the method of irrigation illustrated above in crop disease control. ( 1 mark)
17 The table below shows a format of at farm record.
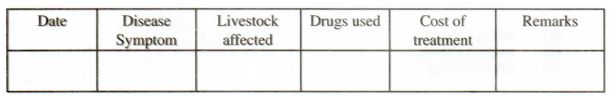
(a) Name the farm record illustrated above.( 1 mark)
(b) Give two uses of the farm record shown above. (2 marks)
18 The table below represents an account in a financial book of a poultry farmer.
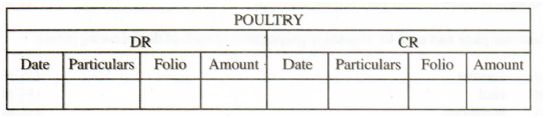
(a) identify the financial book. (1 mark)
(b) On 10th January 20ll . the poultry farmer bought 5 bags of layers mash worth Ksh. I000O/- and sold 100 trays of eggs for Ksh.2000O/- on 10 January 2011. Enter these transactions in the account above. (3 marks)
19 The following illustrations show different production function curves in agricultural economics. Study them and answer the questions that follow.
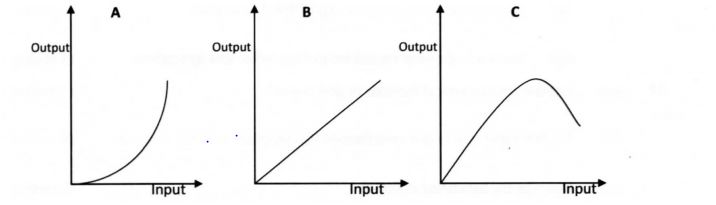
(a) ldentify the production function curves labelled a and b. (2 marks)
a …………… ..
b …………… ..
(b) What does the law derived from the production function labelled C state? (1 mark)
(i) Which one of the three production function curves is rare in Agriculture? (1 mark)
(ii) Give a reason for your answer in (c)(i) above. (1 mark)
20 The following is a list of plant nutrients; Copper, Calcium, Nitrogen, Molybdenum, Zinc, Phosphorus. Carbon. Sulphur. Iron and Magnesium.
(a) Which of the above plant nutrients are:
(i) Answer any two questions from this section in the spaces provided after question
21(a) macro-nutrients
(i) micro—nutrients
(ii) fertilizer elements
(iii) liming elements.
SECTION c (40 marks)
(b) Explain eight cultural methods of soil and water conservation. (8 marks)
(c) Explain four ways in which:
(i) HIV/AIDS limits agricultural production (4 marks)
(ii) government policy improves agricultural production (4 marks)
(iii) low level of education and technology influences agriculture. (4 marks)
(22a) Explain seven physical methods of pest control. (7 marks)
(b) Explain eight factors that contribute to the competitive ability of weeds. (8 marks)
(c) Describe the harvesting of coffee. (5 marks)
(23a) Describe the preparation and handling of stem cuttings when planting napier grass. (5 marks)
(b) Describe the production of onions under the following sub-headings:
(i) seedbed preparation (3 marks)
(ii) field management (4 marks)
(iii) harvesting. (3 marks)
(c) Give five reasons why land consolidation should be encouraged in Kenya. (5 marks)
4.8.2 Agriculture Paper 2 (443/2)
SECTION A (30 marks)
Answer ALL the questions in this section in the spaces provided.
1 State four ways of controlling lice in poultry.
2 State three signs of heat observed in rabbits.
3 Name three methods of extracting honey from combs.
4 State three signs of broodiness in a hen.
5 Give the main reason for each of the following in dairy farming:
(a) milking quickly and evenly;
(b) milking at regular times;
(c) complete milking.
6 State four factors that stimulate milk let-down in a lactating cow.
7 State four signs of infestation by external parasites in goats.
8 Give four disadvantages of inbreeding in livestock production.
9 State four advantages of fish farming in Kenya.
10 Give two reasons for castration in piglets.
11 Name two practices that are carried out on eggs in preparation for marketing. (1 mark)
12 State two precautions that should be observed when shearing sheep to ensure production of high quality wool.
l3 Name four pans of a farm building that can be reinforced using concrete.
14 State four factors that can affect digestibility of a feedstuffs in livestock.
15 State two causes of soft shelled eggs.
16 Give four characteristics of a good site for a fish pond.
17 State four disadvantages of fold systems in poultry rearing.
SECTION B (20 marks)
I9. Below arc photographs showing parts of a ruminant stomach, Study them and answer the questions that below.
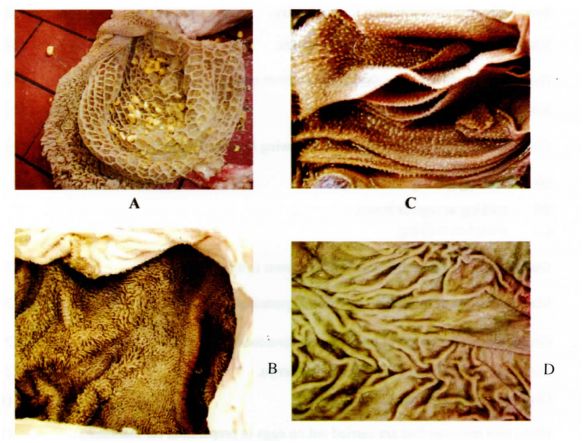
(a) Identify the pans labelled A and B (2 marks)
A ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. ..
B ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. ..
(b) State one function of the part labelled
A …………………………………………………………………………………………………………. ..
C ………………… ..
(c) Name one enzyme that is produced in the part labelled D. (1 mark)
20 Below is a diagram illustrating the reproductive system of a bull. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
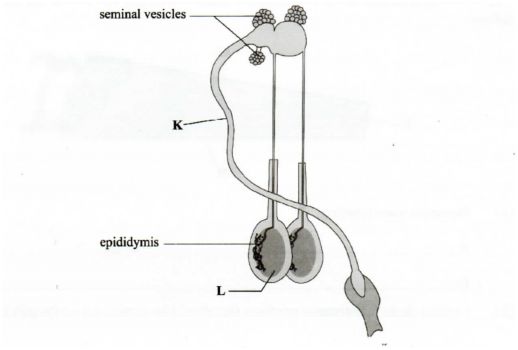
(a) Identify the pans labelled
K ………………. ..
L ………………. ..
(b) State the function of the part labelled
Epidermis
…………………………………………………………………………………………… .. (1 mark)
Seminal (l mark)
21 Below is a photograph showing an egg being candled. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
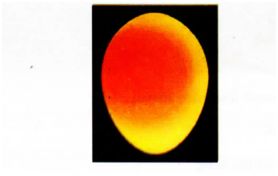
(a) Why is candling important in poultry farming? (1 mark)
(b) What changes will be observed on the same egg if it was candled on the 18th day of incubation? (2 marks)
22 The following is an illustration of a handsaw. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow.
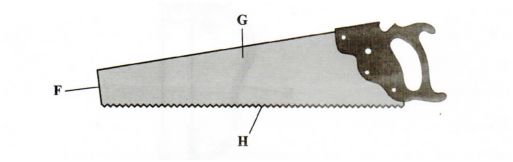
G
F
(a) Name the pans labelled
F
…………………………………………………………………………….. .. (1 mark)
G
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………. .. (1 mark)
(b) Explain three maintenance practices that should be carried out on the pan labelled H.
(3 marks) 23 Below is a diagram illustrating a farm implement Study it and answer the questions that follow.

(a) Identify the implement illustrated above. (1 mark)
(b) State the use of the:
(i) implement on the farm; (1 mark)
(ii) pan of the implement labelled J. (1 mark)
SECTION C (40 marks)
Answer any TWO questions from this section in the spaces provided after question 26.
(24) (a) Give five reasons for keeping livestock healthy. (5 marks)
(b) Describe the symptoms of roundworm infestation in livestock. (7 marks)
(c) Describe the control measures for cannibalism in layers. (8 marks)
(25)(a) Describe the body conformation features of a dairy heifer. (5 marks)
(b) State the disadvantages of using live fences on a farm. (7 marks)
(c) Describe how a four-stroke cycle petrol engine works. (8 marks)
(26)(a) Describe the disease control routine management practices in calf rearing. (7 marks)
(b) Describe contagious abortion (Brucellosis) disease under the following sub-headings: (i) causal organism; (1 mark)
(ii) animals affected; (2 marks)
(iii) symptoms; (4 marks)
(iv) control measures. (6 marks)
2013 KCSE Agriculture Past Paper-Marking Scheme/Answers
5.8.1 Agriculture Paper 1 (443/1)
SECTION A (30 marks)
(1) Reasons for inter-cropping Conserve soil/water (cover cropping); Maximise production; Maximise utilization of nutrients in the soil; Control weeds; Control pests/diseases; Diversification’/spread risks Maximise labour utilisation/save costs on labour. Improve soil fertility if legumes are included. Maximise utilisation of land.
(2) Advantages of intensive farmingIncreases production per unit area; Farm supervision is easy: Maximises utilization of available land; Ideal for densely populated areas/small land holdings; Utilizes technology to increase production.
(3) Reasons for early land preparationAllow time for weeds to dry and decompose; Allow for proper soil aeration; Allow timely planting / subsequent operations; Allow time for soil clods to disintegrate/soften.
(4) Reasons for deep ploughingFacilitates aeration; Facilitates drainage; Breaks hard pans/facilitates water infiltration; Bring up previously leached nutrients; Facilitate development of deep rooted crops; I Expose lower soil layers to weathering; I Expose soil bone pests and disease agents. Remove deeply rooted weeds.
(5) Conditions for purely competitive market
. Large number of sellers: Large number of buyers; Homogeneous product; Same price for the product; Free entry and exit from the market:Buyers and sellers have perfect knowledge of market trends.
(2 x 1/2= 1 mark)
(6) Grading – is the sorting of the produce into different lots.
each with the same characteristics market quality while Standardization is the establishment of uniformity in the quality and quantity of the product.
Mark as a whole 2 marks
(7) Benefits of agroforestry to a maize crop.Leguminous trees fix nitrogen into the soil: Trees act as windbreaks: Trees stabilize soil against soil erosion; Leaf litter decompose to form humus/recycle nutrients: Trees improve and act as water catchment areas/conserve water.
4 x 1/2= 2 marks
(8) Intensive hedgerow:- trees or shrubs are planted between rows of crops. Border planting:- trees or shrubs are planted on the borders of the farm.
Mark as a whole 2 marks
(9) (a) Mixed cropping:- ls the growing of two or more crops on the same field but on different sections.
(b) Mono cropping:- Is the growing of only one type of crop.
(c) lnter cropping:- ls the growing of two or more crops in the same field at the same time.3 x 1 3 marks
(10) Advantages of timely plantingDisease and pest control; Benefit from nitrogen flash: Weed control: Maximises rainfall utilization by the crop: Crop matures early when market prices are high/high demand.
(4 x 1/2 =2 marks)
(11) Advantages of row plantingField operations can be mechanized; Easy to establish plant population; Low seed rate than broadcasting; cultural practices/accept specific practices; Ensures proper spacing Ensures uniform germination of seeds.
(4 x 1/2= 2 marks)
(12) Importance of a nurseryMany seedlings can be produced in a small area; Facilitates timely routine management practices: best conditions for growth of seedlings: Small seeds and delicate seedlings grow into healthy and vigorous seedlings to facilitate transplanting; Reduced growth period in the field; Excess seedlings can be sold for income: Facilitate selection of healthy and vigorous/true to type seedlings for transplanting.
(4 x 1/2= 2 marks)
(13) (a)Monopoly:- Market dominated by only one seller:
(b) Monopsony:- Market dominated by only one buyer. Mark as a whole 2 marks
(14)(a) Cassava: – stem cuttings/stems
(b) Sisal: – Bulbils
– Suckers
pyre thrum: – Splits
(d) Sweet potatoes: – Vines/stem cuttings
4 x 11- 2 marks
(15) Characteristics of a good vegetable seedlingFree from disease/pest/healthy; Vigorous growing: Free from physical deformities; High yielding:Correct stage of growth/height 10 – 15 tall/4 – 6 true leaves.
4 x 1/2 =2 marks
(16)(a) Sprinkler/overhead irrigation. 1 x 1 =l mark
(b)Cleaning after use:Unblocking blocked nozzles: Lubricating rotating pans; Repairing/replacing broken/wom out parts; Proper storage after use: Oiling to prevent rusting; Tighten loose nuts.
2 x 1= 2 marks
(c)Drip irrigation does not wet the foliage hence controls fungal diseases l x l= 1 mark
(17) (a)Health record; 1 x 1 =1 mark
(a)Selection/culling;Show health status: Determination of treatment costs; Show prevalence diseases; Trace history of disease for effective treatment eg. drugs used, action taken; Show schedules for routine practices e.g. vaccination. deworming, etc.. 2 x l 2 marks
(18)Ledger 1 x 1 l mark
19 (a)
A – Increasing returns -production function curve.
B — Constant retums production function curve.
2 x 1= 2 marks
(b)The Law of diminishing returns.
If successive units of one variable input are added to fixed quantities of other inputs, a point is reached where additional (marginal/extra) product per additional unit of input declines.
(b)(ii) Other factors influence / limit agriculture production.
1 x 1 =1 mark
(20)(a)Macro-nutrients:- Calcium: Nitrogen; Phosphorous; Carbon: Sulphur; Magnesium.
1 mark Mark as a_ whole
(b)Micro-nutrients:- Copper; Molybdenum; Zinc; Iron.
( Mark as a whole 1 mark)
(c)Fertilizer elements:- Nitrogen. Phosphorous & Potassium.
Mark as a whole 1 mark
(d)Liming elements:- Calcium; Magnesium and Sulphur.
Mark as whole 1 mark
SECTION C (40 marks)
(a) Cultural soil and water conservation Grass/Filter strips:- reduce speed of flowing water/filter soil; Cover cropping:- prevents surface flow/reduces impact of rain drops/prevents evaporation/ volatilization; Contour farming:- creates ridges of soil which hold up \vater/reduce speed of run-off; Mulching:- reduces impact of rain drops/prevents evaporation/surface run-off: Rotational grazing:— allows grass to recover for soil and water conservation: Crop rotation:- maintain soil cover for protection against erosion/improves soil structure thus increasing infiltration: Inter cropping:- provides adequate cover on the soil; Strip cropping:- the different strips reduce speed of run-off/filter soil: Grassed/vegetated waterways:- slow the speed of water/trap eroded soil: Afforestation/Re-afforestation; Act as water catchments/stabilizes soil/canopy intercepts raindrops/wind; Agroforestry – stabilises soil/canopy intercepts raindrops/act as water catchment/wind; Use of manures/fertilizers; Promotes vegetative growth which covers soil against evaporation and erosion; Correct spacing of crops; Ensure adequate soil cover. 8 x 8 marks
(b) (i) Shortage of labour; Lack of motivation to invest in agriculture Increased cost of living leading to low investment in agriculture/lack of resources for Agricultural production.; Government and NGOs are spending a lot of time and resources controlling the disease instead of investment in agriculture. Lack of market for agricultual produce.
4 x l =4 marks
(ii) Establishment of national food security policy to supply free farm input to farmers to improve production: Facilitate soil conservation; Imposes laws to regulate quality of agriculture products; lmposes laws to regulate production and sale of agricultural produce to ensure sustainability: Imposes high taxes on imported agricultural products; Providing subsidies on agricultural inputs, e.g. fertilizers; Establishment of govemment agencies to supply inputs and market agricultural products; Construction of bulky handling and storage facilities for agricultural products; Funding research into new and improved agricultural production technologies: Ensures control of parasites/diseases/weeds is done effectively: Provision of extension services/education.
4 x l= 4 marks
(iii)Improper timing of routine practices; Lack of agricultural skills Low production of low quality I Inappropriate decision – making e.g. disease observation and control: Delayed adoption of new and improved production technologies. Lack of knowledge to apply / types and / of inputs; Inability to collect market information.
4 x l= 4 marks
(22)(a)Physical Pest Control Use of lethal temperature to kill the pests; Proper drying of produce to make it hard for pest to penetrate; Flooding drowns and kills pests; Suffocation to kill the pests in air tight containers; Physical killing ofthe pests /trapping and killing; Use of scarecrows /scaring away the pests: Use of physical barriers to prevent infestation by the pests; Use of electromagnetic radiation to kill the pests.
7 x 1 7 marks
(b) Factors for competitive ability of weeds Some produce large seed quantities to enhance survival chances; Some remain viable in the soil for a long time to await favourable conditions to germinate Some are easily and successfully dispersed to enhance chances of survival; Some have ability to propagate vegetatively into new plants: Some have extensive root system to enhance survival in drought conditions: Some have adaptations to survive where \vater/nutrients are limited through water and food storage modifications Some have a short life cyle which is completed early before adverse climatic conditions set in: Some initate animals as a protective measure against grazing, trampling/some are tolerant to pests and diseases. Some are heavy feeders they make food faster than crop establishes. Some weeds have allelopathic effects which suppresses growth of other plants enhancing their survival.
8 x 1 8 marks
(b) Harvesting of Coffee Pick red ripe ben’ies/cherries; Spread the berries on sisal mats and sort them out into Grades l. 2 and 3 (Mbuni) Deliver grades l and 2 to the factory for pulping same day; Dry grade 3; Deliver grade 3 to factory at the end of harvesting season: Picking interval of 7 – I4 days.
5 x 1 5 marks
(23) (a) Stem cuttings for Napier grass Select cuttings from a desirable variety: Select cuttings from healthy and high yielding mother plants; Make cuttings with 2 – 3 nodes: Place cuttings in planting holes in a slanting manner: Cover two nodes underground and one node above the ground.
5 x l 5 marks
(b) Production of onions
(i) Clear the land; Prepare the land early: Plough/dig deeply and eradicate all weeds: Harrow to a moderate tilth/tine tilth/appropriate tilth. 3 x 1 3 marks (ii) Thinning in directly planted crops to reduce competition; Weeding should be done carefully so not to damage shallow roots. Remove excess soil from root region. Do not compact the soil around the bulb: Top dress with nitrogenous fertilizer/CAN at a rate of 250 Kg per ha three months after planting: Spray with appropriate pesticide/chemical to control pests especially thrips; Spray with fungicides or practice crop rotation to control fungal diseases; Watering during dry spell/season.
4 x 1 4 marks
(iii) Harvest after 5 months; Harvest when leaves start drying; Break or bend the tops at the neck to hasten withering; Dig up the bulb and leave them to dry under shade; Tum daily to ensure uniform drying; Store in slatted boxes; Leave bulb to dry under shade.
(c) Reasons for land Consolidation Proper supervision Saves time and travel costs between plots; Easy to offer extension services on the actual and on-spot inspection of land; Encourages sound farm planning and adoption of crop rotation programmes; Encourages soil conservation and land improvement; Encourages mechanization due to enlarged holdings; Encourages construction of permanent structures/undertake long term project investments; Enhances weed, pest and disease control.
5 x 1 = 5 marks
5.8.2 Agriculture Paper 2 (443/2)
SECTION A: (30 MARKS)
(1) Dusting the birds with insecticide – sodium chloride. Observing good hygiene. Fumigation/smearing the affected perches with volatile insecticides. Picking and killing.
(2) The doe throws herself on its side. Frequent urination. Vulva turns red and swells. Doe becomes restless. ” Doe rubs her body against the wall. Peeping/contacting other rabbits in adjacent hutches.
(3) Crushing and straining /squeezing method. Heating method. Use of centrifugal extractor.
(4) Hens stop laying eggs. Hens sit on eggs for long periods /continuously. Hen plucks off feathers to make a nest. Hens are aggressive when approached/walks with wings open. Characteristics cracking sound.
(5)(a) Oxytocin effects last for five to seven minutes;
(b) Milk let-down is initiated when the milking time is reached;
(c) Prevent drying of /prevents reduce in yealds /prevents mastitis infection
(6)Sight of calf Washing/massaging the udder. Feeding Sounds associated with milking. Sticking to a regular milking routine. Sight of milkman
(7) Presence of sores/wounds on the skin. Irritation/scratching by the animal Loss of hair/alopecia. Anaemia Presence of various developmental stages of the parasite on the animal.
(8) Reduction of vigour in animalslloss of hybrid vigour/heterosis. Quality of products is lowered. Reduction in disease resistance ability. Appearance of undesirable hereditary defects. Increase in abortion/embryonic mortality. Decline in fertility Reduced production.
(9) Cheap source of protein for the family. Require little land and is possible where land is limiting. Quick souroe of income for the farmer. Makes fish to be available within the locality.
(10) Allow for even distribution of fat in the body. Control breeding. Increasing growth rate. To make them docile. Control breeding diseases.
(11) Checking for abnormalities/candling. Selecting eggs of the right size/weight. Cleaning/wiping often. Sorting and grading.
(12) Do not make half-cuts/make complete cuts. Shear sheep during the dry warm season. Do the operation on a clean dry floor/use clean shearing equipment. Do not cut body pans. Use clean shearing equipment
(13) Foundation of the building. The floor slab/floor. The Lintel. Pillars. Walls.
(14) Ratio of energy to protein in the feedstuff Form in which the feed is fed to the animal/method of feed preparation. Chemical composition of the feedstuff. Species of the animal. Amount of feed already present in the digestive system of the animal. Rate of feeding/frequency of feeding.
(15) Lack of calcium in the feed Disease attack such as Newcastle
(16) Topography/slope of land should be gentle sloping. Reliable water source. Area with cracks/anthills should be avoided. » Secure from predators and thieves. The site should be accessible.
(17)Disadvantages of fold system: Few birds per unit area. Laborious in moving the folds. Difficult to keep individual bird production records. Produces dirty eggs. Fold breaks easily due to constant movement.
(18)Dehorning methods:
Q Use of sharp knife.
v Burdizzo and knife.
Rubber ring and elastrator.
Use of hot iron.
. SECTION B: (20 marks)
(19)(a) A – Reticulum/Honey comb.
B – Rumen/pauch.
(b) A : Separat.ing fine and course food materials.
Retaining indigestible food materials.
C: Absorption of water.Grinding and sieving food particles Temporary food storage
(c) Pepsin/Renin
(20)(a) K – Urethra
L – Testes/testis
(b) Epididymis – stores sperms
Seminal Vesicles – Secrete seminal fluid in which sperms move.
Soil type/site should be free of gravel/stone/sand/preferably clay soil. Check egg abnormalities Monitor chick development during incubation Check whether the egg is fertile A large dark section of developing chick. A small clear section of air space.
F – Toe
G – Blade Sharpening of teeth regularly to improve efficiency. Regular cleaning after use to remove dirt. Setting the teeth to maintain cutting angles. Apply oil before storage to prevent rusting.
A Ridge/mould board ridge.
(i) To make ridges/furrows (ii) I used to attach the implement to a tractor.
v Adjusting the depth of operation.
SECTION C: (40 marks)
Reasons for keeping livestock healthy Good health ensures a long economic and productive life. Healthy animals give maximum production/high performance. Healthy animals grow fast and reach maturity early. Healthy animals are economical to keep/reduce production costs. Healthy animals produce quality products which fetch good prices. Healthy animals do not spread diseases to other animals/human beings.
Symptoms of roundworm attack. Anorexia/loss of appetite under heavy infestation. Stiff dry coat or starring coat Dehydration and pale mucosa. Eggs and adults are seen in faeces General emaciation Animal may diarrhoea Anaemic condition when infestation is heavy Pot-bellies especially in young animals. Coughing.
Control measure for cannibalism Avoid bright light in the house. Avoid overcrowding Provide balanced diet. Control extemal parasites. Hang vegetables in the house to keep birds busy. Debeak birds which peck at others. Cull perpetual cannibals/birds with prolapse. Provide adequate equipment feeders, waters, perches. Avoid introduction of new birds in the stock.
8 x l = 8 marks
Body conformation features of a dairy heifer. Straight topline. . Have large and well developed udder with large teats. l-lave large stomach which makes them heavy feeders Have prominent milk veins. Have less flesh on their bodies/lean bodies. Have well set hind quarters to allow room for large udders. Prominent pin bones. Wedge shaped. Long thin neck.
Any 5×1=5marks
Disadvantages of live fences May take long to establish into an effective fence. Not effective in sub-dividing land into paddocks/occupies a large space. May harbour pests. May create hiding places for thieves. wild animals and vermin. May be labour demanding to trim and infill regularly. May have shading effects on crops/competition for nutrients, moisture. May leave gaps which allow animals and thieves to pass through. Some may injure both livestock and the farmer. (7 marks)
How a four stroke cycle Engine works Induction stroke/intake Piston moves down the cylinder causing the inlet valve to open drawing in fresh supply of petrol vapour and air into the cylinder. Compression stroke The inlet valve closes and the piston moves up the cylinder. This compresses the fresh fuel mixture in the combustion chamber. Power Stroke/ignition _ A spark is produced at the spark plug. This causes the fuel mixture to ignite and expand resulting in pressure that forces the piston to move down the cylinder. Both valve closed. Exhaust stroke The piston moves up the cylinder to eliminate the bumt fuel mixture through the open exhaust valve.
Management practices on calves Culling highly susceptible calves. Drenching with antihelminthes to control intemal parasites. Vaccinate as appropriate against diseases – Castration of males not required for breeding. Identification at the appropriate age to facilitate record keeping Removal of any extra teats if more than four. Debudding/Dehoming Proper feeding of the calf. Treat the sick. Isolate the sick calves. Maintenance of hygiene.
Brucellosis
(i) Causal organism Bacteria/Brucella abortus/meIlitensis/suis/sp
(ii) Animals affected Cattle Sheep Goats Pigs
(iii) Symptoms Sponteneous abortion/premature births. Retained placenta. Infertility in females. Low libido in males. Orchitis/inflamed testis. Yellowish/brown slimy discharge.
(iv) Control Use of A.I. Culling/slaughter and properly dispose the carcass. Vaccination. Avoid contact with aborted foetus. Blood test to detect infected animals. Observe proper hygiene.

