2013 KCSE Maths B Past Paper
Mathematics Alt. B Paper 1 (122/1)
SECTION 1 (50 marks)
Answer all questions in this section in the spaces provided.
1.Without using a calculator, evaluate:
–3(-5 — + 7) + 2(-3 + +6).
2. The first four prime numbers are written in descending order to form a number.
(a) Write down the number.
(b) Find the total value of the hundreds digit in the numbers,
3. Without using a calculator evaluate:(3 marks)
4. Tito owned Ksh 600 to Nekesa, Ksh 750 to Mwita and Ksh 650 to A uma. He had Ksh 1200 to repay to the three people in proportion to what he owed them. Calculate the amount of money Mwita rcceived more than Nekesa. (3 marks)
5. Given that r — 2 and h = 3r — 1, evaluate 7r2 + 2rh/√ 4h – 2r (3 marks)
6. The surface area of a cube is 1176 cm3. Determine the length of one of” its sides. (3 marks)
7. By construction, divide the line PQ below into six equal parts. (3 marks)

8. Given that tan x = 3/4 and .r is an acute angle, without using mathematical tables or a calculator, find the value of 2 sin x — cosx. (3 marks)
9.A box contains Cve shillings coins and ten shillings coins. The number of ten shillings coins are 6 times as many as the five shillings coins.
The total value ot’all the coins in the box is Ksh 2600. Determine the total number of coins in the box. (4 marks)
10. Simplify 3-2 x 813/2/4-3 ÷ 81/3
leaving your answer in index form. Hence evaluate the expression. (4 marks)
11. A retailer bought a mobile phone for Ksh 5750. The marked price at the retailer’s shop was 12% higher than the buying price.
After allowing a certain discount, the retailer sold the mobile phone for Ksh 6118. Calculate the percentage discount. (3 marks)
12. Factorise 9a2 — 16/b2c2
(2 marks)
13. Three types of books A, B and C were each piled on a table to attain the same height. The thickness of the books were 12 mm, 28 mm and 54 mm for types A, B and C respectively. Find:
(a) the least height attained;
(b) the number of type A books piled. (3 marks)
14. The sum of the interior angles of a regular polygon is 1260°. Find the size of each interior angle. (3 marks)
15. The corresponding lengths of two similar triangles are 5 cm and 7.5 cm. If the area of the larger triangle is 22.5 cm2, calculate the area of the smaller triangle. (3 marks)
16. The area of a sector of a circle is 77 cm2‘. The arc of the sector subtends an angle of 45° at the centre of the circle. Find the circumference of the circle. (Take ℿ=22/7 (4 marks)
SECTION II (50 marks)
Answer only Ave questions in this section in the spaces provided.
17. The figum below represents a solid prism with a semi-circular groove. The dimensions are as shown.
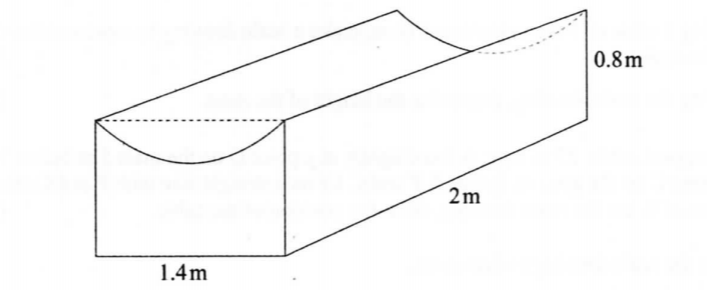
(a) Calculate:
(i) the volume of the prism;
(ii) the total surface area of the prism. (4 marks)
(b) All the rectangular faces are painted. Calculate the percentage of the surface of the prism that is painted correct to 1 decimal place. (2 marks)
18. (a) Three vertices of a parallelogram ABCD are A(—7, 3), B( 1. — I) and C(5, 1). On the grid provided, draw the parallelogram ABCD.
(b) Determine:
(i) the gTadient of the line AB; (2 marks)
(ii) the equation or line AB in the form y = m.r + c, where m and c are constants. (2 marks)
(c) Another line L is perpendicular to CD and passes through point (1, 3). Determine:
(i) the equation of L in the form ax + by = c where a, b and c are constants; (3 marks)
(ii) the coordinates of the y-intercept of line L. (1 mark)
19. (a) The roots of a quadratic equation are 2 and — 1. Write down the quadratic equation in the form ar° + bx + c = 0, where a, b and c are integers. (3 marks)
(b) (i) Barasa bought (2y + l ) mangoes at y shillings each. The total cost of the mangoes was Ksh 55. Find the cost of each mango. (4 marks)
(ii) Karau spent Ksh 95 more than Barasa to buy the same type of mangoes. For every 6 mangoes he bought, he was given one extra mango. Calculate the total number of mangoes Karau got. (3 marks)
20. The angle of elevation of the top T, of a vertical mast from a point P, 100 m away from the foot F, o(the mast is 14°.
(a) Using a scale of l cm to represent 10 m, make a scale drawing to represent the above information. (3 marks)
(b) Using the scale drawing, determine the height of the mast. (2 marks)
(c) A support cable, 27 m long, is fixed tightly at a point D on the mast 5 m below T and at a point C on the ground. Points P, F and C lie on a straight line with P and C on opposite sides ot’ F. On the scale drawing, show the position of the cable. (2 marks)
(d) Use the scale drawing to determine:
(i) the angle of depression of C from D; (1 marks)
(ii) the distance of C from P. (2 marks)
21. ln the figure below, P, Q, R and S are points on the circumference of the circle centre O.
TP and TR are tangents to the circle at P and R respectively. POQ is a diameter of the circle and angle PQR = 64°.
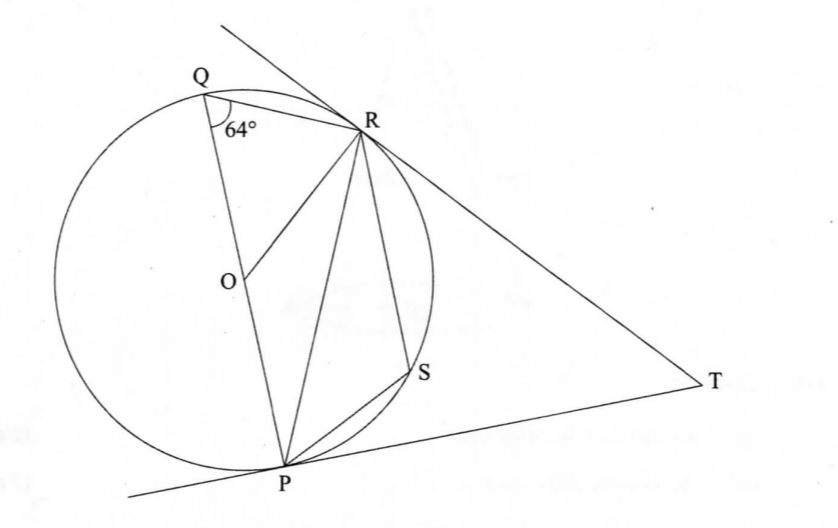
Giving reasons in each case, find the size of:
(a) ∠ ROP; (2 marks)
(b) ∠ PSR; (2 marks)
(c) ∠ ORP; (2 marks)
(d) ∠ RP; (2 marks)
(e) ∠RTP. (2 marks)
22. The figurc below represents a cone whose vertical height is 12 cm and slant hcight is 13 cm.
(a) Calculate:
(i) the radius, OA. of the cone; (2 marks)
(ii) the volume of the cone. (2 marks)
(b) A smaller cone of radius 6 cm is cut off’ from the com: alx» c to leave a i?ustum. Calculate:
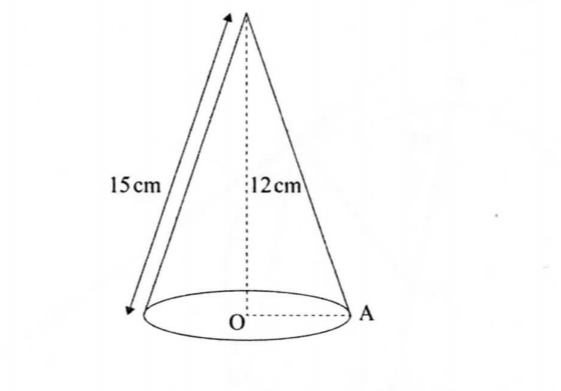
(i) thc height of the smaller cone;
(ii) the volume of the smaller cone:
(iii) the volumc of the frustrum.
23. The vertices of a trapezium ABCD are A(2, 0), B(4, 0), C(6, 2) and D(2, 2).
(a) On the grid provided below, draw:
(i) the trapezium ABCD; (1 mark)
(ii) A’B’C‘D’ the image of ABCD under a reflection in the line y — -x, (2 marks)
(iii) A”B”C“D“ the image of A’B’C’D’ under a rotation of —90°, centre (0, 0). (2 marks)
(b) Describe a transformation that maps A”B“C”D” onto ABCD. (2 marks)
(c) State pairs of trapezia that are directly congruent and those that are oppositely congruent. (3 marks)
24. A racing motorcycle started from rest and moved with a constant acceleration ot” 1 m/s2for 15 seconds. lt then accelerated at 3.5 m/s2 for the next 10 seconds and maintained a constant speed for the next 10 seconds. It decelerated constantly and came to rest after 25 seconds.
(a) On the grid provided, draw the velocity—time graph for the motorcycle. (4 marks)
(b) Use the graph to determine:
(i) the deceleration of the motorcycle; (2 marks)
(ii) the total distance travelled; (2 marks)
(iii) the average speed for the motorcycle, correct to 3 significant figures. (2 marks)
| https://googleads.g.doubleclick.net/pagead/ads?client=ca-pub-0326674550430411&output=html&h=280&slotname=5740034820&adk=426665019&adf=1697964612&pi=t.ma~as.5740034820&w=336&lmt=1640794296&psa=1&format=336×280&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.advance-africa.com%2FKCSE-Past-Papers-Maths-B-2013.html&flash=0&wgl=1&dt=1640794296001&bpp=3&bdt=3314&idt=380&shv=r20211207&mjsv=m202112060101&ptt=9&saldr=aa&abxe=1&cookie=ID%3D87de00f0c876c980-22afddb0dcce0092%3AT%3D1640760436%3ART%3D1640760436%3AS%3DALNI_MbO5KvUEkn_9Lf85NifGlSAHi4D8A&prev_fmts=0x0%2C336x280%2C336x280&nras=1&correlator=8408053816387&frm=20&pv=1&ga_vid=771581788.1594825585&ga_sid=1640794297&ga_hid=1153977752&ga_fc=1&u_tz=180&u_his=1&u_h=900&u_w=1600&u_ah=860&u_aw=1600&u_cd=24&u_sd=1&adx=565&ady=7203&biw=1583&bih=747&scr_x=0&scr_y=3&eid=44750774%2C182982000%2C182982200%2C31063824&oid=2&pvsid=3796900760782816&pem=734&tmod=277&ref=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.advance-africa.com%2FKCSE-Past-Papers.html&eae=0&fc=1920&brdim=-8%2C-8%2C-8%2C-8%2C1600%2C0%2C1616%2C876%2C1600%2C747&vis=1&rsz=d%7C%7CEebr%7C&abl=CS&pfx=0&fu=0&bc=31&ifi=4&uci=a!4&btvi=1&fsb=1&xpc=wh0tua92Q6&p=https%3A//www.advance-africa.com&dtd=724 |
Questions and Answers Mathematics ALT. B (I22) 2013
1.Without using a calculator, evaluate:
–3(-5 — + 7) + 2(-3 + +6).

2. The first four prime numbers are written in descending order to form a number.
(a) Write down the number.
7532
(b) Find the total value of the hundreds digit in the numbers,
Total Value of hundreds digit = 500
3. Without using a calculator evaluate:(3 marks)
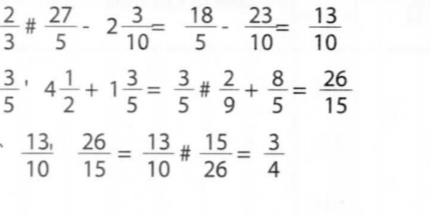
4. Tito owned Ksh 600 to Nekesa, Ksh 750 to Mwita and Ksh 650 to A uma. He had Ksh 1200 to repay to the three people in proportion to what he owed them. Calculate the amount of money Mwita rcceived more than Nekesa. (3 marks)

5. Given that r — 2 and h = 3r — 1, evaluate 7r2 + 2rh/√ 4h – 2r(3 marks)
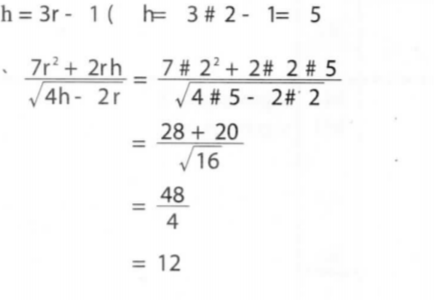
6. The surface area of a cube is 1176 cm3. Determine the length of one of” its sides. (3 marks)
Area of each face = 1176/6 =196 Lenght of one side √ 196 =14
7. By construction, divide the line PQ below into six equal parts. (3 marks)

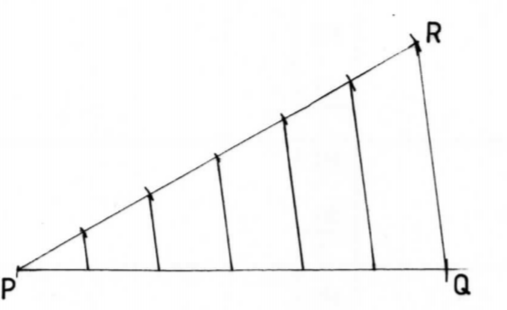
8. Given that tan x = 3/4 and .r is an acute angle, without using mathematical tables or a calculator, find the value of 2 sin x — cosx. (3 marks)
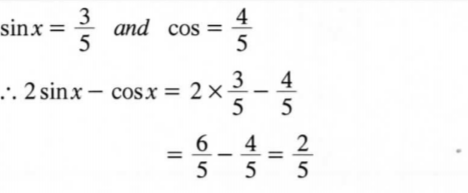
9.A box contains Cve shillings coins and ten shillings coins. The number of ten shillings coins are 6 times as many as the five shillings coins.
The total value ot’all the coins in the box is Ksh 2600. Determine the total number of coins in the box. (4 marks)

10. Simplify 3-2 x 813/2/4-3 ÷ 81/3
leaving your answer in index form. Hence evaluate the expression. (4 marks)
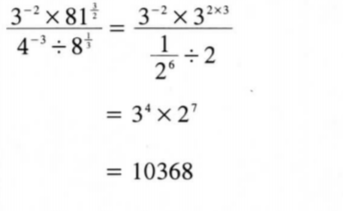
11. A retailer bought a mobile phone for Ksh 5750. The marked price at the retailer’s shop was 12% higher than the buying price.
After allowing a certain discount, the retailer sold the mobile phone for Ksh 6118. Calculate the percentage discount. (3 marks)

12. Factorise 9a2 — 16/b2c2
(2 marks)
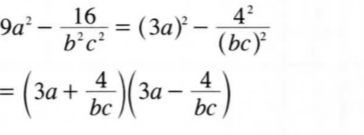
13. Three types of books A, B and C were each piled on a table to attain the same height. The thickness of the books were 12 mm, 28 mm and 54 mm for types A, B and C respectively. Find:
(a) the least height attained;
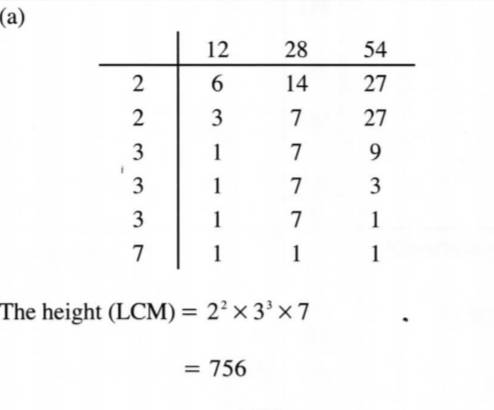
(b) the number of type A books piled. (3 marks)
Number of books = 756/12 =63
14. The sum of the interior angles of a regular polygon is 1260°. Find the size of each interior angle. (3 marks)

15. The corresponding lengths of two similar triangles are 5 cm and 7.5 cm. If the area of the larger triangle is 22.5 cm2, calculate the area of the smaller triangle. (3 marks)
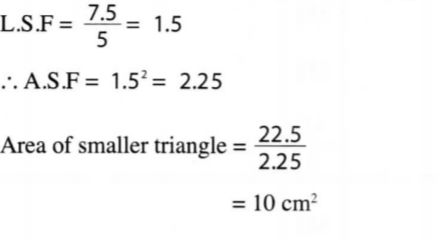
16. The area of a sector of a circle is 77 cm2‘. The arc of the sector subtends an angle of 45° at the centre of the circle. Find the circumference of the circle. (Take ℿ=22/7 (4 marks)

SECTION II (50 marks)
Answer only five questions in this section in the spaces provided.
17. The figum below represents a solid prism with a semi-circular groove. The dimensions are as shown.

(a) Calculate:
(i) the volume of the prism;
(ii) the total surface area of the prism. (4 marks)
(b) All the rectangular faces are painted. Calculate the percentage of the surface of the prism that is painted correct to 1 decimal place. (2 marks)

18. (a) Three vertices of a parallelogram ABCD are A(—7, 3), B( 1. — I) and C(5, 1). On the grid provided, draw the parallelogram ABCD.
(b) Determine:
(i) the gradient of the line AB; (2 marks)
(ii) the equation or line AB in the form y = m.r + c, where m and c are constants. (2 marks)
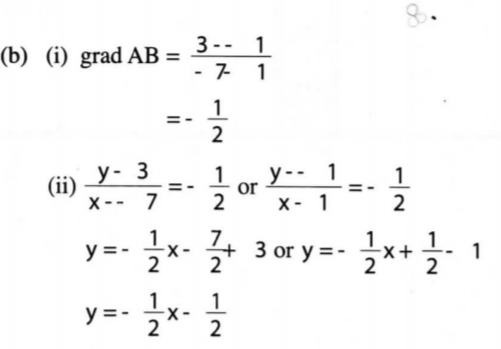
(c) Another line L is perpendicular to CD and passes through point (1, 3). Determine:
(i) the equation of L in the form ax + by = c where a, b and c are constants; (3 marks)
(ii) the coordinates of the y-intercept of line L. (1 mark)

19. (a) The roots of a quadratic equation are 2 and — 1. Write down the quadratic equation in the form ar° + bx + c = 0, where a, b and c are integers. (3 marks)
(b) (i) Barasa bought (2y + l ) mangoes at y shillings each. The total cost of the mangoes was Ksh 55. Find the cost of each mango. (4 marks)
(ii) Karau spent Ksh 95 more than Barasa to buy the same type of mangoes. For every 6 mangoes he bought, he was given one extra mango. Calculate the total number of mangoes Karau got. (3 marks)
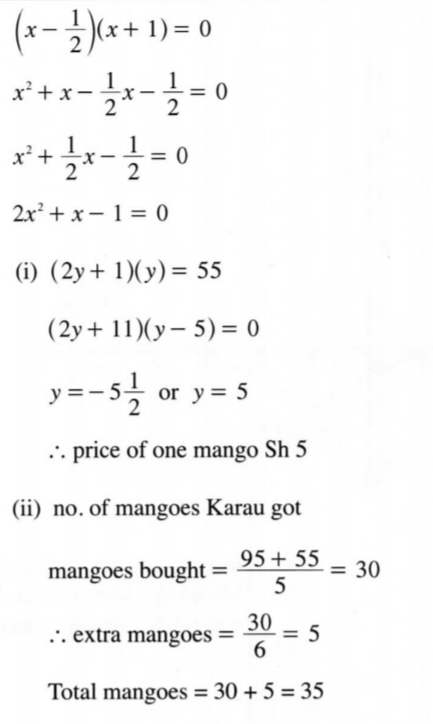
20. The angle of elevation of the top T, of a vertical mast from a point P, 100 m away from the foot F, o(the mast is 14°.
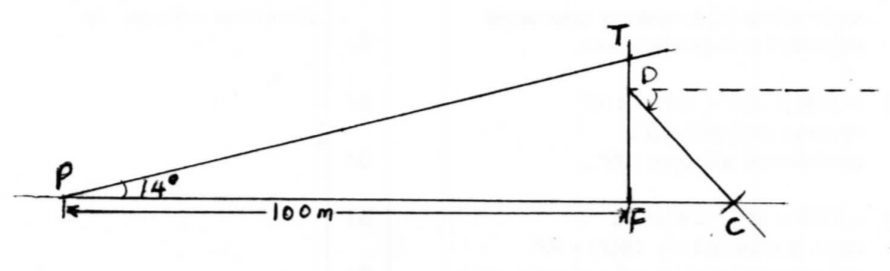
(a) Using a scale of l cm to represent 10 m, make a scale drawing to represent the above information. (3 marks)use of scale angle of elevation 14∘ drawn completion of scale drawing
(b) Using the scale drawing, determine the height of the mast. (2 marks)
Height of mat → 2.5± 0.1
=2.5×10
=25m
(c) A support cable, 27 m long, is fixed tightly at a point D on the mast 5 m below T and at a point C on the ground. Points P, F and C lie on a straight line with P and C on opposite sides ot’ F. On the scale drawing, show the position of the cable. (2 marks)
Position of cale drawn (d) Use the scale drawing to determine:
(i) the angle of depression of C from D; (1 marks)
∠ of depression of c from D 48 ∘ ±+ 1∘
(ii) the distance of C from P. (2 marks)
(10+1.8∘ 1.8 .1)x10
=118 ∘ 1m
21. ln the figure below, P, Q, R and S are points on the circumference of the circle centre O.
TP and TR are tangents to the circle at P and R respectively. POQ is a diameter of the circle and angle PQR = 64°.

Giving reasons in each case, find the size of:
(a) ∠ ROP; (2 marks)
+ ROP = 2 4 64′ = 1 28′ angle subtended at centre is twice angle subtended at O circumference,
(b) ∠ PSR; (2 marks)
(b) -r PSR = 180”- 64’ = 116°
opposite angles of cyclic quadrilateral add up to 180°.
(c) ∠ ORP; (2 marks)
+ ORP = 90‘ – 64‘ =• 26‘
angle in semicircle (+ QRP) = 90° and base angles of isosceles triangle equal.
(d) ∠ RP; (2 marks)
+ TRP = 64° angle in alternate segment.
(e) ∠RTP. (2 marks)
+ RTP = 180 – 2 ^64 h= 52° + TRP = 64° angle in alternate segment and sum of angles in triangle PRT = 180°.
22. The figurc below represents a cone whose vertical height is 12 cm and slant hcight is 13 cm.
(a) Calculate:
(i) the radius, OA. of the cone; (2 marks)
(ii) the volume of the cone. (2 marks)
(b) A smaller cone of radius 6 cm is cut off’ from the com: alx» c to leave a frustrum. Calculate:

(i) thc height of the smaller cone; (ii) the volume of the smaller cone:
(iii) the volumc of the frustrum.

Add New Post
(opens in a new tab)about:blankParagraph: Change block type or styleChange text alignmentAdd title
2013 KCSE Maths B Past Paper
Mathematics Alt. B Paper 1 (122/1)
SECTION 1 (50 marks)
Answer all questions in this section in the spaces provided.
1.Without using a calculator, evaluate:
–3(-5 — + 7) + 2(-3 + +6).
2. The first four prime numbers are written in descending order to form a number.
(a) Write down the number.
(b) Find the total value of the hundreds digit in the numbers,
3. Without using a calculator evaluate:(3 marks)
4. Tito owned Ksh 600 to Nekesa, Ksh 750 to Mwita and Ksh 650 to A uma. He had Ksh 1200 to repay to the three people in proportion to what he owed them. Calculate the amount of money Mwita rcceived more than Nekesa. (3 marks)
5. Given that r — 2 and h = 3r — 1, evaluate 7r2 + 2rh/√ 4h – 2r (3 marks)
6. The surface area of a cube is 1176 cm3. Determine the length of one of” its sides. (3 marks)
7. By construction, divide the line PQ below into six equal parts. (3 marks)

8. Given that tan x = 3/4 and .r is an acute angle, without using mathematical tables or a calculator, find the value of 2 sin x — cosx. (3 marks)
9.A box contains Cve shillings coins and ten shillings coins. The number of ten shillings coins are 6 times as many as the five shillings coins.
The total value ot’all the coins in the box is Ksh 2600. Determine the total number of coins in the box. (4 marks)
10. Simplify 3-2 x 813/2/4-3 ÷ 81/3
leaving your answer in index form. Hence evaluate the expression. (4 marks)
11. A retailer bought a mobile phone for Ksh 5750. The marked price at the retailer’s shop was 12% higher than the buying price.
After allowing a certain discount, the retailer sold the mobile phone for Ksh 6118. Calculate the percentage discount. (3 marks)
12. Factorise 9a2 — 16/b2c2
(2 marks)
13. Three types of books A, B and C were each piled on a table to attain the same height. The thickness of the books were 12 mm, 28 mm and 54 mm for types A, B and C respectively. Find:
(a) the least height attained;
(b) the number of type A books piled. (3 marks)
14. The sum of the interior angles of a regular polygon is 1260°. Find the size of each interior angle. (3 marks)
15. The corresponding lengths of two similar triangles are 5 cm and 7.5 cm. If the area of the larger triangle is 22.5 cm2, calculate the area of the smaller triangle. (3 marks)
16. The area of a sector of a circle is 77 cm2‘. The arc of the sector subtends an angle of 45° at the centre of the circle. Find the circumference of the circle. (Take ℿ=22/7 (4 marks)
SECTION II (50 marks)
Answer only Ave questions in this section in the spaces provided.
17. The figum below represents a solid prism with a semi-circular groove. The dimensions are as shown.

(a) Calculate:
(i) the volume of the prism;
(ii) the total surface area of the prism. (4 marks)
(b) All the rectangular faces are painted. Calculate the percentage of the surface of the prism that is painted correct to 1 decimal place. (2 marks)
18. (a) Three vertices of a parallelogram ABCD are A(—7, 3), B( 1. — I) and C(5, 1). On the grid provided, draw the parallelogram ABCD.
(b) Determine:
(i) the gTadient of the line AB; (2 marks)
(ii) the equation or line AB in the form y = m.r + c, where m and c are constants. (2 marks)
(c) Another line L is perpendicular to CD and passes through point (1, 3). Determine:
(i) the equation of L in the form ax + by = c where a, b and c are constants; (3 marks)
(ii) the coordinates of the y-intercept of line L. (1 mark)
19. (a) The roots of a quadratic equation are 2 and — 1. Write down the quadratic equation in the form ar° + bx + c = 0, where a, b and c are integers. (3 marks)
(b) (i) Barasa bought (2y + l ) mangoes at y shillings each. The total cost of the mangoes was Ksh 55. Find the cost of each mango. (4 marks)
(ii) Karau spent Ksh 95 more than Barasa to buy the same type of mangoes. For every 6 mangoes he bought, he was given one extra mango. Calculate the total number of mangoes Karau got. (3 marks)
20. The angle of elevation of the top T, of a vertical mast from a point P, 100 m away from the foot F, o(the mast is 14°.
(a) Using a scale of l cm to represent 10 m, make a scale drawing to represent the above information. (3 marks)
(b) Using the scale drawing, determine the height of the mast. (2 marks)
(c) A support cable, 27 m long, is fixed tightly at a point D on the mast 5 m below T and at a point C on the ground. Points P, F and C lie on a straight line with P and C on opposite sides ot’ F. On the scale drawing, show the position of the cable. (2 marks)
(d) Use the scale drawing to determine:
(i) the angle of depression of C from D; (1 marks)
(ii) the distance of C from P. (2 marks)
21. ln the figure below, P, Q, R and S are points on the circumference of the circle centre O.
TP and TR are tangents to the circle at P and R respectively. POQ is a diameter of the circle and angle PQR = 64°.

Giving reasons in each case, find the size of:
(a) ∠ ROP; (2 marks)
(b) ∠ PSR; (2 marks)
(c) ∠ ORP; (2 marks)
(d) ∠ RP; (2 marks)
(e) ∠RTP. (2 marks)
22. The figurc below represents a cone whose vertical height is 12 cm and slant hcight is 13 cm.
(a) Calculate:
(i) the radius, OA. of the cone; (2 marks)
(ii) the volume of the cone. (2 marks)
(b) A smaller cone of radius 6 cm is cut off’ from the com: alx» c to leave a i?ustum. Calculate:

(i) thc height of the smaller cone;
(ii) the volume of the smaller cone:
(iii) the volumc of the frustrum.
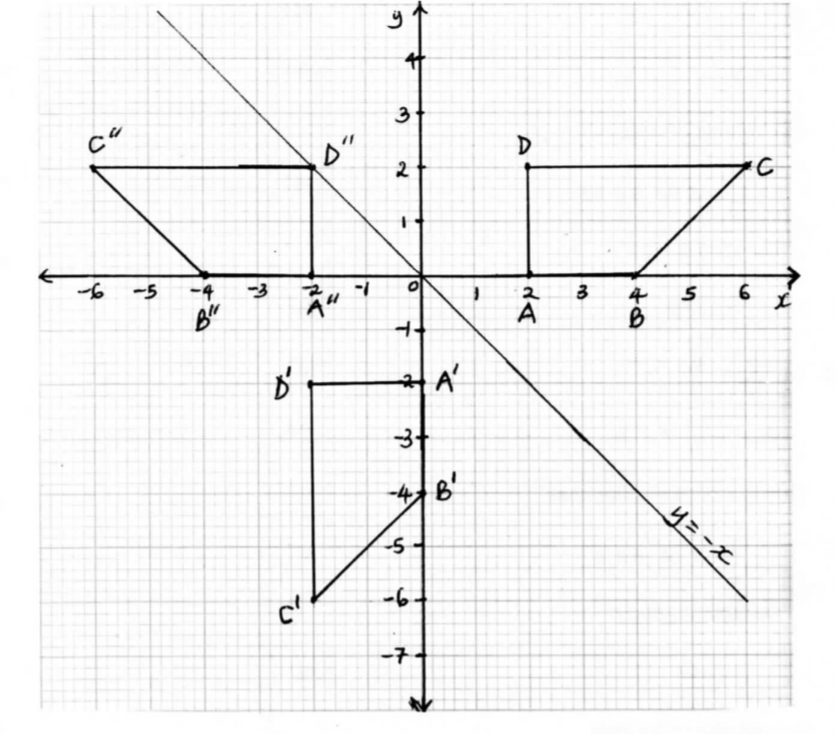
23. The vertices of a trapezium ABCD are A(2, 0), B(4, 0), C(6, 2) and D(2, 2).
(a) On the grid provided below, draw:
(i) the trapezium ABCD; (1 mark)

(ii) A’B’C‘D’ the image of ABCD under a reflection in the line y — -x, (2 marks)
(iii) A”B”C“D“ the image of A’B’C’D’ under a rotation of —90°, centre (0, 0). (2 marks)
(b) Describe a transformation that maps A”B“C”D” onto ABCD. (2 marks)
(c) State pairs of trapezia that are directly congruent and those that are oppositely congruent. (3 marks)
24. A racing motorcycle started from rest and moved with a constant acceleration ot” 1 m/s2for 15 seconds. lt then accelerated at 3.5 m/s2 for the next 10 seconds and maintained a constant speed for the next 10 seconds. It decelerated constantly and came to rest after 25 seconds.
(a) On the grid provided, draw the velocity—time graph for the motorcycle. (4 marks)
(b) Use the graph to determine:
(i) the deceleration of the motorcycle; (2 marks)
(ii) the total distance travelled; (2 marks)
(iii) the average speed for the motorcycle, correct to 3 significant figures. (2 marks)
2013 KCSE Maths B Past Paper-Marking Scheme/Answers
1.Without using a calculator, evaluate:
–3(-5 — + 7) + 2(-3 + +6).

2. The first four prime numbers are written in descending order to form a number.
(a) Write down the number.
7532
(b) Find the total value of the hundreds digit in the numbers,
Total Value of hundreds digit = 500
3. Without using a calculator evaluate:(3 marks)
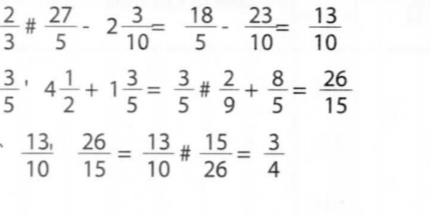
4. Tito owned Ksh 600 to Nekesa, Ksh 750 to Mwita and Ksh 650 to A uma. He had Ksh 1200 to repay to the three people in proportion to what he owed them. Calculate the amount of money Mwita rcceived more than Nekesa. (3 marks)

5. Given that r — 2 and h = 3r — 1, evaluate 7r2 + 2rh/√ 4h – 2r(3 marks)
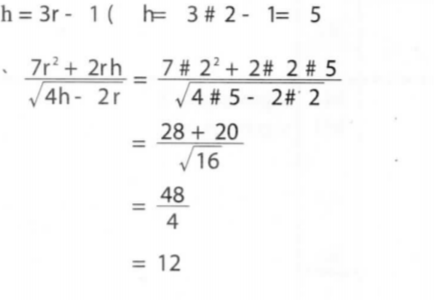
6. The surface area of a cube is 1176 cm3. Determine the length of one of” its sides. (3 marks)
Area of each face = 1176/6 =196 Lenght of one side √ 196 =14
7. By construction, divide the line PQ below into six equal parts. (3 marks)


8. Given that tan x = 3/4 and .r is an acute angle, without using mathematical tables or a calculator, find the value of 2 sin x — cosx. (3 marks)
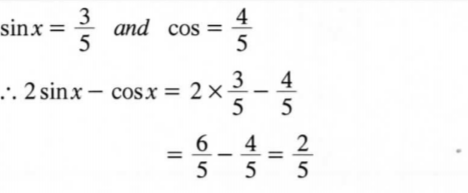
9.A box contains Cve shillings coins and ten shillings coins. The number of ten shillings coins are 6 times as many as the five shillings coins.
The total value ot’all the coins in the box is Ksh 2600. Determine the total number of coins in the box. (4 marks)

10. Simplify 3-2 x 813/2/4-3 ÷ 81/3
leaving your answer in index form. Hence evaluate the expression. (4 marks)
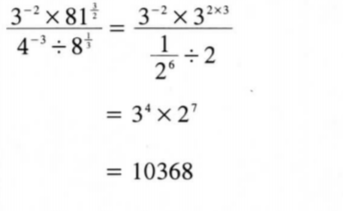
11. A retailer bought a mobile phone for Ksh 5750. The marked price at the retailer’s shop was 12% higher than the buying price.
After allowing a certain discount, the retailer sold the mobile phone for Ksh 6118. Calculate the percentage discount. (3 marks)

12. Factorise 9a2 — 16/b2c2
(2 marks)
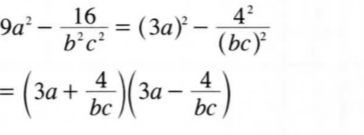
13. Three types of books A, B and C were each piled on a table to attain the same height. The thickness of the books were 12 mm, 28 mm and 54 mm for types A, B and C respectively. Find:
(a) the least height attained;

(b) the number of type A books piled. (3 marks)
Number of books = 756/12 =63
14. The sum of the interior angles of a regular polygon is 1260°. Find the size of each interior angle. (3 marks)

15. The corresponding lengths of two similar triangles are 5 cm and 7.5 cm. If the area of the larger triangle is 22.5 cm2, calculate the area of the smaller triangle. (3 marks)
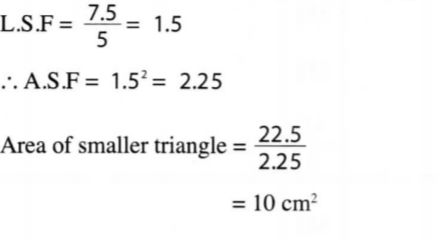
16. The area of a sector of a circle is 77 cm2‘. The arc of the sector subtends an angle of 45° at the centre of the circle. Find the circumference of the circle. (Take ℿ=22/7 (4 marks)

SECTION II (50 marks)
Answer only five questions in this section in the spaces provided.
17. The figum below represents a solid prism with a semi-circular groove. The dimensions are as shown.

(a) Calculate:
(i) the volume of the prism;
(ii) the total surface area of the prism. (4 marks)
(b) All the rectangular faces are painted. Calculate the percentage of the surface of the prism that is painted correct to 1 decimal place. (2 marks)

18. (a) Three vertices of a parallelogram ABCD are A(—7, 3), B( 1. — I) and C(5, 1). On the grid provided, draw the parallelogram ABCD.

(b) Determine:
(i) the gradient of the line AB; (2 marks)
(ii) the equation or line AB in the form y = m.r + c, where m and c are constants. (2 marks)
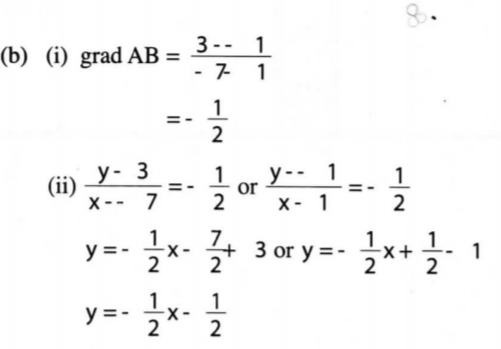
(c) Another line L is perpendicular to CD and passes through point (1, 3). Determine:
(i) the equation of L in the form ax + by = c where a, b and c are constants; (3 marks)
(ii) the coordinates of the y-intercept of line L. (1 mark)

19. (a) The roots of a quadratic equation are 2 and — 1. Write down the quadratic equation in the form ar° + bx + c = 0, where a, b and c are integers. (3 marks)
(b) (i) Barasa bought (2y + l ) mangoes at y shillings each. The total cost of the mangoes was Ksh 55. Find the cost of each mango. (4 marks)
(ii) Karau spent Ksh 95 more than Barasa to buy the same type of mangoes. For every 6 mangoes he bought, he was given one extra mango. Calculate the total number of mangoes Karau got. (3 marks)
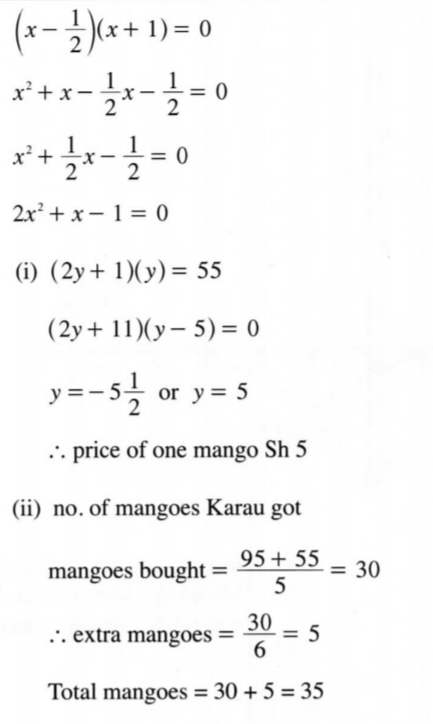
20. The angle of elevation of the top T, of a vertical mast from a point P, 100 m away from the foot F, o(the mast is 14°.

(a) Using a scale of l cm to represent 10 m, make a scale drawing to represent the above information. (3 marks)use of scale angle of elevation 14∘ drawn completion of scale drawing
(b) Using the scale drawing, determine the height of the mast. (2 marks)
Height of mat → 2.5± 0.1
=2.5×10
=25m
(c) A support cable, 27 m long, is fixed tightly at a point D on the mast 5 m below T and at a point C on the ground. Points P, F and C lie on a straight line with P and C on opposite sides ot’ F. On the scale drawing, show the position of the cable. (2 marks)
Position of cale drawn (d) Use the scale drawing to determine:
(i) the angle of depression of C from D; (1 marks)
∠ of depression of c from D 48 ∘ ±+ 1∘
(ii) the distance of C from P. (2 marks)
(10+1.8∘ 1.8 .1)x10
=118 ∘ 1m
21. ln the figure below, P, Q, R and S are points on the circumference of the circle centre O.
TP and TR are tangents to the circle at P and R respectively. POQ is a diameter of the circle and angle PQR = 64°.

Giving reasons in each case, find the size of:
(a) ∠ ROP; (2 marks)
+ ROP = 2 4 64′ = 1 28′ angle subtended at centre is twice angle subtended at O circumference,
(b) ∠ PSR; (2 marks)
(b) -r PSR = 180”- 64’ = 116°
opposite angles of cyclic quadrilateral add up to 180°.
(c) ∠ ORP; (2 marks)
+ ORP = 90‘ – 64‘ =• 26‘
angle in semicircle (+ QRP) = 90° and base angles of isosceles triangle equal.
(d) ∠ RP; (2 marks)
+ TRP = 64° angle in alternate segment.
(e) ∠RTP. (2 marks)
+ RTP = 180 – 2 ^64 h= 52° + TRP = 64° angle in alternate segment and sum of angles in triangle PRT = 180°.
22. The figurc below represents a cone whose vertical height is 12 cm and slant hcight is 13 cm.
(a) Calculate:
(i) the radius, OA. of the cone; (2 marks)
(ii) the volume of the cone. (2 marks)
(b) A smaller cone of radius 6 cm is cut off’ from the com: alx» c to leave a frustrum. Calculate:

(i) thc height of the smaller cone; (ii) the volume of the smaller cone:
(iii) the volumc of the frustrum.

23. The vertices of a trapezium ABCD are A(2, 0), B(4, 0), C(6, 2) and D(2, 2). (a) On the grid provided below, draw: (i) the trapezium ABCD; (1 mark)

(ii) A’B’C‘D’ the image of ABCD under a reflection in the line y — -x, (2 marks)
(ii) line of reflection y = — x drawn trapezium A’B’C’D’drawn
(iii) A”B”C“D“ the image of A’B’C’D’ under a rotation of —90°, centre (0, 0). (2 marks)
points A”B”C”D” plotted trapezium A”B”C”D” drawn
(b) Describe a transformation that maps A”B“C”D” onto ABCD. (2 marks)
(b) transformation which maps A”B”C”D” onto ABCD reflection on line x = 0
(c) State pairs of trapezia that are directly congruent and those that are oppositely congruent.(3 marks)
(c) directly congruent pair A’B’C’D’ and A”B”C”D” oppositely congruent pairs ABCD and A’B’C’D’ ABCD and A”B”C”D”
24. A racing motorcycle started from rest and moved with a constant acceleration ot” 1 m/s2for 15 seconds. lt then accelerated at 3.5 m/s2 for the next 10 seconds and maintained a constant speed for the next 10 seconds. It decelerated constantly and came to rest after 25 seconds.
(a) On the grid provided, draw the velocity—time graph for the motorcycle. (4 marks)
(b) Use the graph to determine:scale acceleration parts constant speed deceleration
(i) the deceleration of the motorcycle; (2 marks)
deceleration = 50/25 = 2 mls2
(ii) the total distance travelled; (2 marks)
Total distance = ( 15 x 15) + 2( 15 + 50) x 10 + 10 x 50 + 1 (25×50) = 112.5 + 325 + 500 + 625 = 1562.5
(iii) the average speed for the motorcycle, correct to 3 significant figures. (2 marks)
Average speed = 1562.5 /60
= 26.0416 = 26.0 m/s2
Focus keyphraseHelp on choosing the perfect focus keyphrase(Opens in a new browser tab)Get related keyphrases(Opens in a new browser window)
Preview as:Mobile resultDesktop resultUrl preview:![]() kenyanlife.info › SEO title preview:-Meta description preview:
kenyanlife.info › SEO title preview:-Meta description preview:

Dec 29, 2021 - Please provide a meta description by editing the snippet below. If you don’t, Google will try to find a relevant part of your post to show in the search results.SEO titleTitle Page Separator Site title Site titleTitlePrimary categorySeparatorSlugMeta description
Site titleTitlePrimary categorySeparator
Subheading (will be displayed below post title)
Alternative ad code (this will overwrite the global content ad code)
Disable Content Ad for this Post
Disable Featured Image for this Post
23. The vertices of a trapezium ABCD are A(2, 0), B(4, 0), C(6, 2) and D(2, 2). (a) On the grid provided below, draw: (i) the trapezium ABCD; (1 mark)

(ii) A’B’C‘D’ the image of ABCD under a reflection in the line y — -x, (2 marks)
(ii) line of reflection y = — x drawn trapezium A’B’C’D’drawn
(iii) A”B”C“D“ the image of A’B’C’D’ under a rotation of —90°, centre (0, 0). (2 marks)
points A”B”C”D” plotted trapezium A”B”C”D” drawn
(b) Describe a transformation that maps A”B“C”D” onto ABCD. (2 marks)
(b) transformation which maps A”B”C”D” onto ABCD reflection on line x = 0
(c) State pairs of trapezia that are directly congruent and those that are oppositely congruent.(3 marks)
(c) directly congruent pair A’B’C’D’ and A”B”C”D” oppositely congruent pairs ABCD and A’B’C’D’ ABCD and A”B”C”D”
24. A racing motorcycle started from rest and moved with a constant acceleration ot” 1 m/s2for 15 seconds. lt then accelerated at 3.5 m/s2 for the next 10 seconds and maintained a constant speed for the next 10 seconds. It decelerated constantly and came to rest after 25 seconds.
(a) On the grid provided, draw the velocity—time graph for the motorcycle. (4 marks)

(b) Use the graph to determine:scale acceleration parts constant speed deceleration
(i) the deceleration of the motorcycle; (2 marks)
deceleration = 50/25 = 2 mls2
(ii) the total distance travelled; (2 marks)
Total distance = ( 15 x 15) + 2( 15 + 50) x 10 + 10 x 50 + 1 (25×50) = 112.5 + 325 + 500 + 625 = 1562.5
(iii) the average speed for the motorcycle, correct to 3 significant figures. (2 marks)
Average speed = 1562.5 /60
= 26.0416 = 26.0 m/s2

