2016 KCSE Biology Paper 1 Past Paper
2016 Biology Paper 1
Answer all the questions in the spaces provided.
1. (a) State two ways in which the muscles of the mammalian heart are special. (2 marks)
(b) Name the type of muscles found in the following organs. (2 marks) Stomach Bone
2. Why are plants able to accumulate most of their waste products for long? (2 marks)
3. State the importance of tactic responses among members of Kingdom Protista. (2 marks)
4. (a) Name one defect of the circulatory system in humans. (1 mark)
(b) State three functions of blood other than transport. (3 marks)
5. State the economic importance of anaerobic respiration in plants. (1 mark)
6. Explain continental drift as evidence of evolution. (3 marks)
(a) Name one defect of the circulatory system in humans. (1 mark)
7. Explain how the following prevent self pollination.
(i) Protandry (1 mark)
(ii) Self-sterility (I mark)
8. State three functions of Golgi apparatus. (3 marks)
9. (a) Name two structures of gaseous exchange in aquatic plants. (2 marks)
(b) What is the effect of contraction of the diaphragm muscles during breathing in mammals. (3 marks)
10. (a) State two disadvantages of sexual reproduction in animals. (2 marks)
(b) State two functions of a placenta. (2 marks)
11. Name two benefits that a parasite derives from its host. (2 marks)
12. Other than using a quadrat give two methods that can be used to estimate the population of grass. (2 marks)
13. (a) State two factors that affect enzymatic activities. (2 marks)
(b) Explain how one of the factors stated in (a) above affects enzymatic activities. (1 mark)
14. Give three factors that determine the amount of energy a human being requires in a day. (3 marks
15. (a) What is seed dormancy? (1 mark)
(b) Name a growth inhibitor in seeds. (1 mark)
16. State one use of each of the following excretory products of plants. (2 marks)
(i) Colchicine
(ii) Papain
17. State the name given to the study of:—
(i) The cell (1 mark)
(ii) Micro-organisms (1 mark)
18. Distinguish between haemolysis and plasmolysis. (2 marks)
19. Explain why it is not advisable to be in a poorly ventilated room with a burning charcoal stove. (3 marks)
20. State three factors that contribute to the deceleration phase in the population curve of an organism. (3 marks)
21. The figure below illustrates a food web in a certain ecosystem.
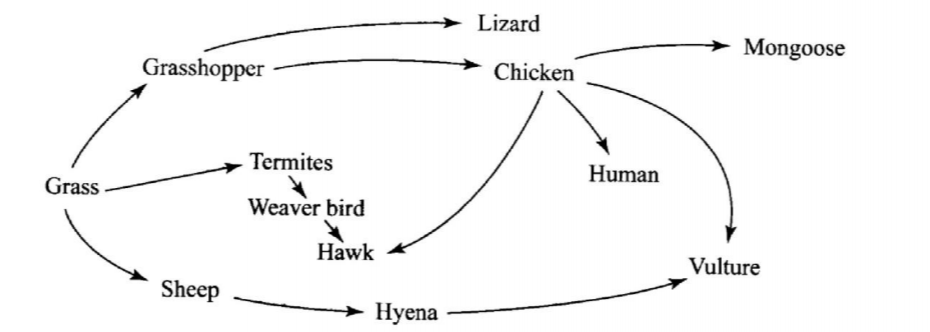
(a) Draw the shortest food chain
(b) Identify the organism with the highest:
(i) number of predators
(ii) biomass (1 mark)
22. State three characteristics of the class Crustacea. (3 marks)
23. (a) Name one salivary gland in humans. (1 mark )
(b) State two functions of saliva. (2 marks)
24. How does nutrition as a characteristic of living organisms differ in plants and animals. (2 marks)
25. Distinguish between diffusion and osmosis. (2 marks)
26. State the functions of the following pans of a microscope. (2 marks)
(a) Objective Lens
(b) Diaphragm
27. (a) What is single circulatory system? (1 mark)
(b) Name an organism which has a single circulatory system. ( I mark)
(c) Name the opening to the chamber of the heart of an insect. (I mark)
28. The diagram below shows a transverse section of a plant organ.

(a) Name the plant organ from which the section was obtained. (1 mark)
(b) (i) Name the class to which the organism from which section was obtained belongs. (1 mark)
(ii) Give a reason for your answer in b (i) above. (1 mark)
29. (a) State a characteristic that is common to all cervical vertebrae. (1 mark)
(b) Name two tissues in plants that provide mechanical support. (2 marks)
30. State two advantages of hybrid vigour. (2 marks)
2016 KCSE Biology Paper 1 Past Paper-Marking Scheme/Answers
No.1.(a) State two ways in which the muscles of the mammalian heart are special. (2 marks)
❖ Muscles are myogenic – able to initiate their own concentration.
❖ Presence of intercalated discs hence Interconnencted.
❖ Can contract continuously without fatigue.
(b) Name the type of muscles found in the following organs. (2 marks)
Stomach Bone ❖ Stomach – Visceral muscles/ smooth muscle.
❖ Bone – Skeletal muscles
No. 2.Why are plants able to accumulate most of their waste products for long? (1 mark)
❖ Most of the waste products are harmless;
❖ Waste products are converted into harmless products;
No. 3.State the important of tactic response among some members of the kingdom protista. (2 marks)
❖ Move towards favorable environment; accept converse
4. (a) Name one defect of the circulatory system in humans. (1 mark)
❖ Thrombosis/ Varicose veins/ Arterion sclerosis/ Antheroma
❖ Antherosclerosis
❖ Accept cerebral vascular thrombosis
(b) State three functions of blood other than transport. (3 marks)
❖ Regulation of the body temperature
❖ Regulation of pH of fluids
❖ Defense against disease – causing organism/ pathogens/ infection.
❖ Prevent excessive bleeding by enhancing clotting/ prevent excessive loss of blood
No. 5. State the economic importance of anaerobic respiration in plants. (2 marks)
❖ Baking of bread.
❖ Biogas production
❖ Compost manure formation
❖ Silage formation
❖ Commercial production of citric acid
❖ Sewage treatment.
No.6.Explain continental drift as an evidence of evolution. (3 marks)
❖ Current continents existed as one large land mass/ Pa.gea/ Laurentia Gondwanaland; the present continents drifted leading to isolation of organisms. Organisms in each continent evolved along different lines hence emergence of new species,
No. 7.( a) Explain how the following prevent self-pollination. (i) Protandry (1 mark)
❖ Male reproduction organ/ anthers androecia/ stamens mature earlier than female reproduction organ/ carpels/ stigma/ pistil/ gynoecium.
(ii) Seir sterility.
❖ Pollen grains are sterile to stigma of some plants/ flowers
No. 8.State three functions of Golgi apparatus.(3 marks)
❖ Form vesicles that transport materials to other parts of the cell e.g. proteins.
❖ Transportation secretions to the cell surface for secretion e.g. enzymes and mucus. Packaging of materials such as glycoproteins.
❖ They form lysosomes
No. 9.(a) Name two structures for gaseous exchange in aquatic plants. (2 marks)
❖ Pneumatophores
❖ Aerenchyma tissues
❖ Cuticle
(b) What is the effect of contraction of the diaphragm muscles during breathing in mammals? (3 marks)
❖ Leads to the flattening of the diaphragm. This increases the volume of the ribcage and lowers pressure inside compared to atmospheric pressure leading to respiration
No. 10.( a) State two disadvantages of sexual reproduction in animals. (2 marks)
❖ Harmful characteristics from the parents may be passed on the off springs
❖ Takes a longer time
❖ Few offsprings are produced at a time
(b) State two functions of the placenta in mammals. (2 marks)
❖ Exchange of nutrients / oxygen / metabolic wastes between the mother and foetus circulation systems.
❖ Secretion of progesterone hormones
No. 11.Name two benefits that a parasite derives from the host (2 marks)
❖ Obtains food/ nutrients
❖ Shelter
No. 12.Other than using the quadrant, give two methods of estimating population of grass.(2 marks)
❖ Belt transect
❖ Line transects
No. 13.(a) State two factors that affect enzymatic activities (2 marks)
❖ Temperature PH co- factors, co- enzymes; enzyme product concentration; substance concentration/ metabolic poison
(b) Explain how one of the factors stated in (a) above affects enzymatic activities. (1 mark)
❖ Temperature- increase in temperature increases rate of enzymatic activity up to an optimum
❖ Low temperature decreases enzymatic activity/ too high temp above optimum point denatures enzymes.
❖ Ph- Enzymes work best at optimum ph/ extreme ph denatures enzymes.
❖ Enzyme conc – Increase in conc. increase enzymatic activity.
❖ Co- enzymes – complements enzymes increasing rate of activity
❖ Substrate concentration increase enzymatic activity up to certain level.
No. 14. Give three factors that determine the amount of energy a human being requires in a day.(3 marks)
❖ Body size
❖ Sex
❖ Age
No. 15. (a) What is seed dormancy (1 mark)
❖ State during which a seed cannot germinate/ state of rest before seed germination; rej inability to germinate
(b) Name a growth inhibitor in seeds (1 mark)
❖ Absisicic acid
No. 16. State one use of each of the following excretory products of plants: (2 marks) (a) colchicine
❖ Inducing polyploidy/ treatment
(b) papain
❖ Meat tenderizer
17. State the name given to the study of (i) The cell (1 mark)
❖ Cytology: Rej cell biology
(ii) Micro-organisms (1 mark)
❖ Microbiology
(ii) Micro-organisms (1 mark)
❖ Microbiology
No. I 8.Distinguish between haemolysis and plasmolysis. (2 marks)
❖ Haemolysis – process by which red blood cells take in water till they burst; while Plasmolysis – loss of water from plant cells until the cell membrane is detached from the cell wall/ until the cell become flaccid.
19. Explain why it is not advisable to be in a poorly ventilated room with a burning charcoal stove.(3 marks)
❖ Charcoal in limited supply of air produces carbon(ii) oxide, which combines with haemoglobin forming Carboxylhaemoglobin which is a stable compound and does not dissociate easily, reducing capacity of the haemoglobin to carry oxygen leading to suffocation hence death
No. 20. State three factors that contribute to the deceleration phase in the population curve of an organism. (3 marks)
❖ Overcrowding
❖ Accumulation of toxic wastes
❖ Limited resources such as nutrients
No. 21. The figure below illustrates a food web in a certain ecosystem.
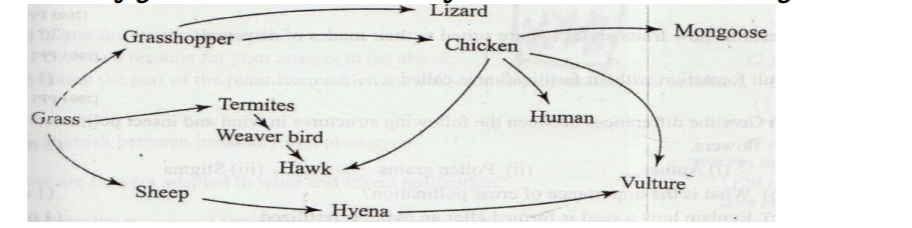
From the food web: (a) Draw the shortest food chain; (1 mark)
❖ Grass grasshopper lizards
b) Identify the organisms with the highest (i) Number of predators; (1 mark)
❖ Chicken
(ii) Biomass. (1 mark)
❖ Grass
No. 22.State three characteristics of the class Crustacea. (3 marks)
❖ Fused head and thorax/ capholothorax (often) protected by carapace.
❖ Gaseous exchange through gills
❖ Two pairs of antennae
❖ Five more pairs of limbs/ five to twenty pairs of limbs; rej five
❖ A pair of compound eyes
❖ Three pairs of mouth parts (consisting of labial pulps / maxillae/ mandible)
No. 23. (a) Name one salivary gland in humans. (1 mark)
❖ Sublingual; submaxillary/ submandibular; parotid
(b) State two functions of saliva (2 marks)
❖ Lubricating food; Digestion of starch; Moistens food; Provides alkaline medium;
❖ Softens food/ Dissolves food.
No. 24.How does nutrition as a characteristic of living organisms differ in plants and animals?(2 marks)
❖ Plants make their own food from carbon (IV) oxide and water in the presence of light /photosynthesize/ autotrophic; while animals eat readymade food (some plants and animals heterotrophic;
❖ If photosynthesis described all raw materials must be mentioned;
❖ Carbon (IV) oxide the (IV) must be bracketed.
❖ If sources of food for animals are mentioned then both plants and animals must appear.

No. 26. State the functions of the following parts of a light microscope. (2 marks)
(a) Objective lens
❖ Magnification of the object/ image
(b) Diaphragm
❖ Regulates amount of light (falling on the object on microscope); Acc: Adjust control amount of light
27. (a) What is single circulatory system? (1 mark)
❖ Blood goes through the heart once in very complete circulation
(b) Name an organism which has a single circulatory system. (1 mark)
❖ Fish
(c) Name the opening to the chamber of the heart of an insect. (1 mark)
❖ Ostium
No. 28. The diagram below shows a transverse section of a plant organ
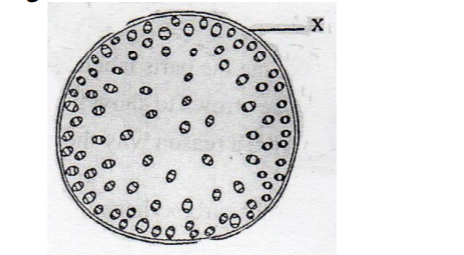
(a) Name the plant organ from which the section was obtained
❖ Stem
(b) (i) Name the class to which the plant organ was obtained. (1 mark)
❖ Monocotyledonae
(ii) Give a reason for your answer in (b) (i) above. (1 mark)
❖ Vascular bundles are scattered and not arranged in a ring
❖ Absence of pith/ cambium
(c)Name the part labeled X (1 mark)
No. 29(a). State a characteristic that is common to all cervical vertebrae (1 mark)
❖ Have short neural spines
No. 29(b).Name two tissues in plants that provide mechanical support (2 marks)
❖ Xylem tissues
❖ Collenchyma tissues
❖ Sclerenchyma tissues
❖ Parenchyma tissues
No. 30. State two advantages of hybrid vigour (2 marks)
❖ Resistance to pests/ disease/ adverse weather conditions
❖ Increase yield
❖ ••• Earlier maturity/ early maturity

