2014 KCSE Geography Past Paper
Section A: (25 marks)
Answer ALL the questions in this section.
1. Name two types of hypabyssal rocks. (2 marks)
2. (a) The diagram below shows intrusive volcanic features.
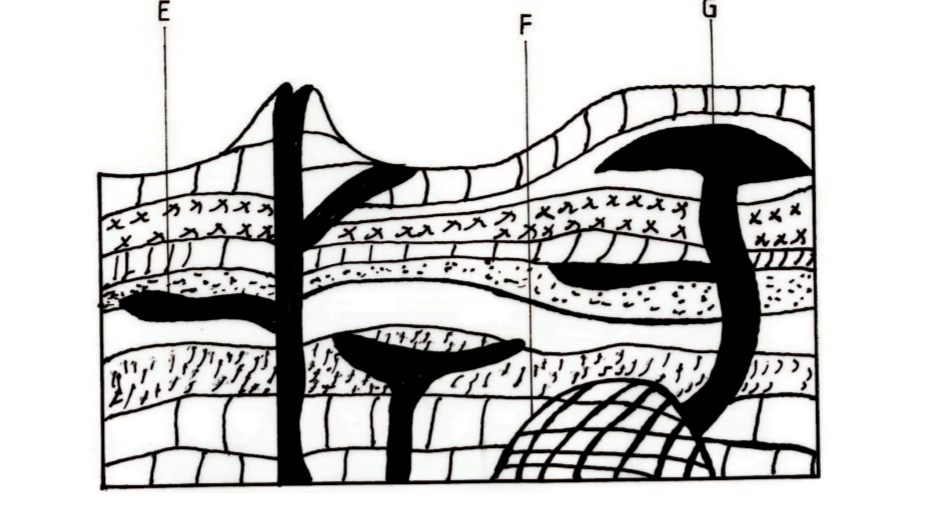

Name the features marked E, F and G.
(b) Name two active volcanoes in Kenya.
3. (a) Give three processes in the hydrological cycle.
(b) State four factors that facilitate deposition in rivers.
4. (a) Explain two reasons why wind is the dominant agent of erosion in arid areas.
(b) Identify two features formed as a result of wind deposition in arid areas.
5. (a) Describe podzolization as a process of leaching. (2 marks)
(b) State three ways in which mulching helps in soil conservation.
(3 marks)
Section B
Answer question 6 and any other TWO questions from this section
6. Study the map of Migwani 1:50,000 (sheet 151/1) provided and answer the following questions.
(a) (i) Give the longitudinal extent of the area covered by the map. (2 marks)
(ii) What is the magnetic variation of the map? (1 mark)(iii)
Give the six-figure grid reference for the junction of the roads D503 and D507. (2 marks)
(b)(i) Using a vertical scale of l cm to represent 100 metres, draw a cross section along the line marked J -K. (4 marks)
(ii) On it, mark and label the following:footpath; (1 mark) road; (1 mark) water pipeline; (l mark) steep slope. (1 mark)
(iii) Calculate the vertical exaggeration of the cross-section. (2 marks)
(c) Citing evidence from the map, give three economic activities carried out in the area covered by the map. (6 marks)
(d) Explain how relief has influenced the distribution of settlement in the area covered by the map. (4 marks)
7. (a) (i) Describe the solar system. (2 marks)
(ii) The local time at Manaul 60°W is 11.30 a.m. What is the time in Nairobi 37° E? (3 marks)
(ii) (b) (i) State five characteristics of the mantle in the interior structure of the earth. (5 marks)
(i) (ii) Outline the evidence which support the theory of continental drift. (4 marks)
(c) The diagram below represents the revolution of the earth.
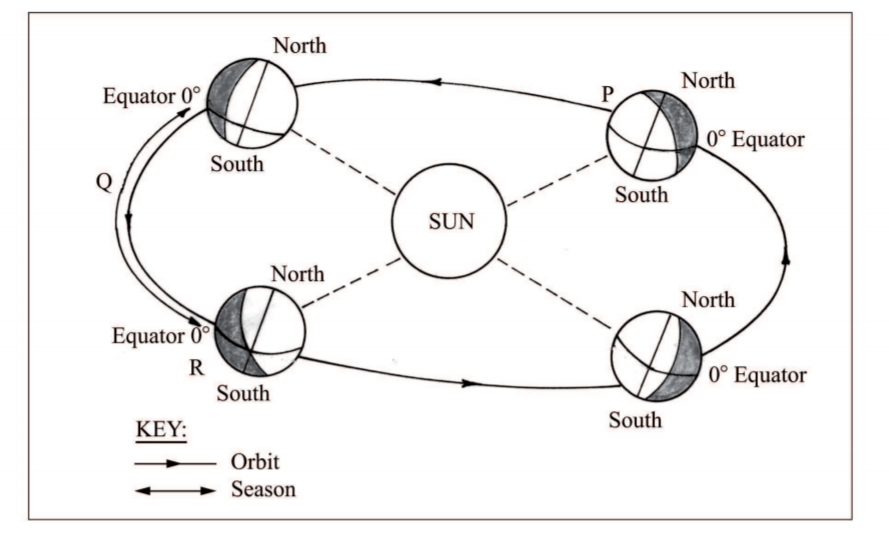
(i) Name the solstice marked P. (l mark)
(ii) ldentify the season represented in the region marked Q. (1 mark)
(iii) Describe the climatic conditions in Europe when the Earth is in position R. (3 marks)
(d) With the aid ofa Well labelled diagram, describe the occurrence ofthe solar eclipse. (6 marks)
8. The map below shows some climatic regions of Kenya. Use it to answer question (a)
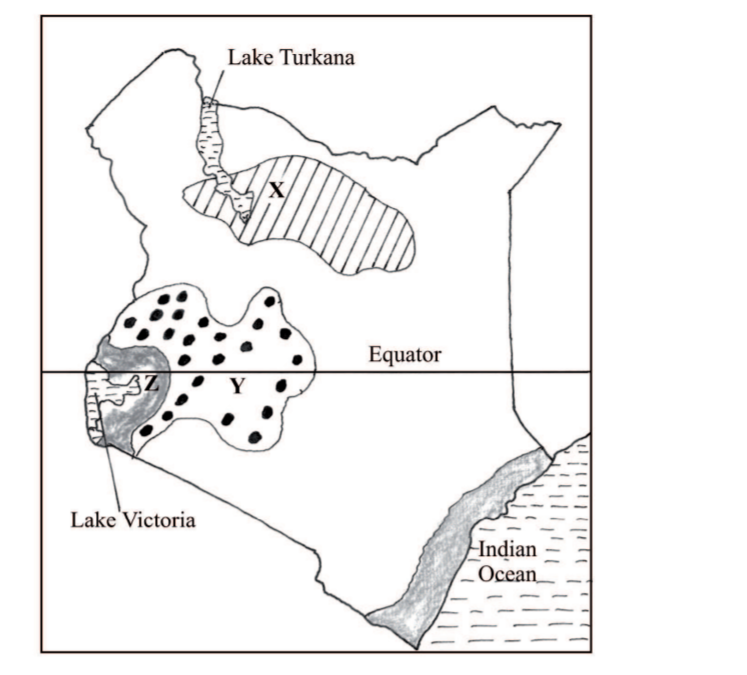
(i) Name the climatic regions marked X and Y. (2 marks)
(ii) State three characteristics of the climatic region marked Z. (3 marks)
(b) Explain how each of the following factors influence climate:
(i) Altitude; (4 marks)
(ii) Ocean currents. (4 marks)
What are the negative effects of climate change on physical environment‘? (6 marks)
(d) Students visited a Weather station to study recording of weather elements.
(i) State three qualities in the construction of a Stevenson screen they would have observed during the study. (3 marks)
(ii) Identify three types of data they are likely to have collected during the study. (3 marks)
9. (a) (i) Name two types of submerged highland coasts. (2 marks)
(ii) Identify two resultant features of the emerged highland coasts. (2 marks)
(b) State three factors influencing deposition by ocean waves. (3 marks)
(c) With the aid of labelled diagrams describe the formation of the following coastal features:
(i) Fringing reef; (5 marks)
(ii) Spit. (5 marks)
Explain the significance of oceans to human activities. (8 marks)
10. (a) (i) Name two mountains in East Africa which are ice capped. (2 marks)
(ii) Identify three ways in which ice moves. (3 marks)
Describe the formation of the following glacial features:
(i) Hanging valley; (6 marks)
(ii) Pyramidal peak. (6 marks)
(c) You are required to carry out a field study on erosional features in glaciated lowland area.
(i) Give two reasons why you would require a working schedule. (2 marks)
(ii) Name three erosional features you are likely to observe during the field study. (3 marks)
(iii) Give three follow-up activities you would undertake after the field study. (3 marks)
Geography Paper 2
Section A: (25 marks)
Answer all the questions in this section,
1. (a) Give two uses of diamond. (2 marks)
(b) Identify three problems facing diamond mining in South Africa. (3 marks)
2 (a) Apart from coniferous forests, name two other types of natural forests. (2 marks)
(b) State three characteristics of coniferous forests which favour their exploitation.
3 Use the map of East Africa below to answer question (a). (3 marks)
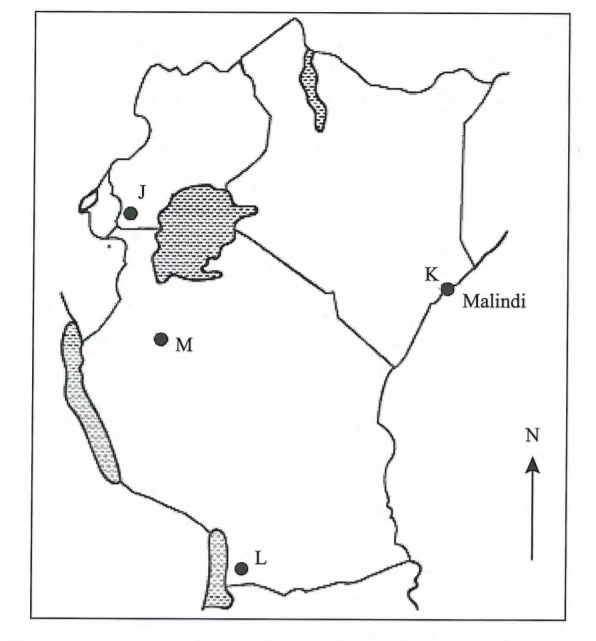
(a) Name the game reserves marked P, Q and R. (3 marks)
(b) State two factors which influence the distribution of wildlife in East Africa. (2 marks)
4 (a) Give two reasons why Geothermal power has not been fully exploited in Kenya. (2 marks)
(b) State three causes of the energy crisis in the world. (3 marks)
5 (a) Identify the two types of internal trade. (2 marks)
(b) Give three factors that limit trade among the member states of the common market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA). (3 marks)
SECTION B: (75 marks)
Answer question 6 and any other two questions in this section.
6 Study the photograph below and use it to answer question (a)
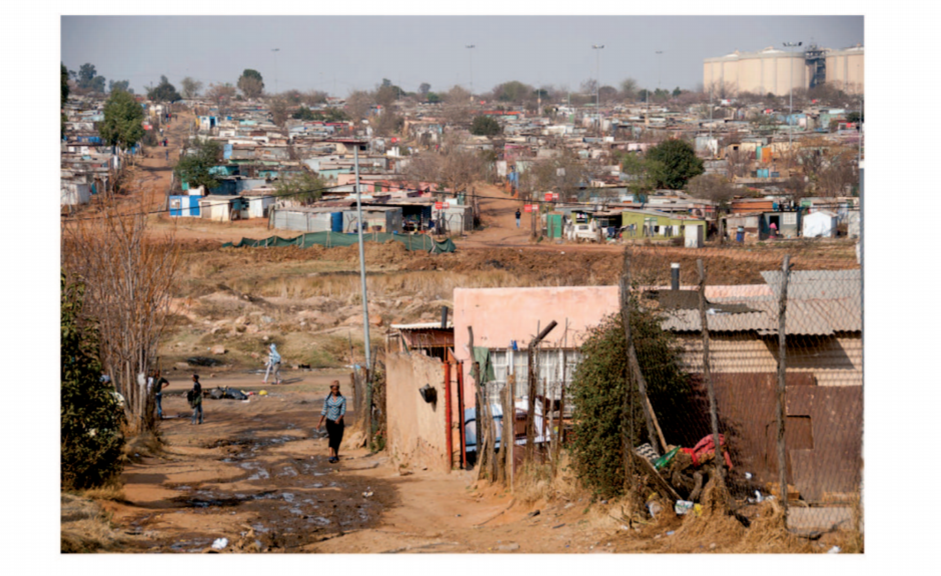

(i) Identify the type of photograph shown above. (1 mark)
(ii) Name the type of settlement shown on the photograph. (1 mark)
(iii) What time of the day was the photograph taken? (1 mark)
(iv) Draw a rectangle measuring 15 cm by 10 cm. On it, sketch and label five human features shown on the photograph.
(b) Explain four economic factors that influence settlement. (8 marks)
(c) Describe four negative effects of urbanization. (8 marks)
Explain three social factors that influence agriculture. (6 marks)
(i) Describe the cultivation of oil palm from land preparation to harvesting. (7 marks)
(ii) Give three uses of palm oil in Nigeria. (3 marks)
(c) Explain three reasons why horticultural farming is encouraged in Kenya. (6 marks)
(d) Give three factors which favours beef farming in the Nyika plateau. (3 marks)
8. (a) Explain four ways in which land is being rehabilitated in Kenya. (8 marks)
(b) (i) State two ways in which the salinity ofthe polders is reduced in The Netherlands. (2 marks)
(ii) Explain four ways in which the Zuyder Zee project benefits The Netherlands. (8 marks)
(c) You intend to carry out a field study on irrigation farming in Mwea Tebere Irrigation Scheme:
(i) Identify the two types of hypotheses you would develop for the study. (2 marks)
(ii) Name three crops, grown in the scheme that you are likely to identify. (3 marks)
(iii) Give two reasons why you need to sample the area of study. (2 marks)
9. (a) Define the term fishing. (2 marks)
(b) Explain two ways in which each of the following factors negatively affects fishing in Kenya.
(i) Agricultural activities. (4 marks)
(ii) Water weeds. (4 marks)
(c) Use the map of North-West Atlantic fishing ground to answer questions (c)(ii) and (iii).
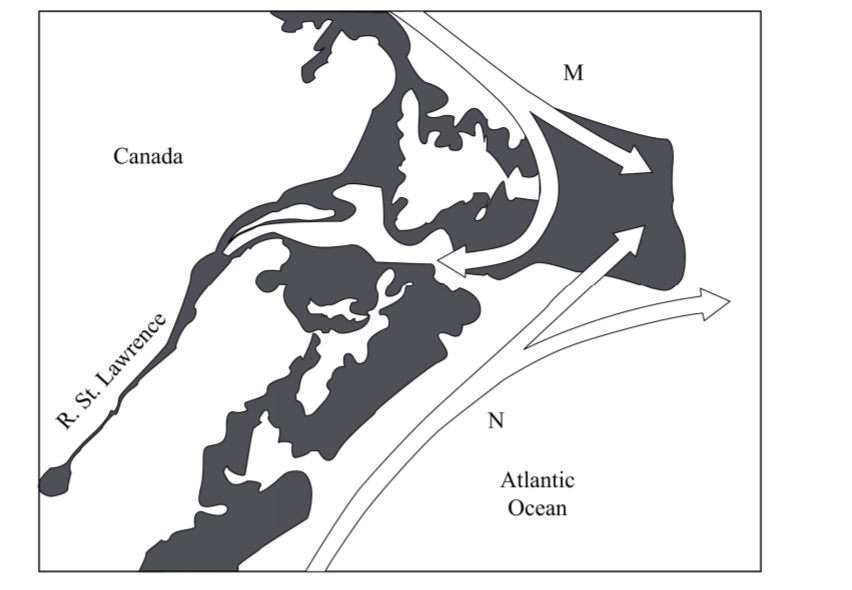
(i) Give three types of fish species caught in the North-West Atlantic fishing ground. (3 marks)
(ii) Name the Ocean currents marked M and N. (2 marks)
(iii) influence fishing. (4 marks)
(iv) Give three differences between fishing in Kenya and Japan. (6 marks)
10 (a) What is environmental management?
(i) Explain four negative effects of floods.(8 markes)
(ii) State two measures being taken to control lightning.(2 marks)
Explain the significance of conserving the environment (8 marks)
(d) Your Geography class carried out a field work on floods along a river.
(i) Name two types of field work they could have used.
(ii) Give three advantages of studying floods through field work. (3 marks) (2 marks)
Explain two ways in which the convergence of Ocean currents marked M and N (3 marks)
2014 KCSE Geography Past Paper-Marking Scheme/Answers
Section A
1. Name two types of hypabyssal rocks.
Dolerite
Porphyry
Diabase
Lamprophyre
Porphyrite.
Granophyre
Any 2 x 1 = (2 marks)
2. (a) The diagram below shows intrusive volcanic features.
Name the features marked E, F and G.
E – A sill
F – A batholith
G – A laccolith/baccolith (3 marks)
Name two active volcanoes in Kenya.
– Longonot
– Teleki
– Likaiyu/ Likaiu
– Ol Donyo Lengai
– Menengai – Suswa
– Homa hills
3. (a) Give three processes in the hydrological cycle.
– Evaporation/ evapotranspiration / moist air rising/moist air rising.
– Condensationl moist air cooling
– Infiltration/ percolation
– Surface runoff/ overland flow
– Precipitationl rainfall / snow fall
Any 3 x l = (3 marks)
(b) State four factors that facilitate deposition in rivers.
– Reduction in river gradient which decreases the velocity of Water.
– Freezing of river Water leads to embedments of the load in the ice.
– River entering a large water body reduces the speed of the river flow.
– Presence of obstacles on the river course which blocks some of the load.
– Reduction in river volume Which reduces the strength of the river.
– Increase in Width of the channel makes Water to spread over wide area.
– Increase in the amount of load / size of the load.
Any 4 x l = (4 marks)
4. (a) Explain two reasons why wind is the dominant agent of erosion in arid areas.
– The areas have scanty/ no vegetation which exposes the land to erosion.
– The areas experience strong tropical winds which erode the materials.
– The areas have dry unconsolidated soils/ materials which are easily eroded.
Any 2 x 2 = (4 marks)
(b) Identify two features formed as a result of wind deposition in arid areas.
– Loess
– drass/ draas
– dunes / self / longitudinal dune, barchan, wake /transverse dunes.
Any 2 x l = (2 marks)
5. (a) Describe podzolization as a process of leaching.
– It occurs in areas with high rainfall and low temperature / cool & Wet conditions (cool temperature regions) / humid temperature regions/ conferous forest.
– Slow decomposition of vegetative matter results in formation of humic acid.
– Calcium / iron/ magnesium / alminium / pottassium / bases / salts/ carbonates minerals in the soil are dissolved and moved/ translocated from horizon A to horizon B.
– The soil is left extremely acidic/ humic / ash grey / broWn-grey/ red-yellow / White/ light in colour.
Any 2 x l = (2 marks)
(b) State three ways in which mulching helps in soil conservation.Plant materials used decompose increasing soil humus. It protects the soil against erosion. It helps to increase infiltration rate of water into the soil. It helps reduce water loss from the soil / retain soil moisture. It helps to increase soil aeration.
Any 3 x 1 = (3 marks)
Section B
6. Study the map of Migwani (1 :50 000) sheet 151/ 1 provided and answer the following
(a) (i) Give the longitudinal extent of the area covered by the map.
38.01 E – 38.13 E/12’E(l1‘.3O” -12.30”)
38°00 30” — 38 13‘ 30 (2 marks)
ii) What is the magnetic variation of the map?
2“ 23 ‘ (1 mark)
(iii) Give the six figure grid reference for the junction of the roads D503 and D507.
119707 / 119708 (2 marks)
(b) (i) Using a vertical scale of 1 cm to represent 100 metres, draw a cross section along the line marked J – K.
On it mark and label the following:
– footpath (1 mark)
– road (1 mark)
– water pipeline (1 mark)
– steep slope (1 mark)
Features
Footpath (1 mark)
Road (1 mark)
Water pipeline (1 mark)
Steep slope(1 mark)
Total = (4 marks)
(iii) Calculate the vertical exaggeration of the cross section
VE= V.S/H.S : 10,000 ” 50,000
_ 1 50,000
– 10,000 X 1
=5
(c) Citing evidence from the map, give three economic activities carried out in the area covered by the map.
– Transport as evidenced by presence of many roads / water pipeline.
– Trade evidenced by presence of many shops / market / petrol station / Water pipeline.
– Communication evidenced by post office.
Activity = 3 marks
Evidence = 3 marks
(6 marks)
(d) Explain how relief has influenced the distribution of settlement in the area covered by the map.
– There are many settlements in the north Western part because the land is gently sloping.
– There are no/few settlements in Mutito forest because the slope is very steep.
– There are few settlements on Kitui hills as the land is rugged/steep.
– There are no settlement on the ridges in the central and southern West areas because they are steep.
– There are few/no settlements in Usian because the land is rugged.
Any 2 x 2 = (4 marks)
7. (a) (i) Describe the solar system.
– It is the sun, planets and other celestrial bodies. They are held together by the force of gravity.
– The celestrial bodies revolve / orbit the sun.
– Most celestrial bodies are spherical in shape. (2 marks)
(ii) The local time at Manau, 60″W is 11.30 am. What is the time in Nairobi 37° E?
‘ The difference in longitude is 60 + 37 = 97° \/
‘ 1° = 4 minutes
(b) (i) 11) 97° => (1975 4 )hrs
= 6hrs 28 mins
Time in Nairobi = 1130
+628
1758 hrs or
5.58 pm v
Total = (3 marks)
(b) (i) State five characteristics of the mantle in the interior structure of the earth.
– The mantle is divided into two parts / the upper mantle and the lower mantle.
– It is about 2900 km thick.
– The average density is between 3.0 – 3.3 gm/cm3
– The upper mantle has a lower temperature than the lower mantle / 1000“ to 3000″ C.
– The upper mantle is in semi-solid state.
– The lower mantle is composed of rocks in viscous fluid state.
– The dominant minerals are silica, iron and magnesium / ferro – magnesium silicate / olivine.
Any 5 X l = (5 marks)
(ii) Outline the evidence which support the theory of continental drift.
– Palaeontological / palaeozological evidence the fossils of plants/ animals found in Africa are also in other continents .
– Adjacent continents have jig saw fitting coastlines or continental margins.
– There exists similarity in animal species/ plant species in the continents.
– Paleoclimatic evidence / Southern continents seem to have experienced large scale glaciation at the same period/presence of ancient glacial deposition in southern continents.
– Sea floor spreading recent volcanic eruption in mid-Atlantic ridges fill the gaps left by drifting continents.
– The location of major world fold mountains of the world/ trend of the folds / age of the fold mountains are similar.
– Paleamagnetism / the alignment of iron minerals in igneous rocks along the earths magnetic field indicate that the continents must have once been together.
– Geological evidence / existence of rocks which are similar in their formation/ structure/types/age along margins of different continents (sharing of oceans).
Any 4 X 1 = (4 marks)
(c) The diagram below represents the revolution of the earth.

(i) Name the solstice marked P.
Winter solstice (1 mark)
(ii) Identify the season represented in the region marked Q.
Spring. (1 mark)
(iii) Describe the climatic conditions in Europe when the earth is in position R.
– High temperatures / hot conditions are experienced.
– There are long hours of sunshine.
– There is precipitation in form of rainfall / wet conditions.
– There is high humidity.
– There is low pressure.
– There is convergence of winds.
– It is cloudy.
Any 3 x l = (3 marks)
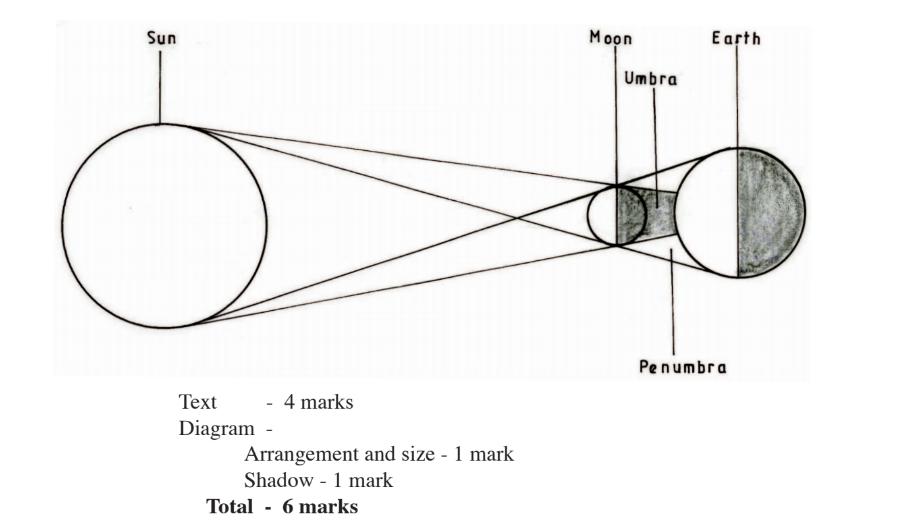
(d) With the aid of a well labelled diagram, describe the occurrence of the solar eclipse.
– It occurs when the moon lies between the earth and the sun / when the sun rays are blocked by the moon from reaching the earth.
– The shadow of the moon is cast on the earth’s surface.
– The shadow is the solar eclipse
– The shadow has two parts namely the umbra and penumbra.
– The umbra shadow causes total solar eclipse.
– The penumbra causes partial solar eclipse.
8. The map below shows some climatic regions of Kenya. Use it to answer question (a).

(a) (i) Name the climatic regions marked X and Y.
X – Desert climate ( l mark)
Y – Modified tropical climate ( l mark)
(ii) State three characteristics of the climatic region marked Z.
– lt has a small annual temperature range / 3“ – 5° C.
– It has a small diurnal range of temperature.
– It has a mean annual temperature of between 20° C and 32° C/ high temperature / moderate temperature.
– Receives moderate to high rainfall / rainfall ranges between 750 mm and 1500 mm per year, with no distinct dry month/ it rains throughout the year.
– The relative humidity is high / 80%
– The area receives convectional type of rainfall / rain falls mainly in the afternoon / accompanied by thunder and lightening.
– It has a double rainfall maxima.
– It experiences low pressure.
– There is a thick cloud cover.
Any 3 x l = (3 marks)
(b) Explain how each of the following factors influence climate.
(i) Altitude.
– Temperature decreases with increasing height above sea level/ decreases at 0.6“ C for every 100 metres rise because the air is at the dense at lower altitude and rarefied at the higher attitude.
– Atmospheric pressure is higher at low altitude and lower at high altitude. This is because the weight of atmospheric air at low altitude is more than at high altitude.
– The temperature is higher at low altitude / lower at high attitude because the air is heated from below and not directly from the sun.
Statement = 3 marks
Explanation = 3 marks
(ii) Ocean currents
– Onshore winds blowing over warm ocean current, are warmed and absorb more warm vapour causes a warming effect on adjacent land resulting into increased rainfall and high humidity.
– Onshore winds blowing over ocean currents are cooled and moisture condenses resulting to rainfall in the water and a cooling effect on adjacent land leading to desertification / little rainfall / fog / mist.
– Onshore winds blow over warm ocean current causing a warming effect on the adjacent lands.
(c) What are the negative effects of climate change on physical environment?
– Disruption of natural ecosystem / loss of biodiversity /abnormal growth of plants caused by the increase in ultraviolet radiation /global warming/ seasons/ rainfall patterns.
– Flooding of land / coastal lands caused by increased temperature which leads to melting of glaciers thereby causing a rise in sea level/ change in rainfall patternl change in seasonal pattern/change in winds / air mass pattern.
– Increased temperatures may lead to drying up of water reservoirs thereby reducing their lifespan.
– Draught caused by increased temperature may lead to high evaporation / change in rainfall pattern/season’s pattern.
– Increase in rainfall leads to flooding / rise in sea level / soil erosion. – Soil erosion by wind caused by change in wind/air mass pattern.
– High ocean/sea waves/storms due to change in wind/air mass pattern when they blow more frequency and are more destructive (such as cyclones)
Any 3 x 2 = (6 marks)
(d) Students visited a weather station to study recording of weather elements.
(i) State three qualities in the construction of a stevenson screen they would have observed during the study.
– It is a wooden box.
– It is raised on stilts/ placed on a stand, about 121 cm above the ground level.
– It is painted white.
– It has a double roof.
– The sides are louvred to allow free circulation of air.
Any 3 x l = (3 marks)
(11) Identify three types of data they are likely to have collected during the study.
– Types of weather measuring/ recording instruments
– Statistical data / tables / diagrams / maps on previous weather records.
– Diagrams/ photographs on instniments.
– Information on weather forecasting.
– Information on operations of weather measuring / recording instruments.
Any 3 x l = (3 marks)
9. (a) (i) Name two types of submerged highland coasts.
– Longitudinal / Dalmation
– Ria
– Fiord / / Fjord
Any 2 x l = (2 marks)
(ii) Identify two resultant features of the emerged highland coasts.
– Raised geos / blow holes
– Raised cliffs
– Raised wave cut-platforms
– Raised beaches
– Raised caves
– Raised notches
– Raised archs / stumps / stacks.
Any 2 x l = (2 marks)
(b) State three factors influencing deposition by ocean waves.
– The existence of gentle sloping shore.
– Presence of shallow water along the coastline.
– The occurrence of a strong swash and weak backwash / constructive waves.
– The existence of indented coastline.
– Ample longshore drift materials to be deposited.
Any 3 x l = (3 marks)
(c) With the aid of labelled diagrams describe the formation of the following coastal features.
(i) Fringing reef.
– It is formed when coral polyps start building a reef near the shore extending seawards.
– The rate of accumulation is faster seawards than towards the shore.
– The reef therefore becomes steeper seaward than towards the shore, enclosing.
a narrow and shallow lagoon.
– The accumulated coral materials form a fringing reef.
(ii) Spit
– It forms on a shallow shore at a point where the coastline bends landward
– Deposition occurs as the longshore drift is halted.
– More materials / deposits are piled up forming an elongated low lying ridge growing towards the sea.
– The elongated low lying ridge with one end attached to the coast and the other projecting into the sea is the spit.
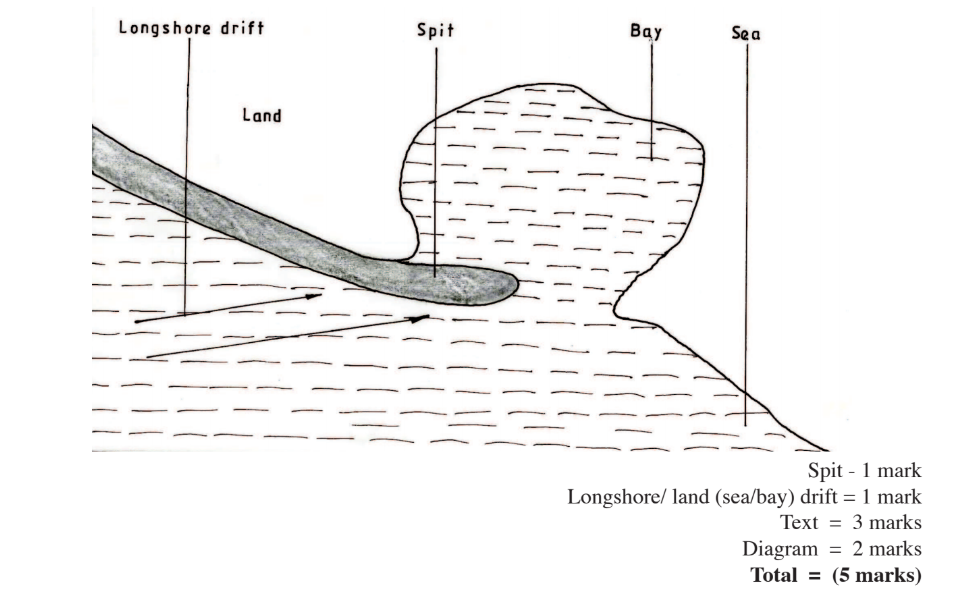
(d) Explain the significance of oceans to human activities.
– Oceans provides building materials.
Text : 3 marks
Diagram : 2 marks
Total = (5 marks)
– Oceans modify the climate of the adjacent lands thus enhancing agricultural activities.
– Oceans are used by water vessels thereby enhancing transportl communication.
– Oceans provide sites for recreational activities thus promoting tourism.
– Oceans are habitats for aquatic life hence providing food/ income to humans.
Oceans habour minerals which are extracted for economic developr””‘
– Ocean waves/ tides are harnessed which generate electric power for industrial/ domestic use.
– Oceans provide water for cooling industrial plants.
– Oceans encourage education and research.
– Ocean provide ideal grounds for testing millitary weapons.
Any 4 x 2 = (8 marks)
10. (a) (i) Name two mountains in East Africa which are ice capped.
– Mt Kenya
– Mt Kilimanjaro
– Ruwenzori mountains
Any 2 x l = (2 marks)
(ii) Identify three Ways in which ice moves.
– Plastic flowage
– Basal slip
– Extrusion flow
– Internal shearing
Any 3 x l = (3 marks)
(b) Describe the formation of the following glacial features:
(i) Hanging valley
– It is formed in glaciated highlands where there is a main valley and a tributary valley.
– The two valleys get filled with ice. The main valley has more ice than the tributary valley.
– As the ice gets heavy/ thick, it begins to flow down the slope eroding by plucking and ubrasion.
– The main river valley is deepened and widened more than the tributary valley.
– When ice melts the tributary valley is left hanging at a higher level.
– The tributary valley left hanging above the main river valley is known as hanging valley.
6 x l = (6 marks)
(ii) Pyramidal peak.
– Ice accumulates in several shallow pre-existing depressions on the mountain sides.
– As the ice moves, it plucks the rocks on the sides of the hollows/ depression.
– Continued erosion by abrasion deepens and widens the hollows forming cirques.
– Adjacent hollows (cirques) continue to be eroded causing back walls to receed until they are separated by narrow steep ridges called aretes.
– Where aretes converge at the top of the mountain, they form a sharp – steep sided peak known as a pyramidal peak.
6 x l = (6 marks)
(c) You are required to carry out a field study on erosional features in glaciated lowland area.
(i) Give two reasons why you would require a working schedule.
– It enables the planned activities to be carried out systematically.
– It allows for proper use of available time.
– It enables the assessment of the progress of the fieldwork.
– It enables the estimation of total time required for the study.
– It confines the researcher to the scope of the topic.
– It ensures all areas are adequately covered.
Any 2 x l = (2 marks)
(ii) Name three erosional features you are likely to observe during the field study.
– Depressions
– Crag and tail
– Ice eroded plain
– Roche montonnee
Any 3 x l = (3 marks)
(iii) Give three follow-up activities you would undertake after the field study.
– Sketching the features.
– Note making/ writing field reports.
– Asking / answering questions/ quizes.
– Discussing the findings.
– Display photographs.
– Analysing data collected.
– Reading more about the topic.
– Drawing conclusions.
Any 3 x l = (3 marks)
Geography Paper 2
Section A
Answer ALL the questions in this section. (25 marks)
1. (a) Give two uses of diamond.For making jewellery. For polishing metals/abbrasive – For making cutting/drilling instruments.
(Any 2 x 1 : marks)
(b) Identify three problems facing diamond mining in South Africa.Fluctuation of prices in the world market. Low mineral content in the ore High cost of mining/processing / deep miner. Reducing/depleting reserves. Competition of skilled labour with other sectors of the economy. Striking workers.
(Any 3 x 1 : 3 marks)
2. (a) Apart from coniferous forests, name two other types of natural forests.Tropical hardwood forests/ Equatorial forest. Temperature hardwood forests / tropical monsoon forests. Mixed forests. Montane forests. Mangrove forests. Temperate decidous. Mediterenean forests. Warm temperate evergreen.
(2 x 1 = 2 marks)
(b) State three characteristics of coniferous forests which favour their exploitation.The tree are light in weight. The trees occur in pure stand There is little undergrowth. The trees have straight trunk. The trees are tall. The trees are soft.
(Any 3 x 1 : 3 marks)
Use the map of East Africa below to answer question (a).
(a) Name the game reserves marked P, G and R.
p – Bokora
Q – Boni
R – Selous (3 x 1 = 3 marks)
(b) State two factors which influence the distribution of wildlife in East Africa.Fairly level grounds favour some animals / rugged terrain discourages some of them. Vegetation variation/distribution influences the type of wild animals/birds found in an area. Drainage of an area influences the distribution/population of different types of species of plants/animals/birds. Human activities conserve/destroy wildlife habitats/wildlife influencing the population/distribution. The soil of a place determines the plant life which influence wild animals/birds. The different types of climate influence the distribution/type of plants/animals/ birds. Change of altitude leads to variation in vegetation types/type of wild animals. In high altitude areas windward slopes are forested / the leeward slopes have grasslands.
(2 x l = 2 marks)
4 (a) Give two reasons why the geothermal power has not been fully exploited in Kenya.The country faces a shortage of capital/inadequate capital required for exploitation. There is shortage of skilled personnel as the country relies on expatriates. The country faces low level of technology which hinders expli”“”” “” “f “‘ ” energy.
– Most of the potential sites are found in remote/inaccessible areas which makes it difficult/expensive.
(2 x 1 = 2 marks)
State three causes of energy crisis in the world.There is a high demand for oil. There are embargoes/controls oil production by the oil producing countries. There is de-regulation of oil prices by the suppliers. There is unequal natural pattern of crude oil occurrence. There is political instability/wars in some of the oil producing countries. (Any 3 x 1 = 3 marks)
5. (a) Identify the two types of internal trade.
– Retail trade
– Wholesale trade
(2 x 1 = 2 marks)
(b) Give three factors that limit trade among the member states of the Common Market for Eastern and Southem Africa (COMESA).Poor infrastructure/transport slows/delays movement of goods/services. Difference in tariffs/custom duties hinders trading activities. Difference in currency makes transactions difficult. Production of similar/duplication of goods limits trade. Different levels of industrial development creates imbalance in trade. Movement barriers limit free movement of people/goods/services. Different political ideologies/political instability/insecurity.
(Any 3 x 1 = 3 marks)
Section B
Answer question 6 and other TWO questions from this section.
6. Study the photograph below and use it to answer question (a).
(a) (i) Identify the type of photograph shown above.
Ground general view/Ground oblique. (1 mark)
(ii) Name the type of settlement shown on the photograph.
Informal settlement/urban/slum. (1 mark)
(iii) What time of the day was the photograph taken.
Afternoon/mid morning. (1 mark)
(iv) Draw a rectangle measuring 15 cm by 10 cm. On it, sketch and label five human features shown on the photograph.
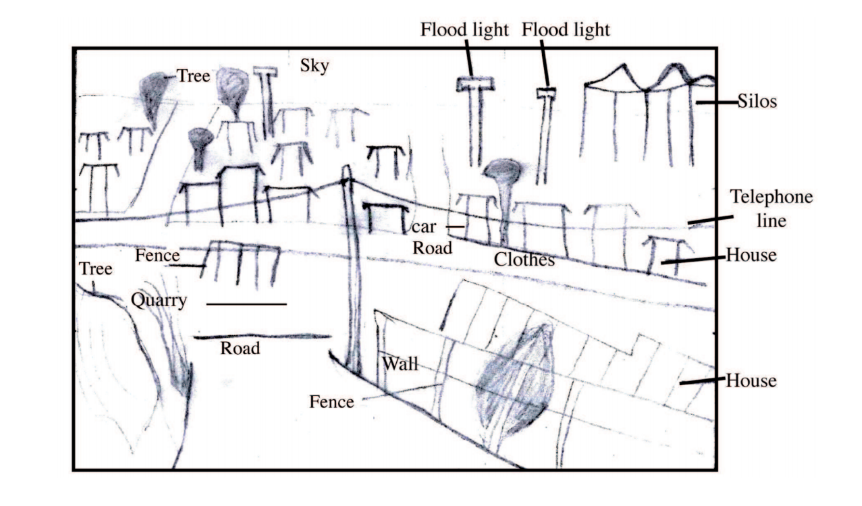
Drawing a rectangle correctly (1 mark)
Roads
Silos
Flood lights
Telephone line
Fences
Planted trees.
Wall.
near industries.
settlement.
centres/new settlements.
(Any 5 x 1 = 5 marks)
(b) Explain four economic factors that influence settlement.Mining/fishing/water points/fertile soils attracts workers who settle near by. Trade leads to development of market centres thereby attracting many people. Industrialisation leads to creation of jobs hence encouraging many people to live Transportation results to accessibility of services/ goods thus attracting more Agriculture leads to siting of collection centres hence development of urban Administration provides security thereby encouraging settlement. To sustain nomadic pastoralism, temporary settlements are put up.
(Any 4 x 2 = 8 marks)
(c) Describe four negative effects of urbanisation.
– Inadequate housing leads to development of slums/shanties in urban centres / resulting in delays.There is traffic congestion in urban centres due to poorly planned roads/traffic control systems resulting in delays. Unemployment in urban centres leads to high crime rate/prostitution. There is pollution in urban centres due in dumping of garbage/disposal of waste into drainage systems/noise from vehicles and industries/emission of smoke from vehicles and industries. There is strain on social amenities in urban centres due to rapid population growth. There are street families in the urban centres due to poverty. Cultural erosion due to cosmopolitan population.
(Any 4 x 2 = 8 marks)
7. (a)Explain three social factors that influence agriculture.Gender influences productivity as the produce will depend on effort of the gender involved. Some religious beliefs determine the type of livestock farming since they discourage rearing of cenain animals. The culture of a people determines the type of crops grown/livestock kept in order to meet their dietary needs. Land tenure system allows/limits individuals/communities to use the available land thus increasing/decreasing produce. The interaction between people leads to adoption of new techniques in fanning / new foods.
(Any 3 x 2 = 6 marks)
(b) (i) Describe the cultivation of oil palm from land preparation to harvesting.The nursery is prepared where the oil palm seeds are planted. The land is cleared of vegetation /ploughed The holes are dug with spacing of 9m X 9m. The seedling are transplanted from the nursery into the holes. Weeding/spraying is done regularly to protect the plants against pests/disease. Manuring/application of fertilizers. The maturing trees flower/bear fruits after three years. The mature/ripe fruits are harvested using a curved knife/chisch/hook. (7 X l =7 marks)
(ii) Give three uses of palm oil.Used as a lubricant. Used in phamaceutical.As a cleansing agent in the tin industry. Used as food. Making margarine/cooking fat. Making soap. Making candles. Making cosmetics. Used in the confectionery industry.
(c) Explain three reasons why horticultural farming is encouraged in Kenya.To earn foreign exchange which help to improve the economy. To create employment which enables people earn income hence improve their living standards/reduces unemployment. To provide raw materials which support the development of related industries. To enable farmers with small pieces of land earn high income. To improve food supply in the country thereby ensuring food security.
(Any 3 x 2 = 6 marks)
(d) Give three factors which favours beef farming in the Nyika plateau.Presence of watering points/rivers/swamps. There are large tracks of flat land with natural grass. The local people who keep livestock as their occupation. The semi-arid conditions of the area favour beef cattle keeping. There are ranching schemes which control grazing/spreading of diseases/pests.
(Any 3 x 1 = 3 marks)
a) Explain four ways in which land is being rehabilitated in Kenya.By filling open pits/land scaping in order to be used for farming/settlement. By constructing terraces thereby reducing the speed of surface runoff. By planting trees / grass strips on degraded land thereby protecting it against the agents of erosion. By building gabions in order to hold/trap the soil carried by water. By constructing dykes along river banks/dams across rivers in order to control floods. By supplying manure /fertilizer on derelict land in order to restore its fertility. By irrigating semi-arid areas/during dry seasons in order to provide water required for crop growth. Bush fallowing to allow land to regia.n fertility. Mulching / cover crops/ cut off drains to retain soil moisture/ add humus. Drainage trenches to remove excess water from the land. Controlled grazing to allow regeneration of pastures. (Any 4 x 2 = 8 marks)
(b) (i) State two ways in which the salinity of the polders is reduced in the Netherlands.
– Chemicals are applied to lower salts in the soils.
– Fresh water is flashed to the soils to remove/dilute the excess salts.
– Reeds are planted to use up the excess salts.
– Continuous pumping of water from the polders.
(Any 2 x 1 = 2 marks)
(ii) Explain four ways in which the Zuyder Zee project benefits the Netherlands. Reclamation has increased the size of the land which is used for farming/ settlement. The reclaimed land has increased agricultural output hence more food/ raw materials for industries.Damming created a freshwater lake thus improving the supply of water for domestic/industrial use/ lowering salinity of the soil. It has led to employment of many people thus improving their standards of living. Roads have been constructed thus improving transportation. Reclamation has created sceneries that have become tourists attractions thereby earning foreign exchange. Construction of the great dyke shortened the coastal distance. It also controlled the disastrous floods. (Any 4 x 2 = 8 marks)
(c) You intend to carry out a field study on irrigation farming in Mwea Tebere Irrigation scheme.
(i) Identify the two types of hypothesis you would develop for the study. Alternative/substantive/positive.Null / negative. Question form. (2 x 1 = 2 marks)
(ii) Name three crops grown in the scheme you are likely to identify.Rice Maize Tomatoes Beans/peas Vegetables Water melons Onions (3 x l = 3 marks)
(iii) Give reasons why you would sample the area of study. (2 marks)It is cheaper to study portions of the scheme.It saves the amount of time spent on the study. I brings out the details of the area under study. It enables one to make generalised conclusion about the area under study. (2 x 1 = 2 marks)
9. (a) Define the term fishing.It is the extraction/exploitation of aquatic animals/fish. (2 marks)
(b) Explain two ways in which each of the following factors negatively affect fishing in Kenya.
(i) Agricultural activitiesPoor farming methods cause soil erosion thereby leading to siltation of the lakes/rivers which hinders the movement of fishing vessels/ death of fish. Agro-chemicals used on farms were washed into the lakes/rivers thus polluting the water/kill fish/eutrophication. Abstraction of water from the river/lakes for irrigation reduces the level of the water thereby limiting the types of fish species.
(Any 2 x 2 = 4 marks)
(ii) Water Weeds
– The growth of the weeds on the surface of the water harbours dangerous animal/predators thereby scaring away the fishermen.
– The weeds growing on the water form a thick barrier/insulate the water thereby hindering the amount of sunlight required for the growth of Planktons
– The weeds on the water choke the fishing vessels thus hindering their movement.
– The Weeds compete for oxygen with fish which leads to death of fish.
(Any 2 x 2 = 4 marks)
(C) Use the map of North-West Atlantic fishing ground to answer question (c) (ii) and (iii).

(i) Give three types of fish species caught in the North-West Atlantic fishing ground.
– Shell fish
– Herring
– Cod
– Mackerel
– Haddock
– Menhaden
– Lobseters
(3 marks)
(11) Name the ocean currents marked.
M – Cold Labrador current (l mark)
N – Warm Gulf Stream (l mark)
(ii) Explain two ways in which the convergence of ocean currents marked M and N influence fishing. (4 marks)
– It causes upwelling of water which increases supply of oxygen/minerals for Planktons required for growth of fish hence presence of alot of fish/ many species of fish.
– The warm current raises the temperature of the ocean water making it ice-free thereby encouraging fishing throughout the year.
– The cold current carries minerals which encourage growth of Planktons thus food for fish thus a lot of fish.
– It causes cool conditions/temperatures thereby favouring the growth of Planktons required by fish hence presence of a lot of fish / many species. (Any 2 x 2 = 4 marks)
(d) Give three differences between fishing in Kenya and Japan.
– In Kenya there is low level of technology/mechanization while in Japan there is advance/efficient technology.
– In Kenya fishing is done on small scale while in Japan fishing is down on large scale.
– In Kenya there is a small domestic/external market while in Japan there is large domestic/external market.
– In Kenya few people market their fish through co-operatives while in Japan marketing is mainly done through co-operatives.
– In Kenya fishing is mainly done near the continental shelf/shallow sea waters / lakes while in Japan fishing it is mainly deep sea fishing.
– In Kenya fishermen face stiff competition from foreigners while in Japan there is little competition from foreigners.
– In Kenya there are few variety of marine species while in Japan the species are many.
– In Kenya the fish eating culture is limited while in Japan it is widespread.
– In Kenya there is limited research while in Japan it is extensive.
– In Kenya fish farming is less developed while in Japan it is highly developed.
(Any 3 x 2 = 6 marks)
l0. (a) What is environmental management.These are measures/controls taken to ensure sustainable utilisation of resources in a given environment./ The planning and implementation of effective and proper utilization of the available resources in the environment. (2 marks)
(b) (i) Explain four negative effects of floods.
– Flooding leads to loss of life/destruction of property therebv causing human suffering/misery.
– It causes destruction of vegetation on slopes thereby enhancing soil erosion.
– It creates pools of water on the land surface forming breeding grounds for pests which causes diseases to people/animals.
– It leads to water logging/leaching hence causing soil infertility.
– It leads to destruction of acquatic habitats hence reduced fish production.
– It causes flooding of settlements thereby leading to new temporary homes/ displacement.
– It destroys transport/communication network thereby hindering movement of goods/services.
– Floods pollutes sources of water/land which causes water borne diseasesl eyesore.
– Floods wash away crops resulting in food shortage.
(Any 4 x 2 = 8 marks)
State two measures being taken to combat lightning.
– By educating the masses on the precautions to take during rains/avoid sheltering under trees/playing games and rain.
– By installing of lightning arrestors
– By launching sound rocket with electronic sensors in thunderstorm prone areas.
– By spraying of carbon iv oxide/silver iodide in the atmosphere to disperse the clouds.
(Any 2 x l = 2 marks)
(c) Explain the significance of conserving the environment.To ensure effective utilisation of the available resources to avoid wastage/depletion. To sustain resources needed by human kind. To reduce pollution which causes diseases to animals/plants resulting into good health/prolonged life. To protect the endangered plant/animal species. Preserving them for posterity. To preserve the scenic value/beauty of landscape/wildlife inorder to promote tourism. To protect the water catchment areas/wetlands inorder to preserve water sources/ maintain water cycle.
(Any 4 x 2 = 8 marks)
(d) Your Geography class carried out a fieldwork on floods along a river.
(i) Name two types of field work they could have used.
– field study
– field excursion/field visit/field trip. 2 x l = 2 marks
(ii) Give three advantages of studying floods through fieldwork. (3 marks)
– The leamers get first hand information.
– The learners appreciate/interact with environment.
– Helps breaks the classroom monotony/arouses interest.
– The learners practice/acquire skills.
– It enhances learners visual memory.
(Any 3 x 1 = 3 marks)

