2018 KCSE Business Studies Paper 2 Past Paper
1. (a)Explain five circumstances that may lead to the existence of a business opportunity to be exploited by the entrepreneur. (10 marks)
(b) Explain five factors that Chuma Steel Manufacturers may consider when choosing a channel for distributing their products. (10 marks)
2. (a)Explain five clauses that must be specified in the Memorandum of Association of a public limited company. (10 marks)
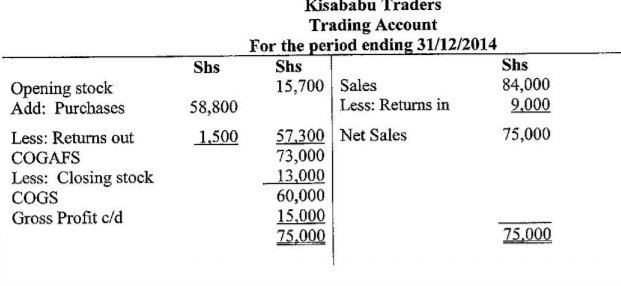
(b) The following information was extracted from the books of Kisababu Traders on 31 December 2014:
| Details | Sh |
| Sales | 84,0000 |
| Purchases | 58,000 |
| Opening Stock | 15,700 |
Required:
i. Prepare Kisababu Traders Trading Account for the period ending 31 December 2014. (5 marks)
ii. Work out Kisababu Traders percentage mark up.(2 marks)
iii. Calculate Kisababu Traders Rate of Stock Turnover.(3 marks)
3. (a)Explain five demerits of using carts as a means of transport in towns. (10 marks)
(b) Explain five types of direct taxes that the government may use to collect revenue from individuals and companies. (10 marks)
4. (a)The demand for soft drinks has been on the increase. Explain five factors that may have contributed to this. (10 marks)
(b) Describe five forms of economic integration that countries may join to promote international trade. (10 marks)
5. (a) Explain five differences between an open office and an enclosed office. (10 marks)
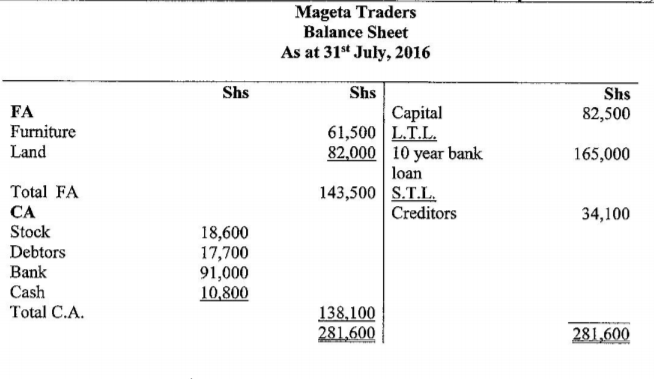
(b) The following opening balances were extracted from the books of Mageta Traders on 1 July 2016:
The following transactions took place in the course of the month:
— Paid a creditor Sh4,500 in cash.
— Took Sh3,000 from the bank for family use.
— Bought stock Sh 18,600 on credit.
— Acquired a 10 year bank loan Sh 165,000 which was credited to the business bank account.
— Purchased land worth Sh 82,000 paying by cheque.
Converted a family table worth Sh5,500 to business use.
— Received Sh 7,300 in cash from debtor.
Required: Prepare Mageta Traders Balance Sheet at the end of July 2016 (10 marks)
6. (a) Explain five problems of using national income statistics to compare the living standards of citizens of Kenya and Tanzania. (10 marks)
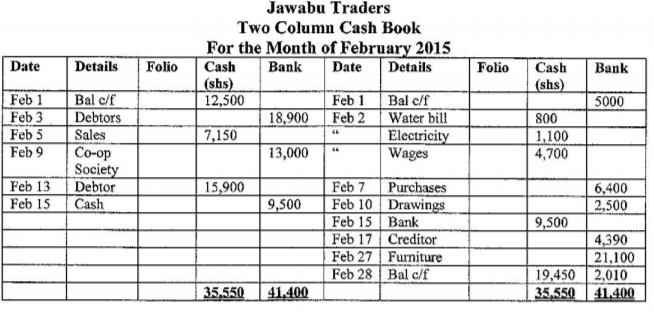
(b) Use the transactions given below to prepare Jawabu Traders two column cash book for the month of February 2015. (10 marks)
1st Feb.Had Sh 12,500 cash and a bank overdraft of Sh 5,000
2nd Feb.Used cash to pay for water bill Sh 800, electricity Sh 1,100 and wages Sh4,700.
3rd Feb.Received a cheque of Sh 18,900 from a debtor
5th Feb.Sold goods worth Sh 7,150 in cash.
7th Feb.Paid for goods bought for resale worth Sh 6,400 by cheque.
9th Feb.Received a cheque of Sh 13,000 from the co-operative society as earnings from dividends.
10th Feb.Withdrew Sh 2,500 from the bank for family use.
13th Feb.Received Sh 15,900 in cash from a debtor.
15th Feb.Deposited Sh9,500 from the office into the business bank account.
17th Feb. Paid a creditor by cheque Sh4,390.
27th Feb.Used all the money in the bank to purchase furniture leaving only a balance of Sh2,010.
2018 KCSE Business Studies Paper 2 Past Paper-Marking Scheme/Answers
1. (a)Explain five circumstances that may lead to the existence of a business opportunity to be exploited by the entrepreneur. (10 marks) Lack of some products/services.
Custoiners may need some products/services which are not easily found in their area. Higher prices of goods/services.
Existing market prices may be unnecessarily high hence offering them at relatively lower prices would create an opportunity. Excess demand.
When the quantities of goods available in the market are not sufficient, an opportunity to supply more exist. Low quality products.
When customers expect better quality products then, this presente an opportunity to offer them. Sub-standard services.
An opportunity will exist where better services are offered in the distribution of goods. Un-met sociocultural needs/conditions.
Goods and ses ices should target the society’s existing attitudes, practices and beliefs which existing products may not be addressing. Innovation.
Discovery of new technology which may lead to reduced costs of production and general efficiency presents an opportunity.
(b) Explain five factors that Chuma Steel Manufacturers may consider when choosing a channel for distributing their products. (10 marks) The geographical spread of customers.
If the customers are spread over a wide area, then a longer channel would be preferable. Durability of the steel products.
Since steel products are not easily spoilt, long channels can be used ln their distribution. Level of competition.
Shorter channels should be used if competition is so stiff. Resources and size of the firm.
If the firm has limited resources and only serves a small market, then a shorter channel is ideal. Government policy.
Chuma steel manufacturers must adhere to government regulation on the distribution of steel products. Marketing risks.
Where marketing risks are higher, more middlemen should be involved to spread such risks. Availability of intermediaries.
Chuma Steel Manufacturers can only use channels where intermediaries are available. Pricing of the steel products.
Shooter channels will be preferred where the prices are to be kept low by avoiding the intermediaries.
2. (a)Explain five clauses that must be specified in the Memorandum of Association of a public limited company. (10 marks) The Name Clause.
This clause states the name of the company and ends with the word “limited”. This name must be unique to the company and not shared with any other. The Objects Clause.
This clause states the objectives of the company and specifies what the company has powers to do. The Situation Clause.
This clause states the physical location of the company’s registered office. The Liability Clause.
This clause states the extent to which members are fiable to the debts of the company.
Shareholders and members have “limited liability”. The Capital Clause.
This clause states the amount of capital that the company is authorized to raise, the capital structure, the composition and the values of the shares. Association and Subscriptions Clause.
This clause contains a declaration by the original members who registered the company about their desîre to form a company, their objectives, the number of shares they will owri and their personal details.
(b) The following information was extracted from the books of Kisababu Traders on 31 December 2014:
| Details | Sh |
| Sales | 84,0000 |
| Purchases | 58,000 |
| Opening Stock | 15,700 |
Required:
i. Prepare Kisababu Traders Trading Account for the period ending 31 December 2014. (5 marks)
ii. Work out Kisababu Traders percentage mark up.(2 marks)
Mark up = GP/COGS x 100
15,000/60000 x 100
60, 000
= 25%
iii. Calculate Kisababu Traders Rate of Stock Turnover.(3 marks)
Rate of Stock Turnover = COGS./Average Stock
60,000/(O.P. Stock * C.L. Stock)
60, 000
15, 700x 3000 2
60000/14350
=4 times
3. (a)Explain five demerits of using carts as a means of transport in towns. (10 marks)
(i) Carts are prone to delays occasioned by their slow speed.
(ii) Movement of carts is affected by extreme weather conditions like rainfall.
(iii) They are unsuitable for transporting goods over long distances as people and animals get tired when pulling them.
(iv) Carts offer little protection to goods against damage by elements of weather such as rain.
(v) Goods transported by carts are susceptible to theft making it an unsuitable means of transporting valuable goods.
(vi) Carts cannot carry very heavy and bulky goods since their carrying capacity is limited.
(vii) Carts inconvenience motor vehicles and other road users since they are slower.
(viii) Carts may be a cause of accidents since those pulling them usually disregard traffic rules.
(b) Explain five types of direct taxes that the government may use to collect revenue from individuals and companies. (10 marks) Personal Income Tax (P.A.Y.E.).
This is tax charged on an individual’s income which may be from salaries, wages and profits made from businesses. This tax is usually progressive in nature. Corporation Tax.
This tax is usually charged on the profits made by companies and other incorporated business. It is a fixed percentage of the profits. Capital Transfer Taa.
This tax is charged when there is change of ownership of capital investment from one person to another. Stamp duty.
This tax is charged on the transfer of land or securities from one person to another. Capital gains tax.
This tax is charged when an asset is sold at a price that is higher than its book value. Estate (death) duty.
This tax is levied when property is transferred to an inheritor/ heir after the death of the original owner. Wealth tax.
This tax is levied on personal wealth that goes beyond a certain limit. This wealth may include realizableassets like land, houses, accumulated profits and even savings. Withholding tax.
This tax is levied on savings like pension dividends and any moneys held by individuals.
4. (a)The demand for soft drinks has been on the increase. Explain five factors that may have contributed to this. (10 marks) Favourable pricing.
The soft drinks are priced at a value that consumers can easily afford. Increasing consurner incomes.
People are able to buy more of the products due to increased earnings. High prices of substitutes.
Most of the products in the market that can serve as substitutes are hîghly priced hence not preferred by buyers. Favourable tastes and preferences.
More consumers now like soft drinks as compared to other drinks. Favourable government policies which keep the prices of soft drinks down/stable hence encouraging their consumption. General increase in population.
With more people, more of the products are consumed. Aggressive marketing/sales promotion.
More consumers are attracted to soft drinks due to intense advertising and other promotional strategies. Equitable distribuôon of income among consumers.
Since many people have access to earning, they are able to buy more of the products.
(b) Describe five forms of economic integration that countries may join to promote international trade. (10 marks) Preferential Trade Area.
In this form ofi integration, trade barriers are reduced among the member nations while the barriers are applied at normal rates for trading activities with non-member nations. Free trade area.
This is economic integration where all trade barriers are removed between the member countries while each country retains its own barriers towards non-members. Customs union.
In this form of integration, tariffs and other trade barriers are removed between member countries whiletheir trade policies are harmonized with regard to treatment of trade with the rest of the world. Common market.
This integration goes beyond harmonizing trade policies and removal of trade barriers but also allows for free movement of labour and capital among member nations. Economic union.
In this form of integration, member countries set up common institutions like central banks, adopt use of common currency (monetary system) and have common public services like railways network. Duty-free zones.
Member countries allow importation of raw materials without charging duty. Exports from these zones to member countries also attract no excise duty. Political union.
In this form of integration, several states form a central government through which, share a central bank, the defense and core ministries that run their affairs.
5. (a) Explain five differences between an open office and an enclosed office. (10 marks)
Open Office
(a) All staff work in one large room.
(b) There is no confidentiality in consultations and discussions.
(c) Senior staff sit together with the juniors hence no status conferred.
(d) Office equipment and machines are easily shared and cannot be misused.
(e) Disruptions and noise from colleagues is high due to overcrowding.
(f) Has fewer partitions hence cheap to construct.
(g) It is easy to supervise the staff since they are all in one room
Enclosed Office
(a) Each staff is allocated a room from where they work.
(b) Discussions and consultations are done in confidence.
(c) Confers status on tap level staff as they are allocated own offices.
(d) Office equipment and machines like telephones are easily misused since they are located in particular offices.
(e) Little noise and disruption from colleagues since each staff work from own offices.
(f) Has more partitions hence costly to construct.
(g) It is difficult to supervise the staff since they are in different rooms.
(b) The following opening balances were extracted from the books of Mageta Traders on 1 July 2016:
The following transactions took place in the course of the month:
— Paid a creditor Sh4,500 in cash.
— Took Sh3,000 from the bank for family use.
— Bought stock Sh 18,600 on credit.
— Acquired a 10 year bank loan Sh 165,000 which was credited to the business bank account.
— Purchased land worth Sh 82,000 paying by cheque.
Converted a family table worth Sh5,500 to business use.
— Received Sh 7,300 in cash from debtor.
Required: Prepare Mageta Traders Balance Sheet at the end of July 2016 (10 marks)
6. (a) Explain five problems of using national income statistics to compare the living standards of citizens of Kenya and Tanzania. (10 marks)
(i) The two countries may have used different currency values to calculate their national income hence different standards of measure.
(ii) One country could be having a large subsistence sector whose income may not have been included in the measure of their income.
(iii) The levels of income distribution in one country may be too skewed compared to the other which may have a fair income distribution.
The two countries may have different references and economic priorities. The two countries could be differcnt in terms of resource endowment hence different abilities to generate income.
(vi) The climatic conditions in the two countries may be different leading to difference in demand and production.
Production activities may affect the health of citizens in the two countries differently. The political realities in the two countries could be different affecting their stability and the security of citizens.
(ix) The degree of accuracy of the national income statistics .
(b) Use the transactions given below to prepare Jawabu Traders two column cash book for the month of February 2015. (10 marks)
1st Feb.Had Sh 12,500 cash and a bank overdraft of Sh 5,000
2nd Feb.Used cash to pay for water bill Sh 800, electricity Sh 1,100 and wages Sh4,700.
3rd Feb.Received a cheque of Sh 18,900 from a debtor
5th Feb.Sold goods worth Sh 7,150 in cash.
7th Feb.Paid for goods bought for resale worth Sh 6,400 by cheque.
9th Feb.Received a cheque of Sh 13,000 from the co-operative society as earnings from dividends.
10th Feb.Withdrew Sh 2,500 from the bank for family use.
13th Feb.Received Sh 15,900 in cash from a debtor.
15th Feb.Deposited Sh9,500 from the office into the business bank account.
17th Feb. Paid a creditor by cheque Sh4,390.
27th Feb.Used all the money in the bank to purchase furniture leaving only a balance of Sh2,010.