2014 KCSE Drawing and Design Past Paper
3.21.1 Drawing and Design Paper 1 (449/1)
SECTION A (50 marks)
Answer all the questions in this section on the answer sheet provided.
1 (a) Write the following in full as applied in industrial training:
(i) TVET;
(ii) NITA;
(iii) T.T.l.
(b) State two uses of a beam compass.
2 (a) Define the following terms as used in the design process:
(i) primary objective;
(ii) secondary objective;
(iii) design brief;
(iv) prototype.
(3 marks )
(b) With the aid of sketches, describe three types of dimensions in technical drawing.
3 State one use of each of the following computer components:
(i) keyboard;
(ii) mouse;
(iii) monitor;
(iv) hard disk.
4 Construct a triangle of perimeter l65 mm Whose sides are in the ratio of 315:6.
5 (a) List four factors to consider when lettering. (2 marks)
(b) State three effects of poor disposal of engineering materials to the environment. (3 marks)
6 Figure 1 shows a block drawn in isometric projection. Sketch in good proponion the orthographic views of the block in first angle projection. (7 marks)

7 Figure 2 shows three views of a block drawn in third angle projection. lid
Fig.2
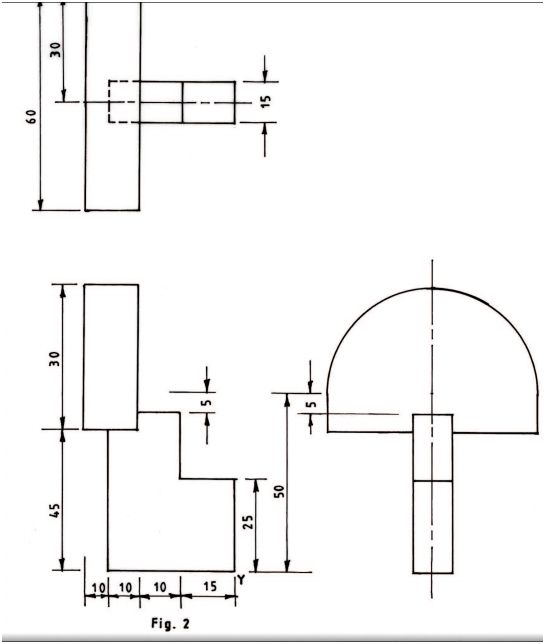
On the isometric grid paper provided, sketch the pictorial view of the block taking “Y” as the lowest point
. (6 marks)
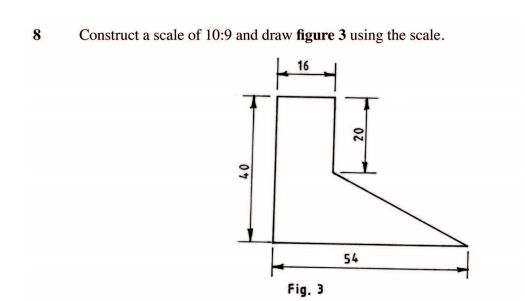
8 Construct a scale of 10:9 and draw figure 3 using the scale. (5 marks)
9 An equilateral triangular prism is intersected by a cylinder at right angles as shown in figure 4.
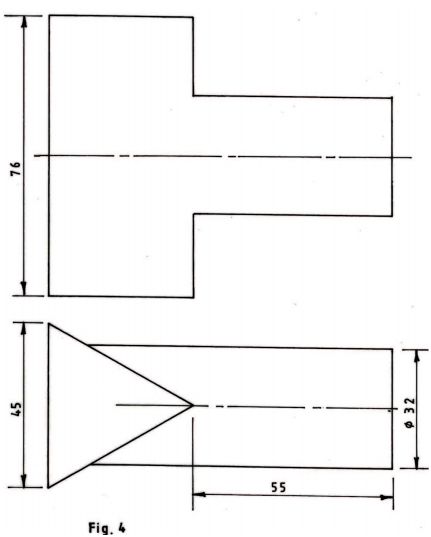
Draw the line of intersection. (5 marks)
10 Figure 5 shows views of two pans of a block drawn in first angle projection.
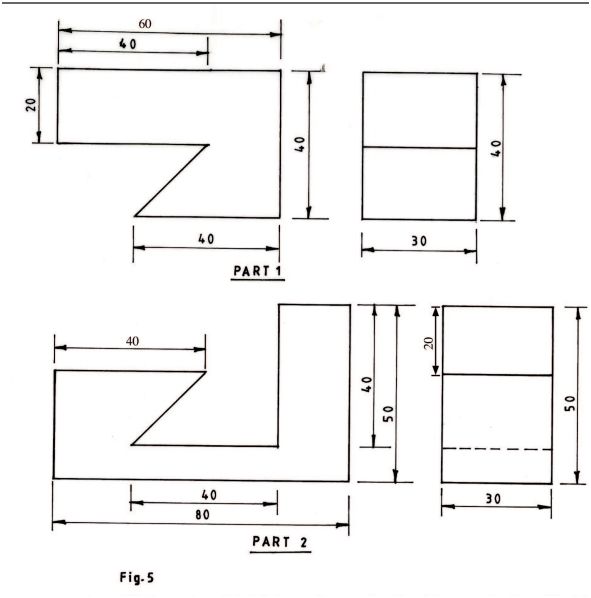
Assemble the pans and sketch in good proportion the oblique projection of the block. (5 marks)
SECTION B (20 marks)
COMPULSORY QUESTION.
11 Figure 6 shows parts of a machine component drawn in first angle projection. Assemble the parts and draw FULL SIZE the following:

(a) sectional front elevation along the cutting plane P – P;
(b) the plan;
Hidden details are not required. Unspecified dimensions are left to the candidate’s discretion.
SECTION C (30 marks)
Answer any two questions from this section.
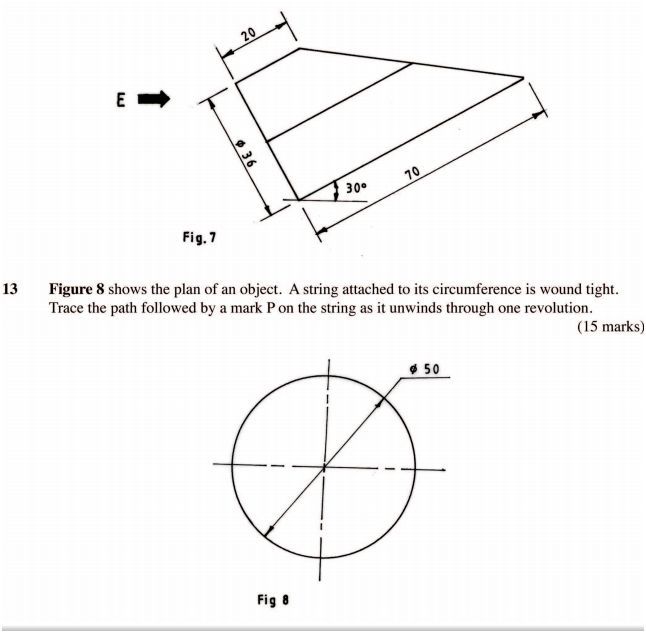
12 Figure 7 shows the front elevation of a truncated hexagonal prism tilting at an angle of 30°.
Copy the given view and draw the following in third angle projection:
(i) end elevation in the direction of arrow E;
(ii) the plan.
(15 marks)
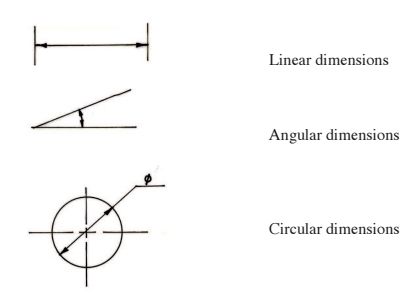
Trace the path followed by a mark P on the string as it unwinds through one revolution. (15 marks)
14 Figure 9 shows a block drawn in isometric projection.
Draw FULL SIZE in first angle projection the three orthographic views of the block. (15 marks)

3.21.2 Drawing and Design Paper 2 (449/2)
DESIGN PROBLEM: (40 marks)
People have had serious accidents caused by the use of ladders that are poorly designed.
Design a ladder considering the following:
l. It should provide a reasonably strong grip when leaning on a cylindrical column.
2. It should have rungs (steps) that make the user comfortable When working.
3. It should have provision for extension as the Working height increases.
4. It should be folded for ease of storage and transportation.
5. Its base should provide a firm grip to the ground.
REQUIREMENTS
(a) Make freehand sketches of TWO possible solutions for your design. (6 marks)
(b) Select ONE of the designs in (a) above and make a refined labelled pictorial sketch. (9 marks)
(c) Make detailed sketches of the mechanisms to allow for each of the considerations 1 to 5 above. (20 marks)
(d) List TWO materials used and state ONE reason for the choice of each. (3 marks)
(e) Name TWO methods of joining the parts and state Where each is used. (2 marks)
2014 KCSE Drawing and Design Past Paper-Marking Scheme/Answers
4.21 DRAWING AND DESIGN (449)
4.21.1 Drawing and Design Paper
1 (449/ 1)
1. (a) TIVET – Technical Vocational Education Training.
NITA – National Industrial Training Authority.
TTI – Technical Training Institute.
(3 x 1 = 3 marks)
(b) Uses of a beam compass:
– Drawing circles and arcs of very large radii.
– Stepping off large distances. (2 x 1 = 2 marks)
2. (a) Terms in the design process:
– Primary objective is the functionality of a design solution or a workable solution.
– Secondary objective refers to value addition, eg. comfort, aesthetics etc.
– Design brief refers to the narration of the problem solution.
– Prototype is the model or sample of the finished product.
(b) Types of dimensions
3. (a) Uses of:
Key board
Mouse
Monitor
Hard disk
(4 x1= 4 marks)
Linear dimensions
Angular dimensions
Circular dimensions
(3 x 1 = 3 marks)
for typing/keying in information and giving commands.
For giving commands.
To display whatever is going on or taking place in the computer.
For storage of information i.e. primary storage media.
4.

Druving and measuring 165mm =
Dividing The line inio1h aquql pm-1
Dzhrming 3 5 8. 6 =1k = 1/2
Identify 3 5 6 portions = 11/2
Juining the points =
_ = 5.Factors to consider when lettering:
– Use of guidelines to give uniformity.
– Proportional and equal spacing of letters and numerical.
– Uniform strength/outline of letters and numerical.
– Consistency in style i.e. italic or gothic.
– Ascending and descending for lower case letters.
– Proportionality with the paper size.
(b) Effects of poor disposal of eng. materials.
– Global Warming.
– Harmful to the soil.
– Harmful to the aquatic life.
– Unsightly environment.
6.

7.

9.

10.

11.

12.

13.

14.


