Kenya High Mock Biology Paper 3 2021
1. (a) You are provided with a solution L.
Using the reagents provided; determine the food compounds in L. Fill in the table below.
FOOD COMPOUND | PROCEDURE | OBSERVATION | CONCLUSION |
|---|---|---|---|
(b) Place 10mls of solution L in a visking tubing.
Tie both ends and place it in 50mls of distilled water contained in a beaker.leave the set up for 20 minutes and make observations.
(i) Observations. (1mark)
(ii) Account for the observation in b (i) above. (2marks)
(iii) Give the equivalent of a visking in the bodies of living organisms. (1mark)
………………………………………………………………………………
2. Study the photomicrograph of the longitudinal section of a maize fruit below and answer the questions that follow.

i) Name the parts labelled A, B, C and D. (4marks) A ……………………………………………………………. B ……………………………………………………………. C ……………………………………………………………. D …………………………………………………………….
(ii) Give the role played by A and D. (2 mark) A ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..…. D …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… (b) (i) Name the type of germination exhibited by maize grain. ( 1 mark) …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… (ii) Place the organisms from where the photomicrograph was obtained into its Kingdom Division Class (3marks)
(iii) State three characteristics of members of the class identified in b (ii) above (3marks) ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… (c) Give one reason why the maize grain is classified as a fruit. (1mark) ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 3. Study the organisms drawn below and answer the questions that follow
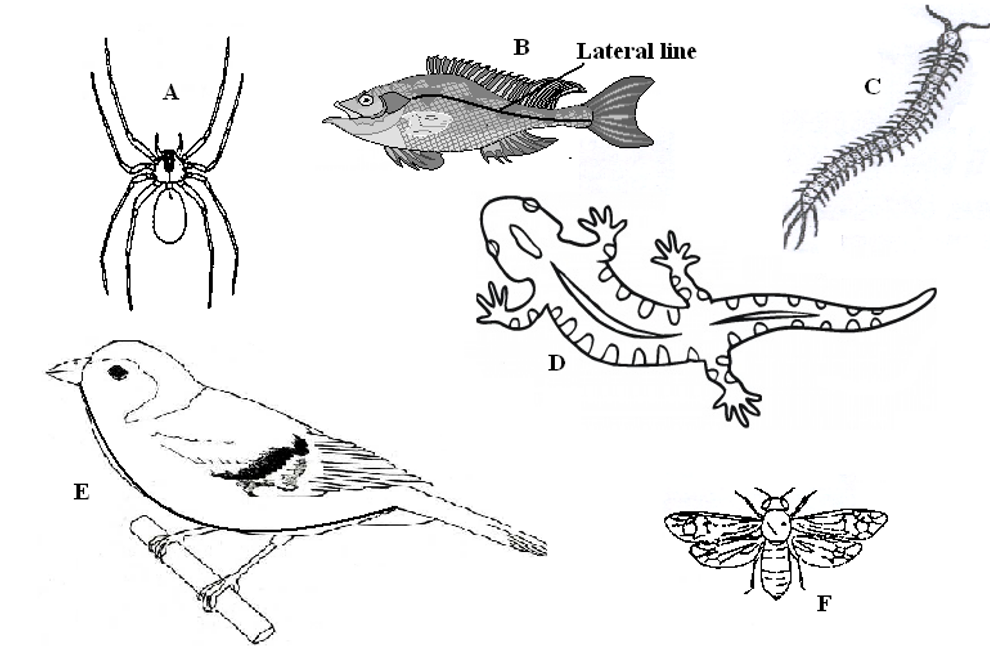
(a) Use the dichotomous key below to identify the class the organisms belong to. (12 marks)
1. (a) Phylum Chordata ……………………………………………………… go to 2
(b) Phylum arthropoda ……………………………………………………. go to 3
2. (a) Has scales on the body ………………………………………………… go to 4
(b) Has no scales on the body …………………………………………..… Mammalia
3. (a) Has cephalothorax ……………………………………………….……. Arachnida
(b) Has no cephalothorax …………………………………………………. go to 5
4. (a) Has fins ………………………………………………………………… Pisces
(b) Has no fins ……………………………………………………………… go to 7
5. (a) Has three pairs of legs …………………………………………………. Insecta
(b) Has more than three pairs of legs ……………………………………… go to 6
6. (a) Two pairs of legs per segment ………………………………………… Diplopoda
(b) One pairs of legs per segment …………………………………………. Chilopoda
7. (a) Has feathers ……………………………………………………………. Aves
(b) Has no feathers ………………………………………………………… go to 8
8. (a) Has a tail ……………………………………………………………….. Reptilia
(b) Has no tail …………………………………………………………….. Amphibia
Specimen | Step followed | Identity |
|---|---|---|
| A | ||
| B | ||
| C | ||
| D | ||
| E | ||
| F | ||
| G |
(b) If the actual length from the tip of the mouth to the tip of the tail of the specimen B is 100mm, calculate the magnification. (2marks)
Marking Scheme
FOOD COMPOUND | PROCEDURE | OBSERVATION | CONCLUSION |
|---|---|---|---|
Starch | To 2cm3 of solution L add drops of iodine√1mk | Colour turns brown /yellow√½ mk | Starch absent½ mk |
Reducing sugar | To 2cm3 of solution L ,add benedicts solution and boil√1 mark | Colour changes from blue to green to yellow/orange√½ mk | Reducing sugars present½ mk |
proteins | To 2cm3 of solution L add 3 drops of NaOH followed by drops of CuSO4 and shake√1mk | solution remains blue√½ mk | Protein absent½ mk |
Ascorbic acid | To 2cm3 of solution DCPIP add solution L dropwise shaking till in excess √1mk | DCPIP decolourised√ ½ mk | Vitamin C /Ascorbic acid present ½ mk |
(b) (i) solution in the visking tubing increases in volume
(ii) Water moves by osmosis; in the visking tubing due to the high osmotic pressure of the solution in the visking tubing
(c) Cell membrane/plasma membrane/plasmalema
2. (a) (i) A – Endosperm
B – Radicle
C – Plumule
D – Plumule sheath/coleoptile
(ii) A – stores food for the embryo;
D – protects the delicate plumule from mechanical damage;
(b) (i) hypogeal;
(ii) Kingdom – Plantae; Rej plant
Division – spermatophyte
Class –Monocotyledonae; rej monocot/monocotyledon
(iii) Fibrousroots
Parallelvenation;
Floral parts occur in three /multiples of three;
Sheath like petiole; Mark first three (c) Has two scars;
3. (a)
Specimen | steps | identity |
|---|---|---|
A | 1b,3a; | Arachnida |
| B | 1a,2a,4a; | Pisces |
| C | 1b,2b,5b,6b; | Chilopoda |
| D | 1a,2a,4b,7b,8a | Reptilia |
| E | 1a,2a,4b,7a; | Aves |
| F | 1b,3b,5a; | Insecta |
b) Magnification = Diagram length = 50mm
Actual length 100mm;
= X 1/2 or X 0.5;


