2022 Mock Examinations Agriculture Paper 2 with Answers- Kapsabet High School
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES:
• Answer all the questions in section A and B
• Answer any two questions in section C.
• Answers should be written in the spaces provided in this booklet.
SECTION A (30MARKS)
1. Give four livestock rearing practices that can be carried out in a crush. (2mks)
2. Name the part of the digestive system of poultry where insoluble grit is found. (i/2Mk)
3. Give two distinguishing external characteristics of Californian breed of rabbit. (1mk)
4. State four pre-disposing factors of livestock diseases. (2mks)
5. Outline four functions of proteins in the body of an animal. (2mks)
6. State four observable features of indigenous cattle (Bos indicus) (2mks)
7. State four importance of creep feeding. (2mks)
8. Name four materials that are collected by bees. (2mks)
9. Give the function of each of the following parts of a fish pond.
a. Spillway (½ mrk)
b. Outlet (½ mrk)
10. State four advantages of cross-breeding. (2mks)
11. Name the part of the digestive system of a non-ruminant animal where cellulose is broken down (l mk)
12. State three field conditions under which a disc plough should be used instead of a mouldboard plough. (½mks)
13. State four advantages of artificial incubation in comparison to natural incubation as a method ofnhatching chicks. (½mks)
14. Give four maintenance practices carried out on the water cooling system of a tractor. (2mks)
15. State four advantages of a four-stroke cycle engine. (2mks)
16. Give three reasons why drenching alone is not an effective method of controlling intestinal parasites in livestock. (½mks)
17. Name three poultry diseases that are controlled by vaccination. (½mks)
18. Give the mineral whose deficiency causes the following disorders in livestock.
a. Anaemia imk
b. Parakeratosis ½mk
19. Give three reasons why liming is done in fish ponds. (½mks)
20. If records show that a rabbit was served on 27th September 2020.Which date did it give birth. (½mk)
SECTION B (20 MARKS)
21. Below is an illustration of part of a wooden post wire fence. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
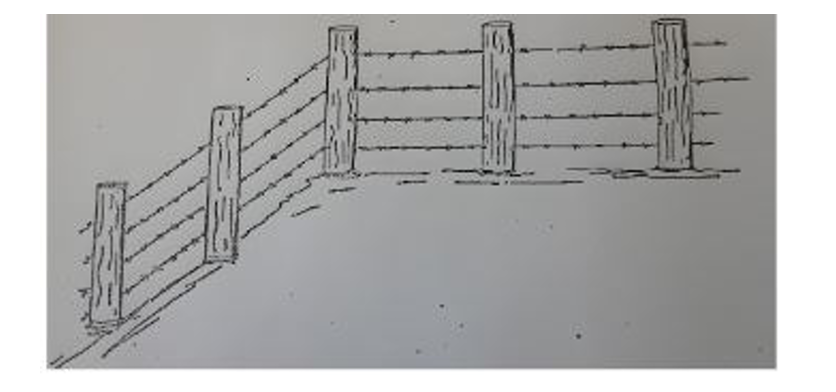
a. Identify the type of wire in the illustration. (1mk)
b. On the illustration show by drawing how the corner post should be supported. (1mk)
c. On the illustration draw, label and give the function of a dropper. (2mks)
d. Name the correct tool for tightening the wire during construction of the fence. (1mk)
22. Observe the tools A, B and C illustrated below then answer the questions that follow.

a. Name tools A, B and C and state the correct use of each tool. (3mks)
b. State two maintenance practices that should be carried out to ensure that tool C is in a good working condition. (2mks)
23. Below is an illustration of an activity carried out by a poultry farmer keeping layers
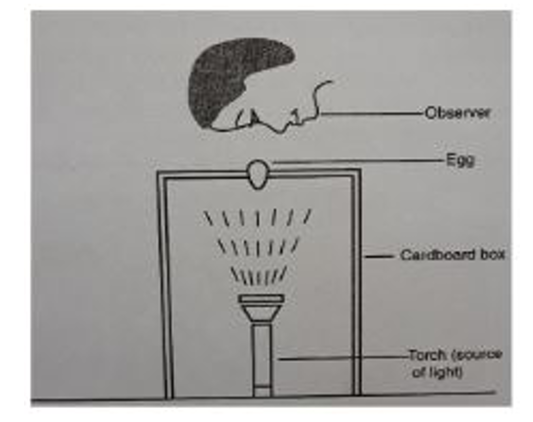
a. Identify the activity carried out using the set-up. (1mk)
b. State four abnormalities in eggs that can be detected using the set-up above. (2mks)
c. How can a farmer improve the following?
i. Hardness of egg shells. (1mk)
ii. Yellowness of the egg yolk. (1mk)
24. The diagrams K, L, M and N below show four possible ways of drawing milk from the teat of a cow during milking.
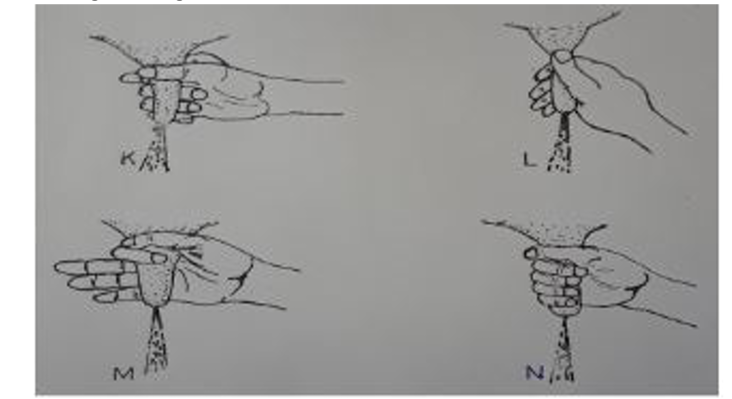
a. Which diagram shows the proper way of drawing milk. (1mk)
b. How long should it take to milk a cow from the start to the end of milking. (1mk)
c. How would a milkman ensure that no milk remains in the udder at the end of milking? (lmk)
d. Give two practices carried out on milk immediately after milking. (2mks)
SECTION C (40MARKS)
25. a. Describe the advantages of battery cage system of rearing layers. (10mks)
b. State and explain five factors affecting milk production. (10mks)
26. a. State the functions of any six parts of a plunge dip. (6mks)
b. State and explain four ways through which power transmitted from the engine is made available for use. (4mks)
c. Explain five mechanical methods of controlling ticks. (10mks)
27. a. State five advantages of embryo transplant. (5mks)
b. Describe coccidiosis disease under the following sub- headings.
i. Animals attacked (2mks)
ii. Causal organism (1mk)
iii. Symptoms (4mks)
iv. Control measures (3mks)
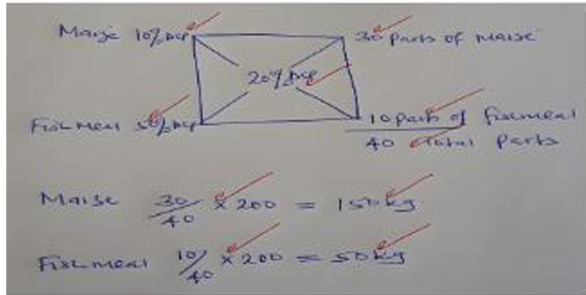
c. A ration containing 20% DCP for growing chicks is to be obtained by mixing ground maize containing 10% DCP and fishmeal containing 50% DCP. Calculate the amount of each feedstuff in kilograms required to prepare 200kg of the feed. (5mks)
Marking Scheme
1. Give four livestock rearing practices that can be carried out in a crush.
• Spraying livestock against external parasites.
• Identifying animals by use of such methods as branding, ear tagging and ear notching.
• Vaccination.
• Administering prophylactic drugs to the animals.
• Treating sick animals.
• Dehorning.
• Pregnancy test.
• Artificial insemination.
• Taking body temperatures.
• Hoof trimming.
• Milking.
2. Name the part of the digestive system of poultry where insoluble grit is found.
• Gizzard.
3. Give two distinguishing external characteristics of Californian breed of rabbit.
• It has a white body.
• It has black ears, nose, paws and tail.
4. State four pre-disposing factors of livestock diseases.
• The species of the animal
• The breed of the animal
• The age of the animal
• The sex of the animal
• The colour of the animal
• Poor/cruel handling.
• Poor housing.
• Extreme weather conditions.
5. Outline four functions of proteins in the body of an animal.
• Growth, repair and replacement of worn out body tissues.
• Production of antibodies which protect the animal from diseases.
• Production of digestive enzymes to break food particles.
• Production of certain hormones in the body.
• Production of such products eg meat, milk, eggs and wool.
6. State four observable features of indigenous cattle (Bos indicus)
• They have humps that store fat which is broken down to energy and water in times of starvation.
• They have long horns.
• They have long legs.
• Their udder is more rounded with a curved sole, poorly suspended and carried in front of rather than between the hind legs.
• Their head is long and comparatively narrow.
• Their skin is very loose and falls away from the body in folds.
• Their dewlap, umbilical fold and brisket are extensively developed.
7. State four importance of creep feeding.
• It ensures higher weights at weaning time eg calves gain 1kg/day more than calves that are not creep fed.
• It will lessen the suckling pressure on the mother and therefore the condition of the dam remains good.
• Weaning stress will be eased. Weaning is easier and earlier in case of beef calves as they could be finished for marketing at one year.
• Uniformity of size at weaning as creep feeding makes up for any shortage during suckling.
• It shortens the fattening period because in case of beef production the calves go to fattening feed lots in better conditions.
• It aids in developing future breeding stock.
8. Name four materials that are collected by bees.
• Nectar
• Pollen
• Propolis
• Water
9. Give the function of each of the following parts of a fish pond.
a. Spillway -Prevents the water from overflowing on the dykes/ To allow excess water to flow out of the pond.
b. Outlet – Prevents the fish from swimming away.
10. State four advantages of cross-breeding.
• Heterosis (hybrid vigour) can be exploited. Hybrids perform better than the original breeds.
• It helps to establish grade animals.
• It can be used to change the breed ie from one breed to another.
• It is a much quicker method of producing the required animal.
11. Name the part of the digestive system of a non-ruminant animal where cellulose is broken down
• Caecum
12. State three field conditions under which a disc plough should be used instead of a moldboard plough.
• If the ground is hard.
• If there are many obstacles in the field.
• If the soil is sticky or heavy.
• If there is little organic matter to be turned into the soil.
• Where a rougher seed bed is required/ where land is liable to erosion.
13. State four advantages of artificial incubation in comparison to natural incubation as a method of hatching chicks.
• Many chicks can be hatched at one time.
• It’s possible to plan when to hatch the chicks.
• The incubator is usually ready when required.
• If management is good, chicks have no danger of suffering from parasites or diseases.
14. Give four maintenance practices carried out on the water cooling system of a tractor. (2mks)
• The water pump should be lubricated regularly.
• Clean water should be used in the radiator and trash removed from the fins.
• All pipes should be fitted tightly to avoid leakage.
• The radiator should be filled with clean water before starting the days work.
• The fan belt tension should be checked regularly and if it is too tight or too loose it should be adjusted accordingly.
15. State four advantages of a four-stroke cycle engine.
• Produce high power and can do heavy farm work.
• They have an efficient fuel and oil utilization.
• They perform a wide range of farm operations.
• The engine is efficiently cooled with water thus allowing the production of large engine sizes.
• Exhaust gases are effectively expelled from the cylinders.
16. Give three reasons why drenching alone is not an effective method of controlling intestinal parasites in livestock. (1 s)
• It does not eradicate other stages of development of the parasite.
• It does not destroy the parasites in the intermediate hosts
• It does not destroy parasites in pastures, water and forage.
17. Name three poultry diseases that are controlled by vaccination. (1 s)
• Fowl typhoid (Kikuyu fowl disease)
• Newcastl
• Fowl pox
• Gumboro (infectious bursa disease)
18. Give the mineral whose deficiency causes the following disorders in livestock.
• Anaemia – Iron
• Parakeratosis – Zinc
19. Give three reasons why liming is done in fish ponds. (1 s)
• Acts as a disinfectant against nematodes.
• Neutralizes acidity in the pond water.
• Makes silt to settle at the bottom of the pond.
20. If records show that a rabbit was served on 27th September 2020.Which date did it give birth.
• 26th ,27th, 28th 29th October 2020.
21. Below is an illustration of part of a wooden post wire fence. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
a. Identify the type of wire in the illustration. (1mk)
• Barbed wire fence.
b. On the illustration show by drawing how the corner post should be supported. (1mk)
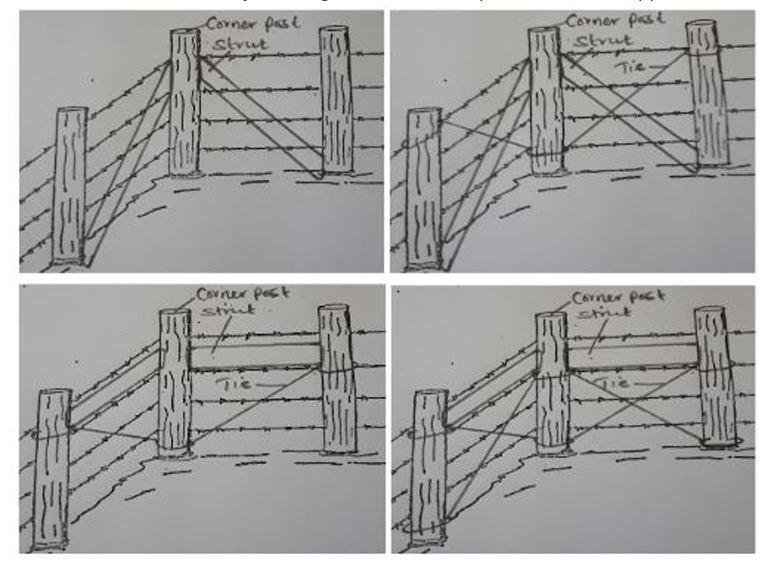
c. On the illustration draw, label and give the function of a dropper. (2mks)
• A dropper on the diagram should be a thin stake fastened to the barbed wires and hanging above the ground. It should touch all the wires.
• Function-Reinforces the barbed wire and prevents sagging.
d. Name the correct tool for tightening the wire during construction of the fence. (1mk)
• Wire strainer /monkey strainer.
22. Observe the tools A, B and C illustrated below then answer the questions that follow.
a. Name tools A, B and C and state the correct use of each tool. (3mks)
Tool | Identity | Function |
|---|---|---|
| A | Sickle | -Harvesting small grains and cereal crops eg rice, wheat and millet -Also ideal for cutting grass. |
| B | B Pruning saw | -Pruning or cutting branches eg coffee, citrus and ornamental plants. |
| C | Jack plane | Smoothing and cleaning up surface of wood to obtain a fine even surface. |
b. State two maintenance practices that should be carried out to ensure that tool C is in a good working condition. (2mks)
• Knobs or handles should be replaced when broken.
• Check and replace any worn out parts of a plane.
• Plane iron and cap iron require replacement when worn-out.
• Cutting edge of the plane iron should be sharpened on an oilstone when blunt.
• The plane should be laid on its side at the work bench when not in use.
• After work the plane iron is drawn back and the plane placed on its side in the tool rack.
23. Below is an illustration of an activity carried out by a poultry farmer keeping layers
a. Identify the activity carried out using the set-up. (1mk)
• Egg candling.
b. State four abnormalities in eggs that can be detected using the set-up above. (2mks)
• Hair cracks on the shell.
• Double yolk/ deformed yolk/ broken yolk
• Absence of yolk.
• Blood spots/ meat spots.
• Dead embryo.
• Inappropriate size and location of the air cell/air space.
c. How can a farmer improve the following?
i. Hardness of egg shells. (1mk)
• Feeding calcium/soluble grit/ oyster shells to the birds.
ii. Yellowness of the egg yolk. (1mk)
• Providing green vegetation/ green vegetables to the birds.
24. The diagrams K, L, M and N below show four possible ways of drawing milk from the teat of a cow during milking.
a. Which diagram shows the proper way of drawing milk. (1mk)
• Diagram N.
b. How long should it take to milk a cow from the start to the end of milking. (1mk)
• Five to eight minutes.
c. How would a milkman ensure that no milk remains in the udder at the end of milking? (lmk)
• By massaging the udder and stripping out milk from the teats.
d. Give two practices carried out on milk immediately after milking. (2mks)
• Weighing.
• Filtering/ sieving.
• Cooling/ storage.
25. a. Describe the advantages of battery cage system of rearing layers. (10mks)
• Higher egg production due to less energy wastage by birds.
• Accurate egg production records can be kept.
• Cannibalism and egg eating are minimized
• Eggs are clean because hens do not step on them.
• The system can easily be mechanized.
• Birds do not contaminate food and water.
• Handling is easy as hens are restricted to a small place.
• Broodiness is discouraged as birds do not reach the eggs.
• A large number of birds’ can be kept in a small space hence higher stocking rate.
• Sick birds can easily be detected and isolated for treatment.
• Wire floors prevent re-infestation of parasitic worms and coccidia.
• There is no bullying during feeding.
• There is low labour requirement.
b. State and explain five factors affecting milk production. (10mks)
• Age of the animal-Young animals produce milk with a higher butter fat content than older animals.
• Condition of the animal-Under extreme emaciation there is a substantial drop in the butter fat content of the milk.
• Stage of lactation and pregnancy-Butter fat content in milk tends to be higher at the middle phase of lactation period. Hormonal changes in a pregnant lactating animal are responsible for the lactation trends in milk composition.
• Completeness of milking-The last milk drawn from the udder produces 10% of the total fats in milk. Milk produced in the morning has lower fat content than that drawn in the evening.
• Breed differences-Most of these differences are more pronounced in terms of fat content.
• Season of the year-Fat % increases during cold seasons of the year.
• The type of food eaten by the animal-The volatile fatty acids produced in the rumen of the animal influence the composition of milk:
• Propionic acid-grain feeds
• Acetic acid-roughages
• An animal eating large quantities of roughages produce milk with high fats, proteins and lactose than an animal fed on a lot of grains.
• Other factors
• eg diseases like mastitis reduce lactose composition.
• Animals under treatment.
26. a. State the functions of any six parts of a plunge dip. (6mks)
| Part | Function |
|---|---|
| Animal holding yard- Has a concrete floor. | Holding animals before dipping. Have stones to ensure that mud from the hooves is removed before getting into the dip wash |
| Foot bath | Washing livestock feet to remove mud Contains copper II sulphate solution that helps in controlling foot rot. |
The jump- This is a narrow entrance to the dip tank with short steps. | Allows animals to jump singly into the dip tank. |
| Dip tank-It should measure 5m long at the bottom8m at the top and 1.6m deep at the highest level of acaricide. | Holds the dip wash. |
| Rump or staircase | Enables animals to climb out of the dip tank. |
| Draining race | Holds livestock after dipping to let the dip wash drain back to the plunge dip. |
| Drying yard | Holds animals for a while before being released to the pastures. |
| Silt trap outlet | Traps mud and dung before the dip wash flows back to the dip tank |
| Dip tank shelter(roof) | Lower the evaporation rate of the dip wash. Avoid the dilution of the dip wash by rain water. |
| Water tank | Stores water used for dipping purposes. |
| Waste pit | Used as a damping site for sediments from the dip tank. |
b. State and explain four ways through which power transmitted from the engine is made available for use. (4mks)
• The propeller shaft-This connects the gearbox to the differential that has axles which drive the wheels making the tractor to move.
• The power take off shaft (PTO shaft)-It is located at the rear part of the tractor and rotates at same speed as the crankshaft. It can be connected to machines such as mowers, planters, rotavators, sprayers and fertilizer spreaders.
• The hydraulic system-It is attached to the three-point linkage which lowers or raises mounted implements like ploughs, mowers, planters and sprayers.
• The draw bar-It serves for the attachment of trailed implements that can be used during harrowing, transportation or rolling.
C. Explain five mechanical methods of controlling ticks. (10mks)
• Burning the infested pastures destroys a large number of eggs, larvae, nymphs and adults.
• Interfering with or altering the tick‘s environment in the following ways:
• Ploughing pasture land to expose the eggs to suns heat for desiccation or by burringthem deeply.
• Top dressing pastures using lime or dressing using an acaricide.
• Fencing off the pasture land and farm combined with regular use of acaricides.
• Starving the ticks to death by keeping the animals away from infested pastures through rotational grazing.
• Hand picking the ticks from livestock and killing them (de-ticking)
27. a. State five advantages of embryo transplant. (5mks)
• It is possible to implant embryo from a high quality female to less valuable female and hence improve the performance of the offspring.
• It stimulates milk production in a female that was not ready to produce milk.
• A highly productive female can be spread over a large area to benefit many farmers.
• It is easier to transport embryos in test tubes than the whole animal.
• Embryos can be stored for long periods awaiting availability of a recipient female.
b. Describe coccidiosis disease under the following sub- headings.
i. Animals attacked (2mks)
• Calves, poultry, lambs and young rabbits.
ii. Causal organism (1mk)
• Coccidia of the Eimeria spp
iii. Symptoms (4mks)
• Diarrhoea which may be whitish.
• Dysentery or blood in the dung.
• Birds have ruffled feathers, dull with drooping wings.
• Animals become emaciated
• Sudden death in birds, rabbits and kids.
iv. Control measures (3mks)
• Use of coccidiostats
• -Observing hygiene.
• Isolation in cattle.
• overcrowding in a poultry house should be avoided.
c. A ration containing 20% DCP for growing chicks is to be obtained by mixing ground maize containing 10% DCP and fishmeal containing 50% DCP. Calculate the amount of each feedstuff in kilograms required to prepare 200kg of the feed. (5mks)