2017 KCSE Building and Construction Paper 1 Past Paper
Section A (40 marks)
Answer all the questions in this section.
1. (a) State two functions of shelter.
(b) State two limitations in starting a small business.
2. (a) Explain each of the following terms as used in roof construction.
(i) Span.
(ii) Hip.
(b) State two factors that influence the choice of roof for a building.
3. Explain each of the following terms as used in construction:
(i) Cladding.
(ii) Terrazzo.
4 (a) Name two types of foundations used on steep slopy sites with stable soil. (2 marks)
5 (a) Explain the term ‘services’ as used in building construction. (2 marks)
(b) State two conditions necessary when installing pipes to convey hot water. (2 marks)
6. Explain the difference between a load bearing wall and a non-load bearing wall. (4 marks)
7. Explain the following terms as used in concreting:
(a) Batching.
(b) Mixing.
8. Distinguish between rigid and flexible damp-proofing materials and give one example of each.
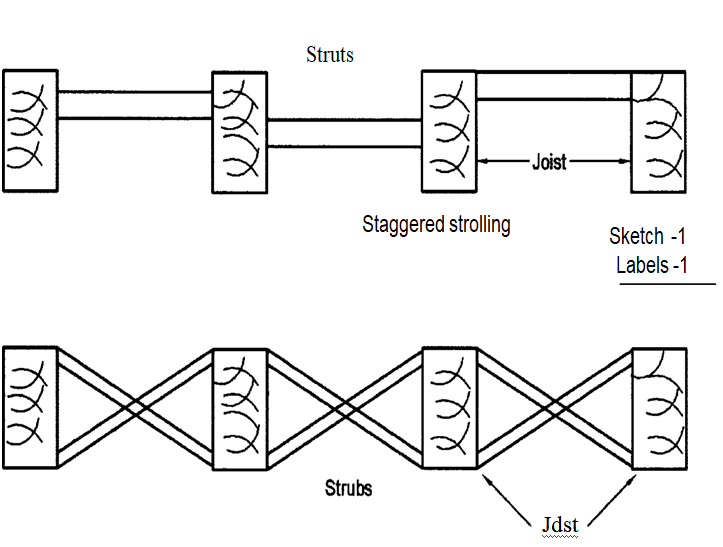
9 Sketch and label each of the following strutting used in timber floors:
(a) Staggered strutting.
(b) Herringbone strutting.
10 Figure 1 shows two orthographic views of a block drawn in first angle projection. (4 marks)
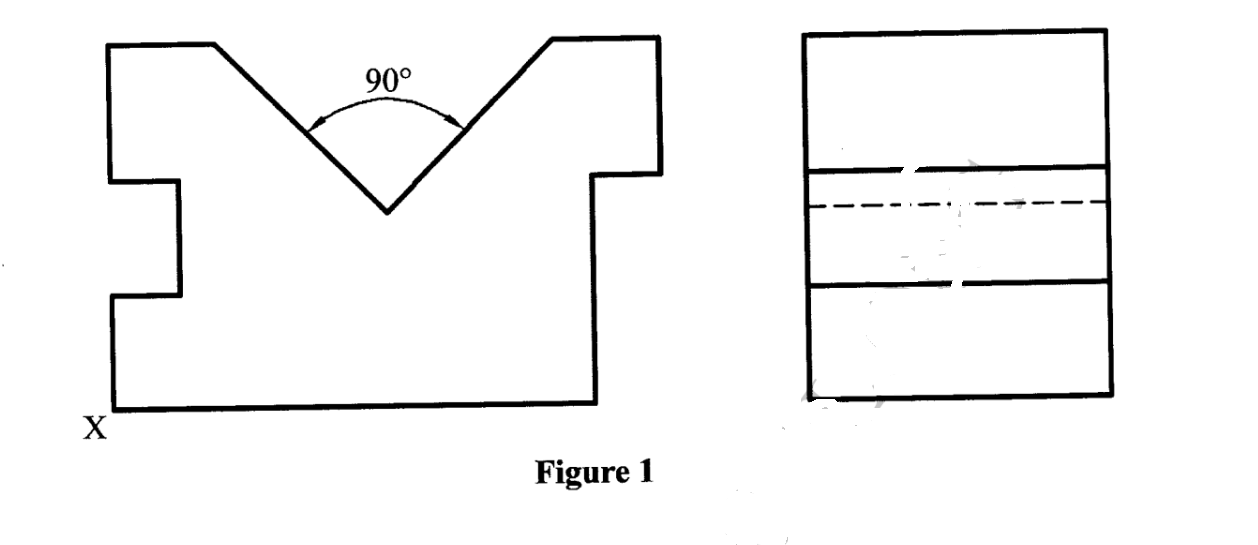
Sketch the block in isometric projection taking X as the lowest point. (6 marks)
Section B (60 marks)
Answer question 11 on the A3 paper and any other three questions from this section in the spaces provided.
Candidates are advised to spend not more than 25 minutes on question 11.
11 Figure 2 shows a shaped block drawn in isometric projection.
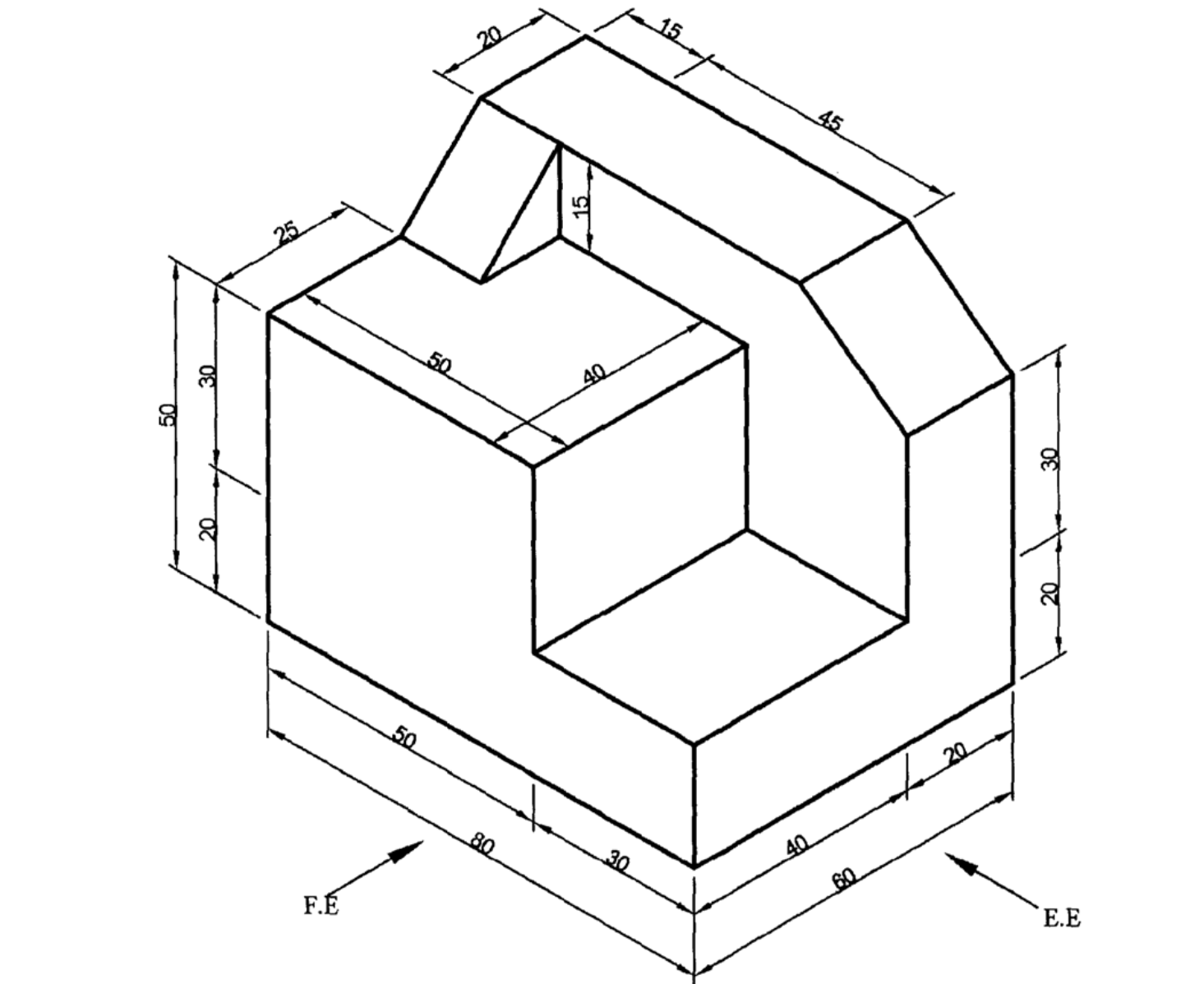
Draw the following views Full Size in first angle projection:
(a) Front elevation as seen in the direction of arrow F.E.
(b) End elevation as seen in the direction of arrow E.E.
(c) Plan. (15 marks)
12 (a) Outline the procedure of laying Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) tiles on a sand-cement floor screed. (8 marks)
(b) State five Kenya Building Code requirements for the construction of stairs.
(c) State two purposes of painting a plastered wall surface.
13 (a) Sketch and label a longitudinal section through a septic tank.
(b) (i) State four advantages of terrazzo as a floor finish.
(ii) Sketch and label a folding wedge and state where it is used.
14 (a) Define each of the following terms as used in stairs:
(i) Balustrade.
(ii) Riser.
(iii) Going.
(b) Sketch the following gardening tools and state one use of each.
(i) Trowel.
(ii) Rake.
(iii) Spade.
(c) State three functional requirements of form work.
15 (a) State three ways of controlling termites on site.
(b) Outline three factors that influence the choice of foundation for a building.
(c) (i) Sketch and label a King Post truss.
(ii) State two advantages and two disadvantages of a direct cold water supply system.
2017 KCSE Building and Construction Paper 1 Past Paper-Marking Scheme/Answers
1. (a) Functions of shelterTo protect man from adverse weather conditions. To offer privacy to man. To protect man from natural enemies.
(b) Limitations in starting a small businessLack of capital required to start a business. Lack of experience to run the business. Government policy, regulations and requirements.
2. (a) Terms used in roof constructions
(i) Span — Horizontal distance between internal faces of a wall in a room.
(ii) Hip — An inclined line produced from the ridge to the intersection of the eaves where external angle is more than 180°.
(b) Factors influencing the choice of a particular type of roof.
– Size and shape of building.
– Appearance of the roof.
– Cost of the roof.
– Climatic conditions of the area.
3. (i) Cladding
This is a type of finish fixed or hanged on external wall whose main purpose is to provide a degree of sound and thermal insulation or resist wind pressures against the wall and maintain wall aesthetics.
It can also be used internally on timber framed walls.
(ii) Terrazzo
This is a type of floor made of marble chips as aggregates.
4. (a) Foundations used on’steep sloppy site with stable soil.
Stepped concrete strip foundation. Short bored pile foundation.
(b) Factors to consider when selecting a site for a building.
Accessibility. Availability of services.
Topography or ground formation. Vegetation on site.
5. (a) Services as used in building construction.
These are installations in a building structure intended to make the conditions in the building and the surrounding comfortable.
(b) Conditions necessary when installing pipes to convey hot water.
Pipe lengths should be short.
– Related appliances should be kept in close proximity.
– Joints should be water tight
– Vertical pipes should be at 90° to the horizontal.
6. Load bearing walls
These are walls in a structure used to transmit both live and dead loads of a structure to the ground.
Non-load bearing walls
Walls which do not carry other loading apart from their own weight to the ground and are mostly used for partitioning and closing open spaces in a structure.
7. Batching
Measuring the correct proportions of materials in correct ratios to be used for making concrete.
Mixing
Blending thoroughly and completely the proportioned materials by either hand or using machine known as concrete mixer.
8. Rigid damp-proofing materials
These are stiff, fixed and rigorous materials which do not permit water pass through. Examples: Slates, Engineering bricks
Flexible damp-proofing materials
These are materials which are capable of being flexed without breaking. They can be turned, bowed or twisted without breaking and do not permit/allow water to pass through.
Examples: Mastic asphalt, bitumen, polythene paper
9.
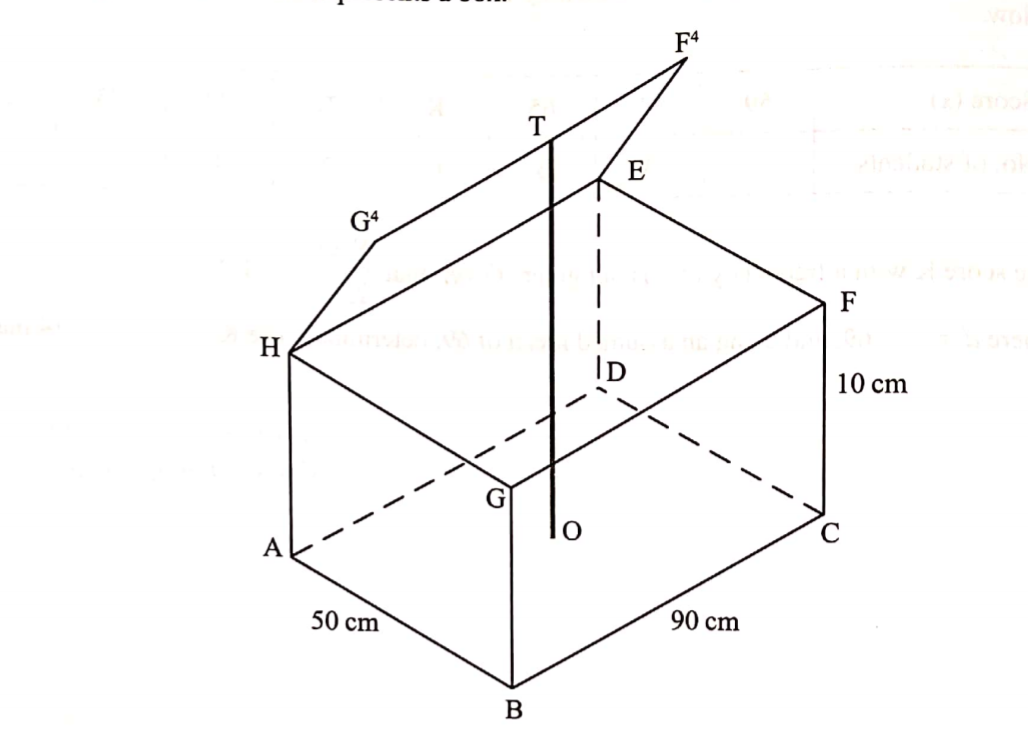
10.
11.
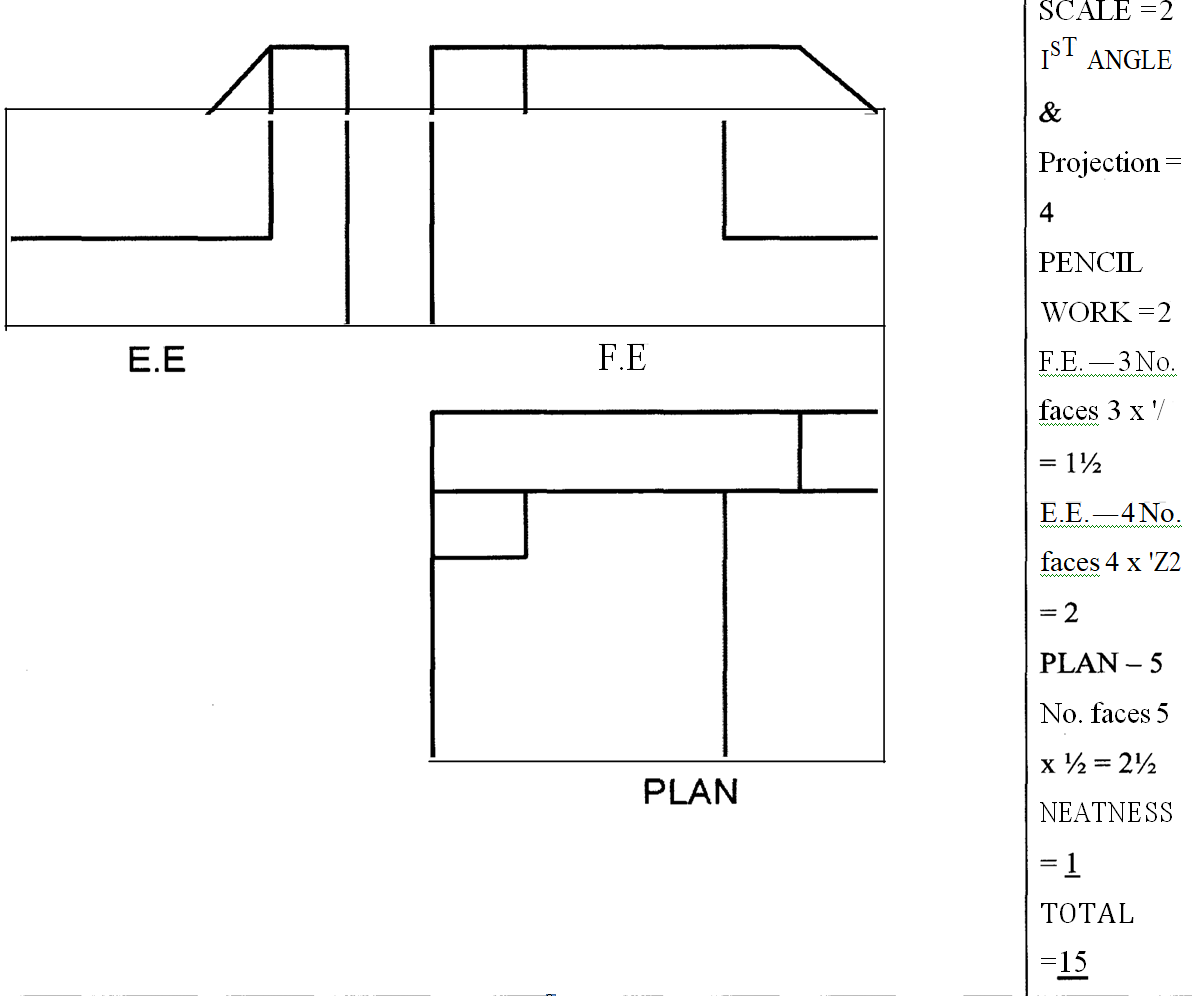
Section B
12. (a) Procedure of laying PVC tiles on a cement-sand screed floor
– The floor screed is cleaned to remove any dust or oils which may be present.
– The centre of the floor area to be tiled is marked to locate a point from which the tiling should commence.
– Lines a — a and b — b are marked on the floor to indicate the limits of two intersecting rows.
– Some adhesive is applied to the floor and a centre tile pressed firmly in position.
– Using lines a — a and b — b as guides the rest of the tiles are laid similarly to the first tile.
– Move away from the laid tiles as you lay the rest so as not to step on any laid tile.
– After all tiles are laid, the tiled floor is cleaned to remove excessive adhesive or mortar.
– Use a blunt object to remove the dirt such that the tile surfaces are not damaged.
(b) Kenya Building code requirements for a stair.
– Stairs should be constructed to have a constant and uniform rises and treads in a flight.
– Risers measured vertically from top of tread to top of tread should not be more than l88mm.
– Treads measured horizontally from faces of two consecutive risers should not be less than 225 mm.
– Vertical balusters on stairs and balconies should not be spaced more than l25mm apart.
– No protective balustrade should be less than 825mm in a height above landings. A handrail should be provided at each stair and will not encroach more than 75mm into the minimum width of the staircase.
(c) Purposes of painting
– Painting helps to protect surfaces from moisture, chemicals, insects and corrosion – Paint provides aesthetics (decorative) to surfaces in the form of colour and hence helps to beautify them.
Painting provides cleanliness and therefore hygienic surfaces.
13. (a)
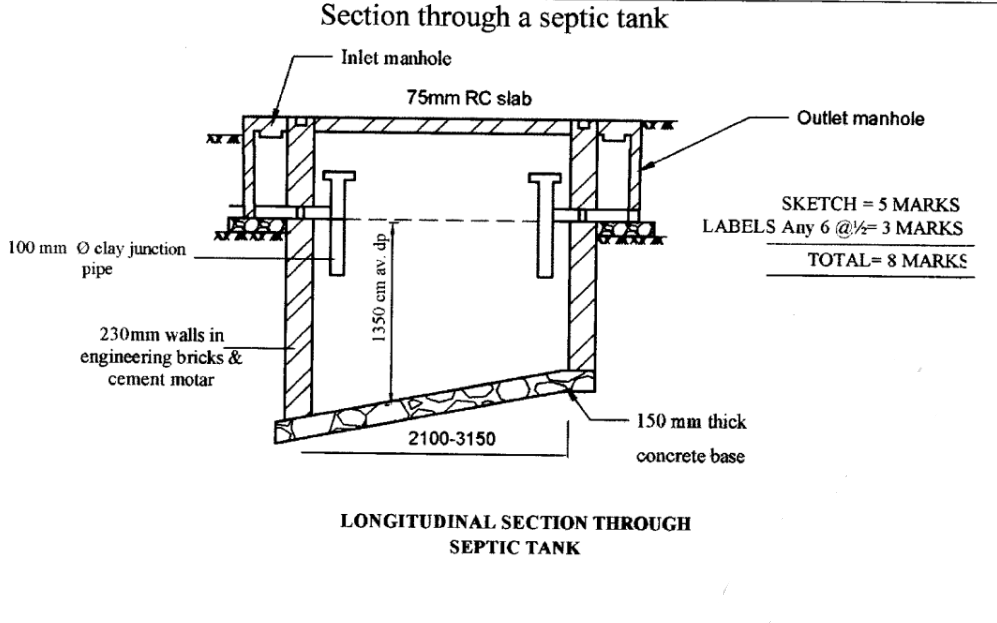
(b) Advantages of terrazzo floor finish.
– High quality floor finish.
– Hard wearing and durable surface.
– Easy to wash and therefore clean surface.
Dust free surface.
– Wide range of colour combination therefore attractive surface.
(c)
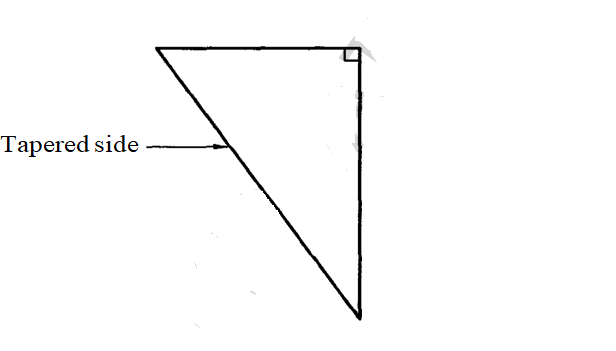
14. (a) Definition of terms
(i) Balustrade is a solid paneling between hand rail and strings.
(ii) Riser is the vertical part of a step between two consecutive treads.
(iii) Going is the horizontal distance between the outer faces of any two consecutive risers.
(b) (i) Gardening tools

– Digging and trenching – Planting trees and shrubs – Mixing compost and other types of manure
(c) Functional requirements of formwork
– Strong enough to withstand working loads and weights of concrete.
– Be sufficiently rigid to prevent undue movement.
– Have tight joints to prevent loss of grout from the concrete.
– Produce a concrete face of the required finish.
– Permit ease of removal when stripping/striking.
– Be economical. i.e. allow reuse of timber.
15. (a) Ways of controlling termites on site
– Ensure all wood used in construction is treated with wood preservatives.
– The soil under the building to be treated with termite pesticide.
– The soil and area around the building should be treated with termite pesticide.
Timber stored on site should be kept on a raised platform.
(b) Factors that influence choice of foundation
– Depth of foundation to the firm ground/bed.
– Type of soil on site.
– Weight of building to be erected.
– Topography of the site.
(c)(i) King post truss
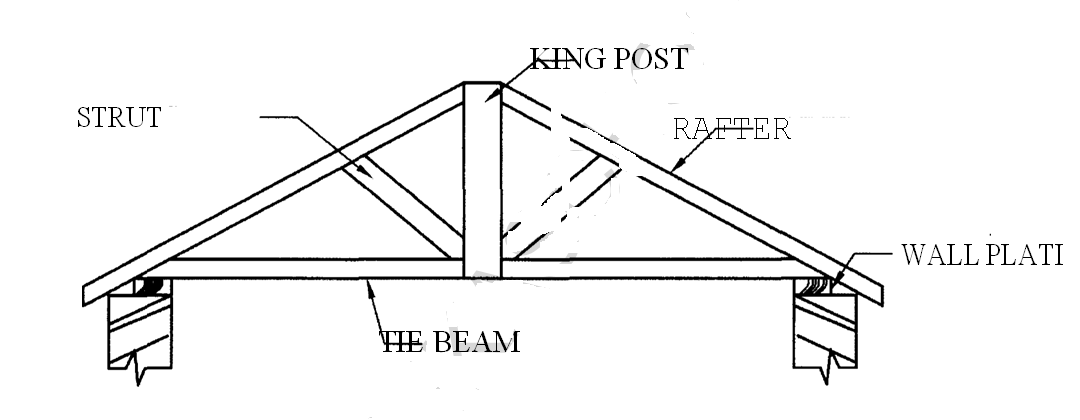
(ii) Advantages of direct cold water supply system
– No danger of contamination of water.
– Drinking water may be obtained at all appliances.
– There is a lot of saving in pipework especially with multi-storey buildings.
Disadvantages of direct cold water supply
– If the supply is disconnected the flow of water immediately drops.
– There is possibility of foul water from sanitary appliances being siphoned back to the mains.
– There is tendency to have water hammer as a result of more points connected directly

