Section A
1.(a) What is environment?
(b) Identify two effects of the following environmental hazards.
(i) Earthquakes (2marks)
(ii) Nuclear wastes (2marks)
2.(a) Name two species of hardwood forests grown in Kenya. (2marks)
(b) State three factors that favour the development of softwood forest in Kenya. (3marks)
3.(a) Define mining. (2marks)
(b) Describe two factors that have influenced exploitation of minerals. (4marks)
4.(a) Give two types of ground photographs. (2marks)
(b) State two limitations of using photographs. (2marks)
5.(a) Name two exotic dairy cattle breeds reared in Kenya. (2marks)
(b) State two physical factors which favour dairy farming in Denmark. (2marks)
SECTION B
Answer QUESTION 6 and any other TWO questions in this section.
6, The table below shows the vehicles moving past the D.C’s gate on Monday between 8:30a.m to 8:30p.m.
| Period | Isuzu | Leyland | Toyota | Nissan | Others | TOTAL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8:30 – 10: 30a.m | 100 | 150 | 300 | 240 | 80 | |
| 2:30 – 4: 30p.m | 40 | 60 | 70 | 20 | 80 | |
| 6:30 – 8: 30p.m | 120 | 130 | 90 | 140 | 120 | |
| TOTAL | 260 | 340 | 460 | 400 | 280 |
(b) Find the grand total of vehicles moving past the gate on Monday. (2marks)
(c) Draw a simple pie chart to show the type of vehicles moving past the gate on Monday (radius = 3cm) (8marks)
(d) Outline the merits of using a simple pie chart to represent the above data. (5marks)
(e) Apart from pie charts, give other five ways used to present statistical date. (5marks)
(f) Identify five methods of collecting statistical data. (5marks)
7.(a) Name the main types of natural forests in the world. (3marks)
(b) Explain the significance of forests and forest products in Kenya. (10marks)
(c) What has Kenya government done to conserve and manage forest? (5marks)
(i) State 5 factors influencing the distribution of natural forests. (5marks)
(ii) Define forest management. (2marks)
8.(a) Define a mineral. (2marks)
(b) Explain the forms in which minerals occur. (8marks)
(c) State five significance of minerals in Kenya. (5marks)
(d) Students from Mtwapa High School went out for a field study in L. Magadi.
(i) Name 3 preparations they made before the study. (3marks)
(ii) Identify 2 problems they might have encountered during the study. (2mark)
(iii) State 5 importance of studying geography through field work. (5marks)
9.(a) (i) State three social factors which influence agriculture . (3marks)
(ii) Name two types of maize grown in Kenya. (2marks)
(b) (i) Name two areas in Kenya where maize is commercially grown. (2marks)
(ii) Describe the stages involved in the industrial processing of maize. (4marks)
(c) Identify 4 problems facing maize farmers in Kenya. (4marks)
(i) Explain ways through which the Kenya government assists small scale maize farmers. (6marks)
(ii) State 4 uses of maize. (4marks)
10 (a) (i) What is Natural vegetation. (1mark)
(ii) State two topographical factors influencing distribution of vegetation. (2marks)
(b) You are required to carry out a field study of vegetation around your school.
State two objectives for your study. (2marks)
How would you record the findings in your study? (4marks)
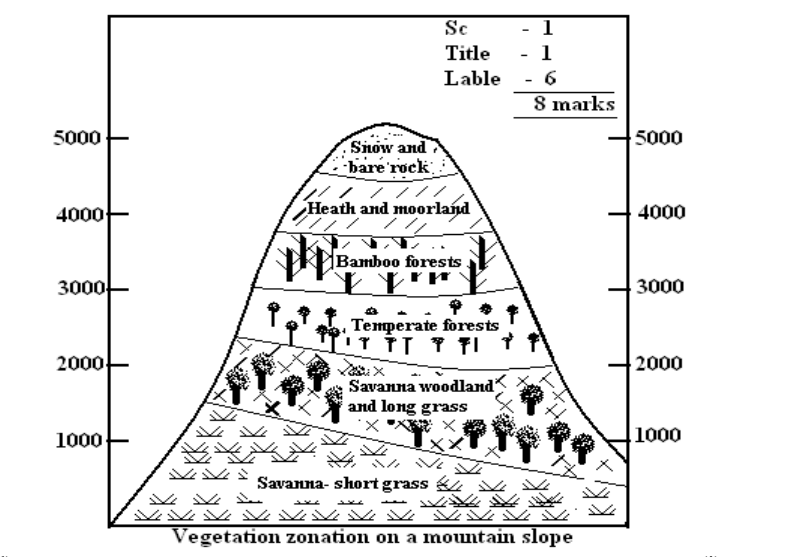
(c) Draw a well labeled diagram to show vegetation zonation on a mountain slope. (8marks)
(d) (i) Highlight five adaptational features of tropical desert vegetation. (5marks)
(ii) Identify two economic importance of desert vegetation.
Marking Scheme
Question 1.
1. (a) An environment is the physical conditions surrounding an organism and which influence the behavior of that organism. (1×2 = 2 marks)
(b) Effects of the following environmental hazards.
(i) EarthquakesLeads to loss of livesDestroys property.
(1 x 2 = 2mks)
(ii) Nuclear wastesReleases harmful radiationsCauses loss of human and animal lives (1 x 2 = 2mks)
Question 2.
(a) Two species of hardwood forests grown in Kenya.Meru oak , Elgon teak, Red Ceda, Mvule, Muringa , Mahogany, Ebony, Cape chestnut
(2 x 1 = 2mks)
(b) Three factors that favor the development of softwood forest in Kenya.Cool climate enable trees to grow / flourishHighlands receive high amount of rainfallRugged highlands discourage settlement and agriculture leaving forestry as the alternativeHigh demand for softwood products encourage tree plantingDeep soils favour forest growthSoft woods grow quite fast due to warm temperatures (Any 3, 3 x 1 = 3mks)
Question 3.
(a) Mining refers to all attempts to attract valuable minerals either solid, liquid or gas from the earth’s crust.
(b) Two factors that have influenced exploitation of minerals.Minerals that are of high demand and economic value may be mined at a very high cost because they can be sold at high prices e.g. gold, petroleum e.t.c.
Question 4
(a) Two limitations of using photographs.Vertical aerial photographs are difficult to interpret without special instruments e.g. stereoscopesPhotographs are expensive to produceCameras need well focusing to avoid blurred imagesObjects that are far away from the camera may not be clear thus leading to wrong interpretation.
(Any 2 points 2 x 1 = 2mks)
(b) Two types of ground photographs.Ground close-up photographsGround general view photographsGround oblique photographs (Any two points 2 x 1 = 2mks)
Question 5.
(a) Two exotic dairy cattle breeds reared in Kenya.Guernsey , Friesian/Holstein, Jersey, Alderney , Aryshire, Brown Swiss (Any 2 points 2 x 1 = 2mks)
(b) Two physical factors which favour dairy farming in Denmark.Gentle sloping landscape ideal for grazingWarm climate / sunny summer/ moderate temperatures 10-170C that allows outdoor grazingCool climates ideal for pasture growthModerate rainfall (500-1000mm) that supports growth of pasture / fodder cropsFertile boulder clay soils(Any 2 points 2 x 1 = 2mks)
Section B.
Question 6
Grand total of vehicles moving past the gate on Monday.
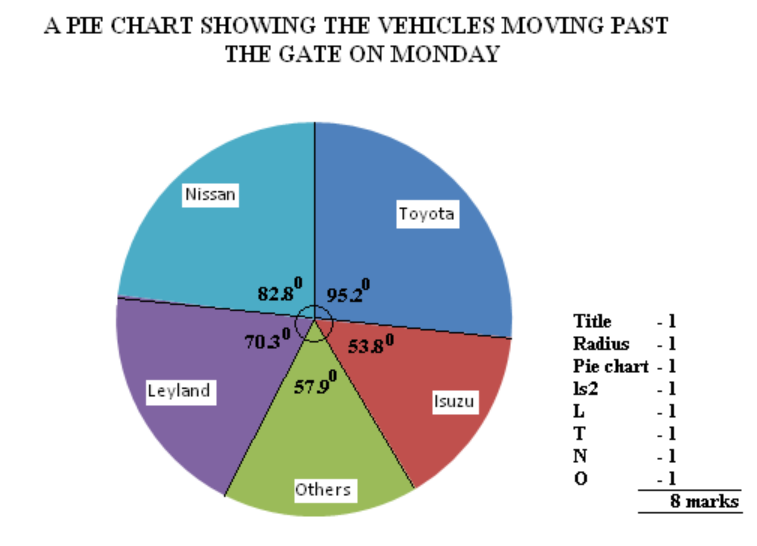
Simple pie chart showing the type of vehicles moving past the gate on Monday (radius = 3cm)
Isuzu – 260 x 360 = 53.80
1740
Leyland – 340 x 360 =70.30
1740
Toyota – 460 x 360 =95.20
1740
Nissan – 400 x 360 =82.80
1740
Others – 280 x 360 =57.90
1740

(c) Merits of using a simple pie chart to represent the above data.
(d) Other five ways used to present statistical date.GraphsProportional circlesPie chartsStatistical tables / chartsAge-sex pyramidsDot maps (1 x 5 = 5mks)
(e)Five methods of collecting statistical data.QuestionnaireInterviewsObservationSamplingTaking measurementsExperimentationContent analysis (secondary sources)Counting (Any 5 = 5 x 1 = 5mks)
Question 7
(a) Types of natural forests in the world.Tropical hardwood forestsTemperate hardwood forestsConiferous forests (3 x 1 = 3mks)
(b) Significance of forests and forest products in Kenya.Preservation and conservation of environmentActs as water catchment areasRegulation of climate / create a micro climateProvide habitat for wildlifeIt’s a source of incomeActs as a raw material for industries e.g. paper industryIt’s a source of employment e.g. forest guards, officersIt promotes tourismIt provides charcoalProvides fodder for animalsForest provide nuts, fruits and dyes, ropes nets, honey.It’s a hiding ground for military.Its an educational and research centreProvides wood and poles for building and constructionIt’s a source of tree leaves which are fed to silkworm (Any 5 explained 5 x 2 = 10mks)
(c) How Kenya government has done to conserve and manage forest.Carrying out public campaigns on the value of forests through mass mediaCarrying out research on suitability of soils and effects of pests and diseasesIt has established training institutions dealing with forestry e.g. KEFRI, Londiani forest training college.It has encouraged rotational felling of treesInfrastructural facilities like roads & mills have been provided by government.The government has introduced alternative sources of energy (fuel) e.g. solar energy, biogas to reduce overdependence on wood fuelIt has enacted laws to govern the management of forests.It has employed forest guards and officials to curb destruction of forestsN.G.O’s like Green Belt Movement and UNEP provide seedlings for forests.It has created forest reservesIt has encouraged agro-forestryExtensive afforestation programme is underway(Any 5 points 5 x 1 = 5mks)
(i) 5 factors influencing the distribution of natural forests.ClimateAltitudeSoilsHuman activitiesAspects & Slope.(5 x 1 = 5mks)
(ii) The management of forests refers to the effective planning and control of forests and forests resources.
(1 x 2 = 2mks)
Question 8
(a) A mineral is a naturally occurring, crystalline, inorganic substance with a definite chemical composition and physical properties.(2 x 1 = 2mks)
(b) Forms in which minerals occur.Veins and lodes; Minerals deposited in crystalline form in crack / creviceBeds and seams; Coal and other minerals may occur in bed / layers as a result of deposition, accumulation and concentration in horizontal layers of earth crust.Weathering products; Like Bauxite is formed by deep weathering of a variety of rocks due to alternating wet and dry seasonsAlluvial / placer deposits;some minerals like gold, tin and platinum occur as alluvial deposits within sand, clay and gravels in the river course. (4 x 2 = 8mks)
(c) Significance of minerals in Kenya.Rocks create beautiful sceneries which attract tourists hence earn Kenya foreign exchange.Rocks act as water reservoirs and store underground waterRocks provide parent material for formation of rich soils for agricultureRocks are used in building and construction industryRocks and mineral are sources of incomeRocks provide main record of past environmentRocks influence landscape featuresExploitation of rocks and minerals has led to dereliction (Any 5 points 5 x 1 = 5mks)
(d) (i) Preparations made before the study.Discussing / studying the topic of studySeek permission from authoritiesCollect required materialsConduct a reconnaissancePrepare questionnairesDivide into groupsPrepare a working schedule(Any 3 pts (3 x 1 = 3mks)
Problems encountered during the study.FatigueUncooperative respondentsFinancial constraintsLanguage barrierUnfavourable weather condition like floodsAccidents in the fieldInaccessibilityThick vegetation that’s difficulty to penetrate (Any 2 points = 2mks)
Importance of studying geography through field work.It gives first hand informationIt breaks classroom monotonyTeaches skills e.g. observation skillsEnhances learning in the real life situationEncourages critical thinkingEnables one to understand his / her environment(Any 5 points 5 x 1 = 5mks)
Question 9
(a) (i) Social factors which influences agriculture .Technology , religion, gender roles, foreign influence (Any 3 = 3mks)
(ii) Types of maize grown in Kenya.Dent cornSweet corn (2 x 1 = 2mks)
(b) (i) Areas in Kenya where maize is commercially grown.EldoretKitaleNakuru (any 2 x 1 = 2mks)
(ii) Stages involved in the industrial processing of maize.Maize grains are weighed and then put on traysAny undesirable grains and broken cobs are removedMaize is then sieved to remove any impurities like soil / rock particlesThe maize is then passed through a milling machine which grinds it into flourThe flour is then packed into small packets and sacks according to the desired weightPackets are sized 1 kg, 2 kg, and 10kg while sacks weigh more than 50kg
(Any 4 pts 4 x 1 = 4mks)
(c) Problems facing maize farmers in Kenya.Pests e.g. stalkborers, army worms, weevilsDiseases e.g. white leaf blightAdverse weather conditions like drought , floodsParasitic plants and weedsPrice fluctuationPoor quality seeds sold by unscrupulous tradersInadequate storage facilitiesExpensive certified seedsExpensive farm inputs (Any 4 pts 4 x 1 = 4mks)
(i) Ways through which the Kenya government assists small scale maize farmers.Arrange buying of maize through the cereal boardsConduct research to establish areas best suited for maize growing and research on diseasesOrganize demonstrations firms and field days to update farmers on current methodsEmploys extension workers who visit farmers and advise them on matters related to maize growingEncourage farmers to set up co-operatives to enable them pool resources togetherImproves feeder roads to ensure smooth transport of maize produce
(Any 3 x 2 = 6mks)
(ii) Uses of maize.Staple foodStalk, leaves and other remains from maize cobs are used to feed domestic animalsStalks and cobs are used to provide domestic fuelStalks and cobs are used as organic manureGrains are used in the making of corn oil.(Any 4 x 1 = 4mks)
Question 10
(a) (i) Natural vegetation is the plant cover that exist naturally in an area without the interference of any external modifying influence e.g. man.(1mark)
(ii) Topographical factors influencing distribution of vegetation.ReliefAspectDrainage(Any 2 well state points 2 x 1 = 2mks)
(b) (i)Objectives for the study.To find out the type of vegetation around the schoolTo determine the use of the vegetation around the school.
(Any other relevant point 2 x 1 =2mks)
(ii)How would you record the findings in your study?Note taking.Sketching.Tabulating.Phototaking. (Any other relevant point 4 x 1 = 4 marks)
(c) Well labeled diagram showing vegetation zonation on a mountain slope.

(d) (i) Adaptation features of tropical desert vegetation.They have succulent stemsLeaves are reduced to thorns / spikesThey have long tap rootsSome plants complete their life cycle within a short periodThey shed their leaves during dry season
(Any other relevant point 5 x 1 = 5mks)
(ii) Two economic importance of desert vegetation.
The vegetation adds beauty to the landscapeThe vegetation prevents soil erosion by binding the soil togetherThe vegetation acts as a habitat for wildlifeSome plants have medicinal valueSome desert vegetation are used in building and constructionSome plants are consumed as food by peopleFibrous vegetation like sisal are used to make ropesThe vegetation is a source of fuel either as firewood or charcoal
(Any 2 points 2 x 1 = 2mks)

